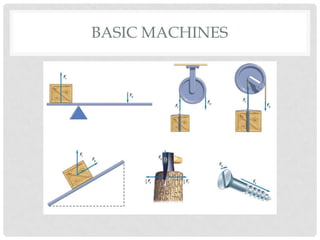
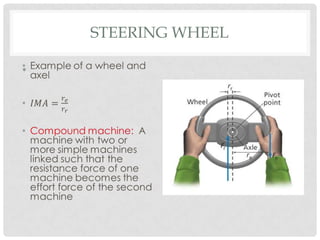
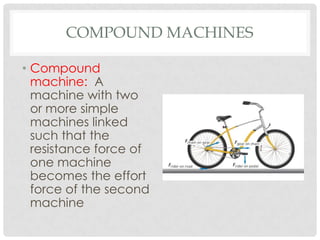
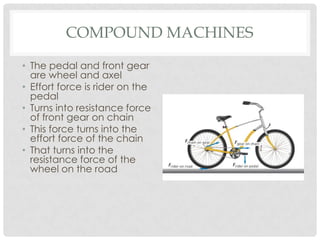
This document discusses simple machines including their definitions, examples, and calculations of mechanical advantage and efficiency. It defines a machine as a device that changes the magnitude or direction of a force. Simple machines include levers, pulleys, inclined planes, screws, and wedges. Complex machines combine two or more simple machines. Ideal mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force to input force. Real machines have efficiencies less than 100% due to friction and other losses. Compound machines link two or more simple machines together such as the combination of a pedal, gear, chain, and wheel that makes up part of a bicycle.