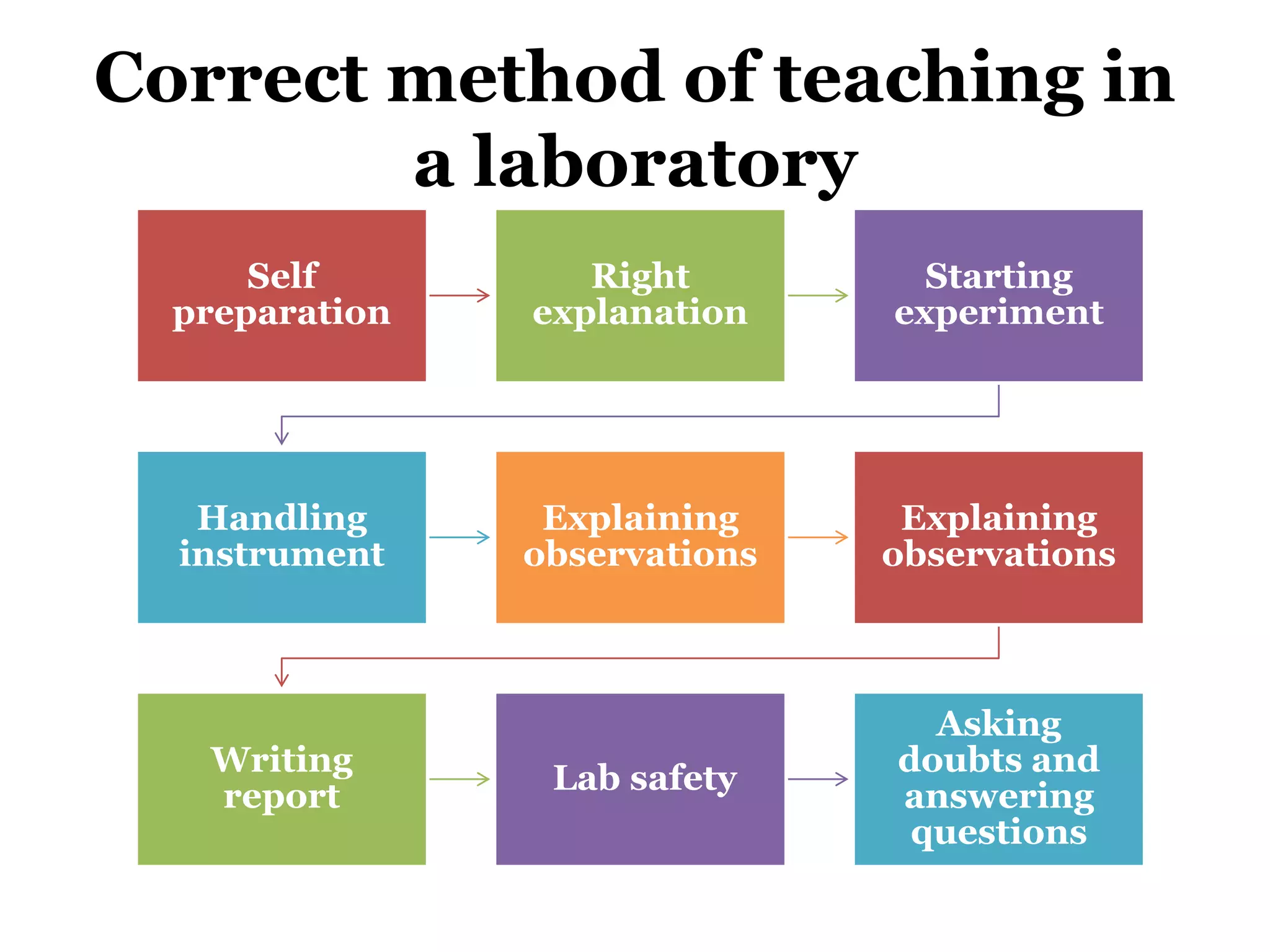
The document discusses the laboratory method in nursing education. It defines the laboratory as a place for experimental study. The laboratory method involves hands-on learning through original data and materials. It aims to provide an active learning experience for students. The purposes of the laboratory include teaching psychomotor skills, orienting students to new equipment and procedures, and supplementing classroom work. Objectives include verifying facts, developing independent work habits, and improving critical thinking skills. Functions include verification, exploration, induction, deduction, and problem solving activities. Guidelines help ensure respect for all and adaptation for individual students. Advantages are gaining real-world experience and mastery of subjects. Disadvantages include time consumption and need for resources.