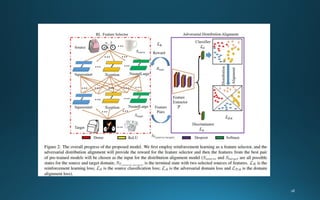
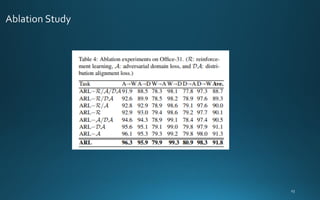
The document presents a framework called adversarial reinforcement learning (ARL) for unsupervised domain adaptation to address the domain shift phenomenon in machine learning. It outlines a methodology that utilizes reinforcement learning to select feature pairs from source and target domains while minimizing discrepancies, and discusses previous works and experiments conducted with benchmark datasets. The study emphasizes the importance of domain adaptation methods in enhancing the generalization of machine learning models.