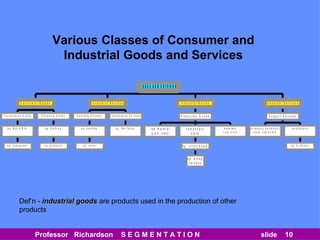
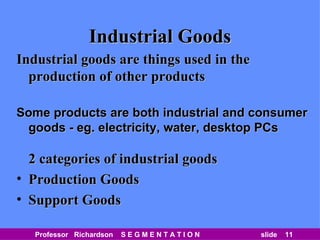
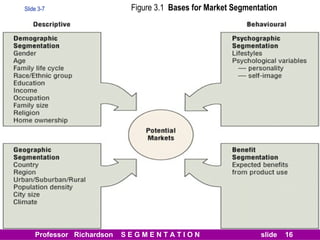
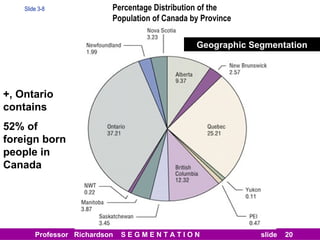
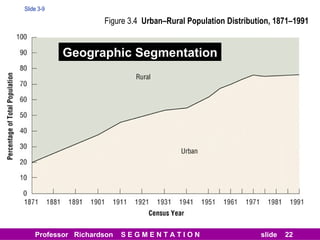
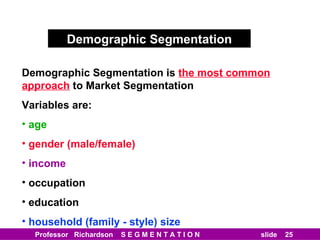
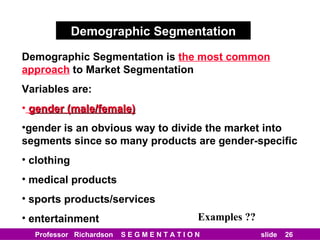
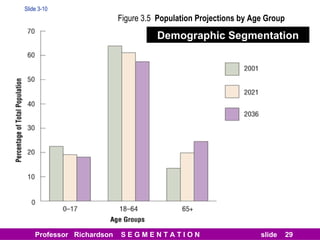
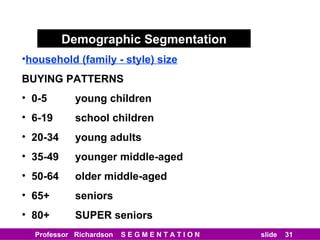
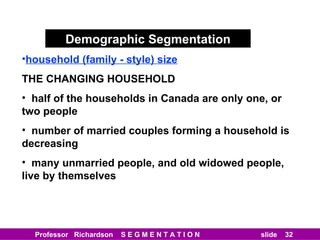
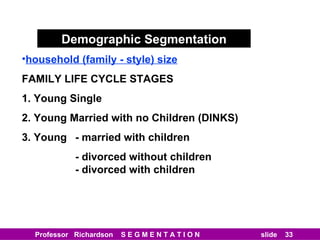
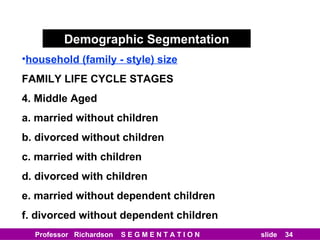
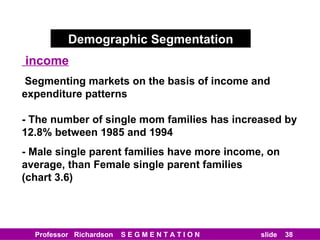
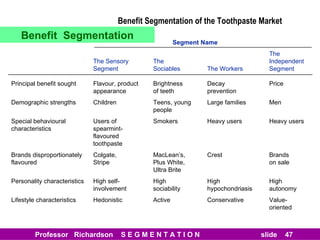
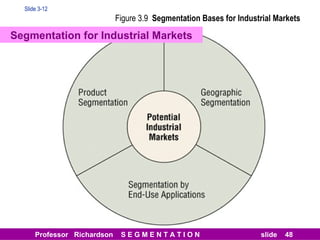
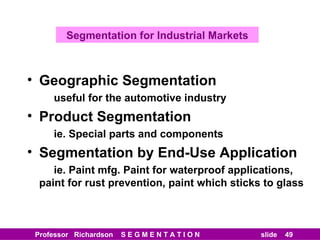
This document discusses different types of market segmentation, including geographic, demographic, psychographic, and benefit segmentation. It provides examples of how markets can be segmented based on location, age, gender, income, lifestyle, and the benefits customers seek from products. Demographic segmentation is described as the most commonly used approach, segmenting markets based on variables like age, gender, income, household size, and family life stage. The importance of understanding consumption trends among different segments is emphasized for developing effective marketing plans.