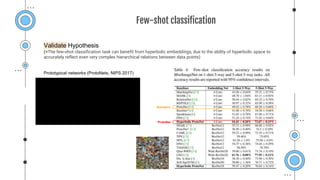
The document discusses the advantages of using hyperbolic geometry for image embeddings in tasks like image retrieval and recognition, particularly for hierarchical data structures. It shows through experiments that models leveraging hyperbolic embeddings outperform traditional Euclidean approaches in accuracy for several tasks, including few-shot learning and person re-identification. The conclusion emphasizes the need for further understanding of hyperbolic geometry's application to image data due to its unique properties.