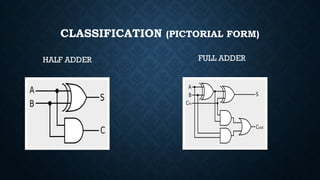
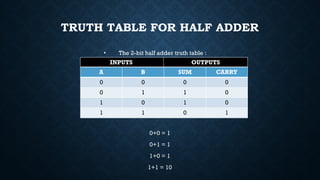
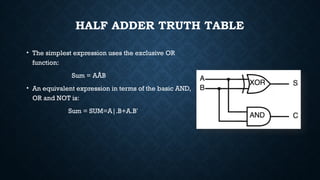
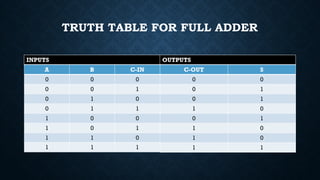
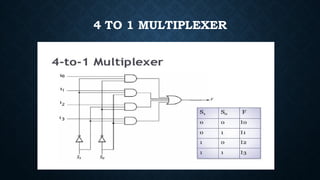
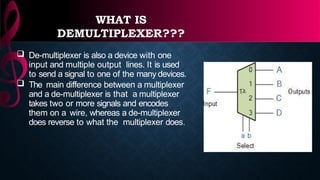
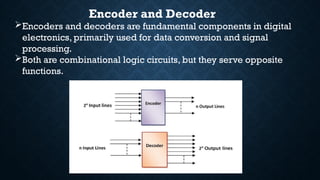
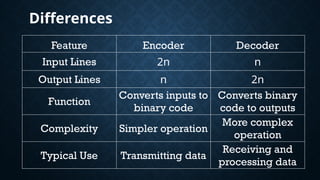
The document provides an overview of digital logic circuits called adders, which are used for adding binary numbers in processors, classified into half adders and full adders. It further explains the roles and truth tables of both types of adders, as well as the concepts of multiplexers and demultiplexers, which handle multiple input/output signals in digital systems. Additionally, it briefly covers encoders and decoders, highlighting their functions in data conversion and processing.