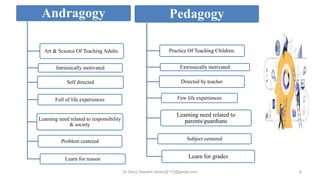
The document discusses adult learning principles, introducing the concept of andragogy and its distinctions from pedagogy. It highlights characteristics and challenges of adult learners, including self-direction, motivation, and time constraints, as well as the benefits of understanding these principles for effective learning. Practical tips, such as mentorship and experiential learning, are also provided to enhance adult learning experiences.