Embed presentation
Download to read offline



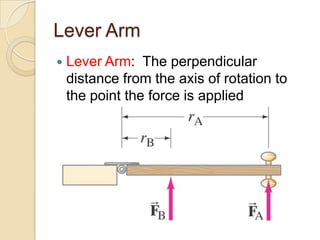
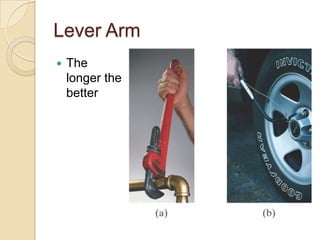
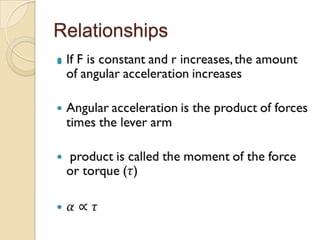
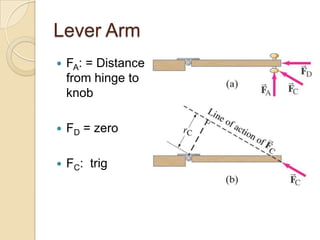
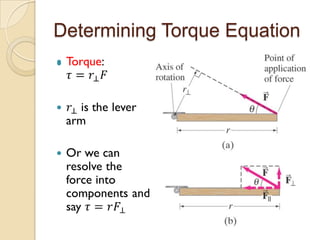
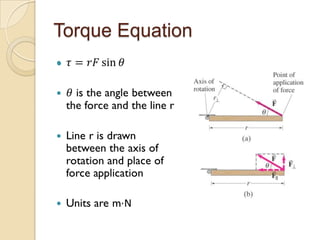
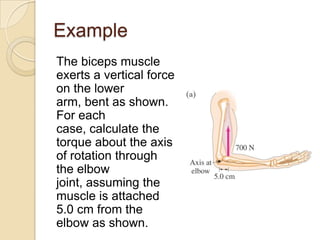
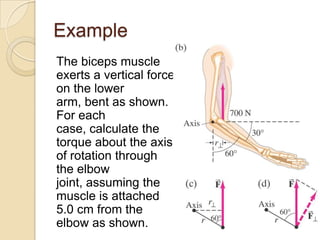
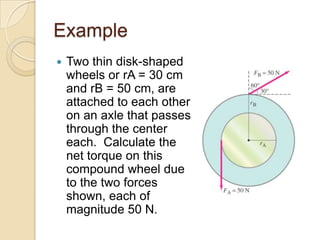

Torque is calculated based on the lever arm, which is the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the point where a force is applied. A longer lever arm results in a greater torque. An example calculates the torque on a bicep muscle attached 5 cm from the elbow joint, based on different forces applied. A second example calculates the net torque on two connected wheels from two 50N forces, based on the wheels' radii serving as lever arms. The document concludes by assigning homework problems related to torque calculations.












