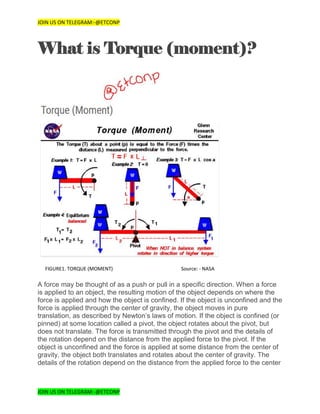
1) Torque, also called moment, is a measure of the turning force on an object such as a bolt or a flywheel. It is calculated by multiplying the force applied by the distance from the axis of rotation.
2) Torque produces rotation, just as a force produces translation. An object at rest will remain at rest until a torque is applied to it. Torque results in angular acceleration.
3) The distance used in the torque calculation is the length of the arm perpendicular to the direction of the applied force. Different arrangements of force and distance will result in different amounts of torque.