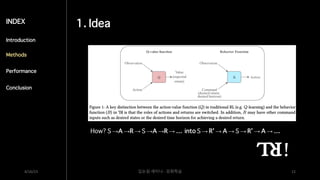
The document discusses the concept of upside-down reinforcement learning (RL), highlighting challenges such as sample inefficiency and the alignment problem while suggesting leveraging supervised learning (SL) advantages for improved performance. It proposes a method to convert RL problems into SL tasks, aiming to maximize returns through understanding agent actions based on past experiences. The document presents methodologies, experiments, and algorithms to demonstrate the proposed approach in various environments.



















![3. Algorithm
4/16/23 딥논읽 세미나 - 강화학습 20
INDEX
Introduction
Methods
Performance
Conclusion
| After each training phase the agent can be given new commands,
potentially achieving higher returns due to additional knowledge gained by further training.
| To profit from such exploration through generalization,
a set of new initial commands c0 to be used in Algorithm 2 is generated.
1. A number of episodes with the highest returns are selected from the replay buffer.
This number is a hyperparameter and remains fixed during training.
2. The exploratory desired horizon 𝑑!
"
is set to the mean of the lengths of the selected episodes.
3. The exploratory desired returns 𝑑!
#
are sampled from the uniform distribution 𝒰[𝑀, 𝑀 + 𝑆]
where 𝑀 is the mean and 𝑆 is the standard deviation of the selected episodic returns.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rlupsidedown-230703071859-5acc9111/85/RL_UpsideDown-21-320.jpg)









