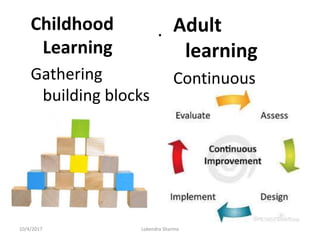
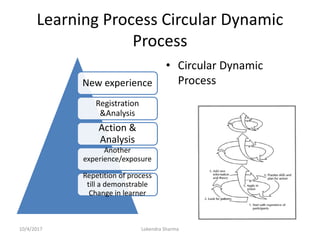
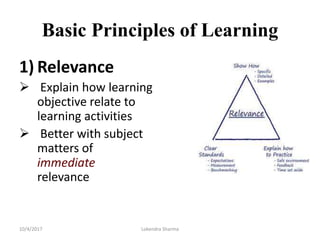
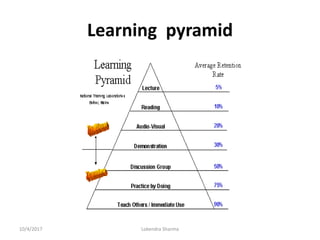
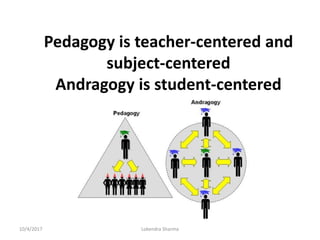
This document discusses adult learning principles and how they differ from traditional pedagogy. It defines key concepts like andragogy, the difference between teaching and learning, and learning theories. The main principles of adult learning are that adults are self-directed, draw on life experiences, are problem-centered, and want learning to be relevant. Effective teaching incorporates these principles by involving learners, acknowledging their expertise, relating topics to real-life, and treating students as equals. The goal is to help adults acquire knowledge and skills in a way that works best for their stage of life.