Embed presentation
Downloaded 10 times


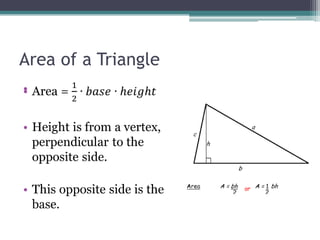
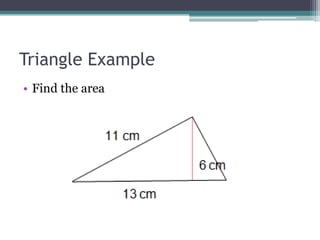
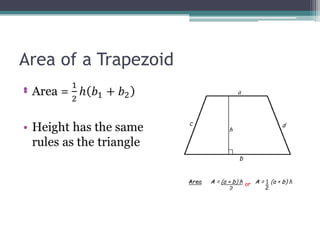
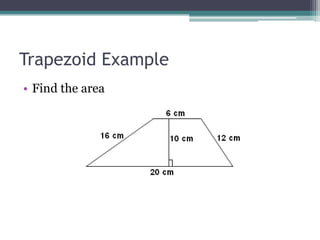
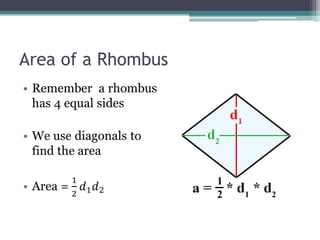
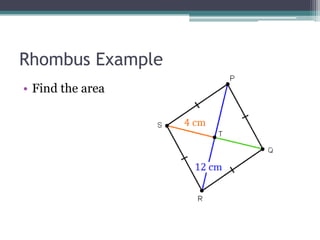
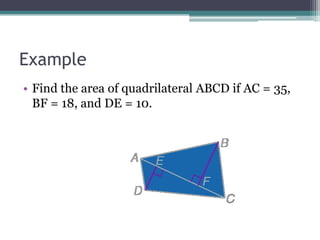
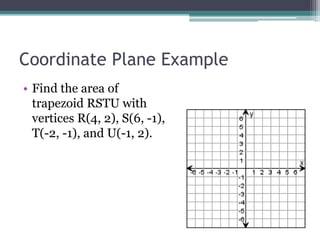
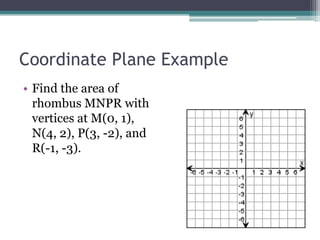
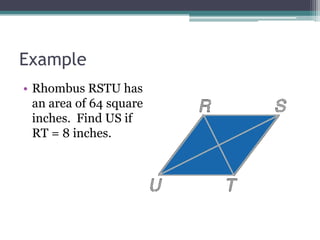

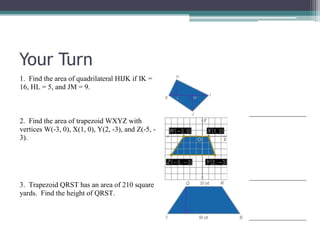


This document provides information on finding the areas of triangles, trapezoids, and rhombi. It gives the formulas for calculating the area of each shape, includes examples of applying the formulas, and provides practice problems for students to work through. The lesson plan is for a two-day unit covering adding the areas of different plane figures, with the first day focused on notes and examples, and the second day devoted to review and assessment.















