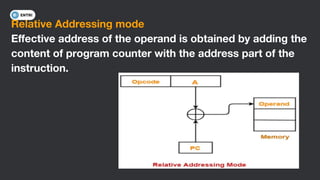
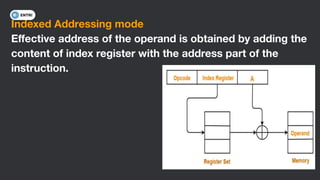
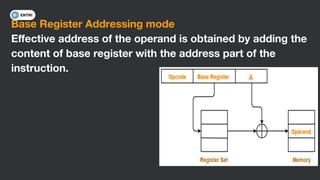
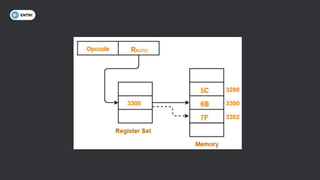
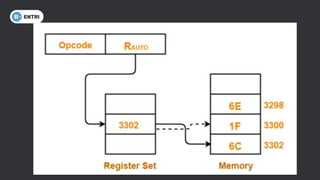
This document discusses different types of memory addressing modes used in computer architecture. It defines addressing modes as the ways of specifying the location of an operand in an instruction. It then describes nine common addressing modes - immediate, direct, indirect, register direct, register indirect, implied, stack, displacement and auto-increment/decrement. For each mode, it provides an example instruction and brief explanation of how the effective address is determined.