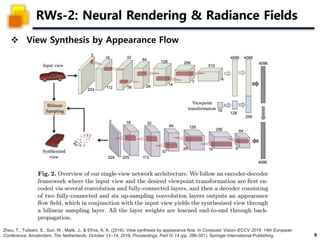
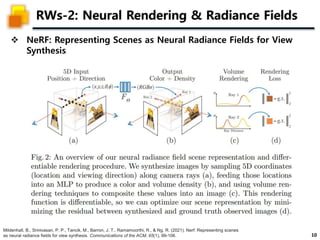
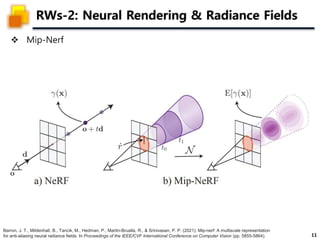
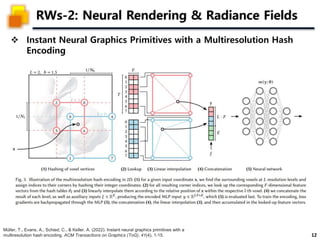
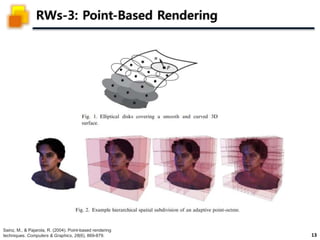
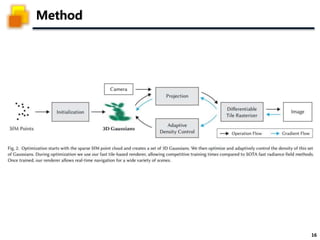
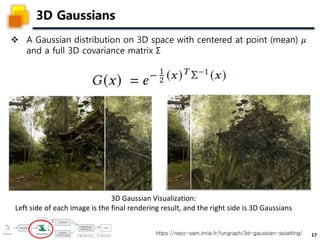
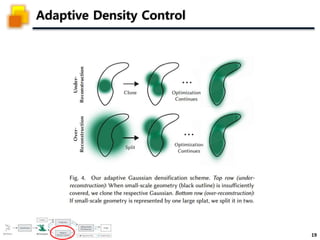
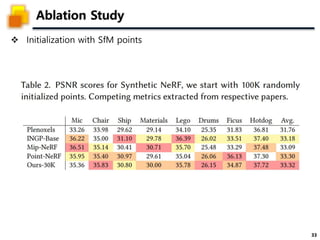
The document presents a method called 3D Gaussian Splatting for high-quality real-time radiance field rendering, achieving over 100 frames per second at 1080p. It discusses various techniques related to scene reconstruction, neural rendering, and point-based rendering, citing multiple research papers that have contributed to these fields. Additionally, it includes information about datasets used for quantitative and qualitative evaluations of the proposed method.