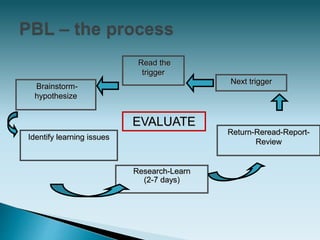
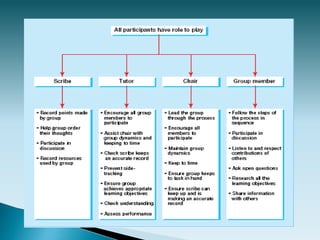
The document discusses various teaching and learning methods. It describes that learning is an individualized process influenced by intrinsic and extrinsic factors. The role of teachers is to facilitate learning through different methods like transmitting information, instructing, coaching, and facilitating problem-based or project-based learning. Some key teaching methods discussed include lectures, small group teaching, individualized teaching, and experiential teaching. Problem-based learning is described as a student-centered approach that uses clinical problems to stimulate self-directed learning.