This document discusses key aspects of constructivism as it relates to teaching mathematics. It covers the following main points:
1. Constructivism is a learning theory that posits people actively construct their own knowledge based on experiences. Pioneers like Piaget, Von Glasersfeld, and Vygotsky contributed influential ideas.
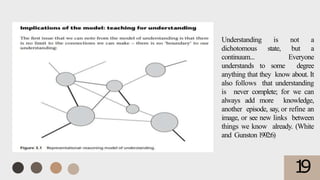
2. Effective constructivist teaching involves students developing more complex mathematical understanding through reflection and social processes. Assessment should be an ongoing part of the learning process.
3. Implications for the classroom include students taking an active role in knowledge construction through exploration, communication, and applying their ideas. The teacher acts as a facilitator rather than solely lecturing.
4. For