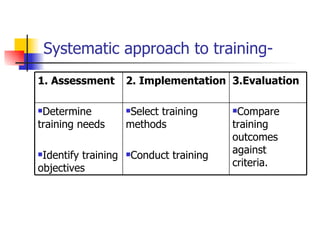
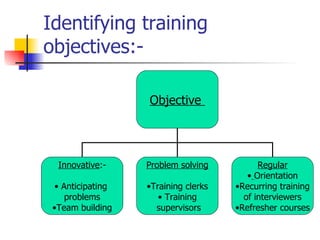
Training involves improving employee skills and knowledge to enhance performance. It aims to close gaps between job needs and employee abilities. There are various types of training like skills training, refresher training, and cross-functional training. A systematic approach to training includes assessing needs, setting objectives, implementing training methods, and evaluating outcomes. Common methods are on-the-job like coaching and off-the-job like lectures. Evaluation determines if training met goals. Executive development improves managerial skills through experiences, courses, and projects.