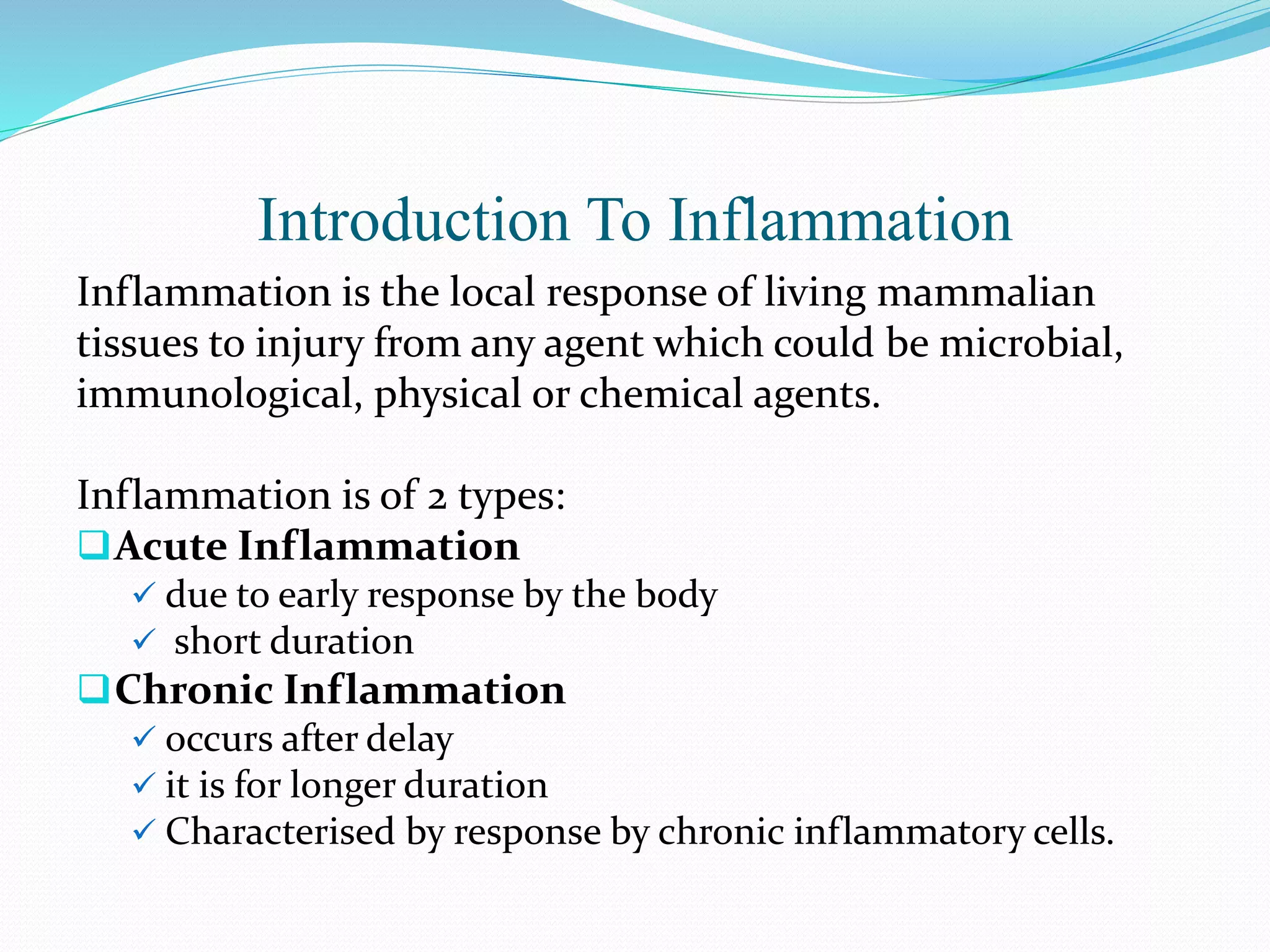
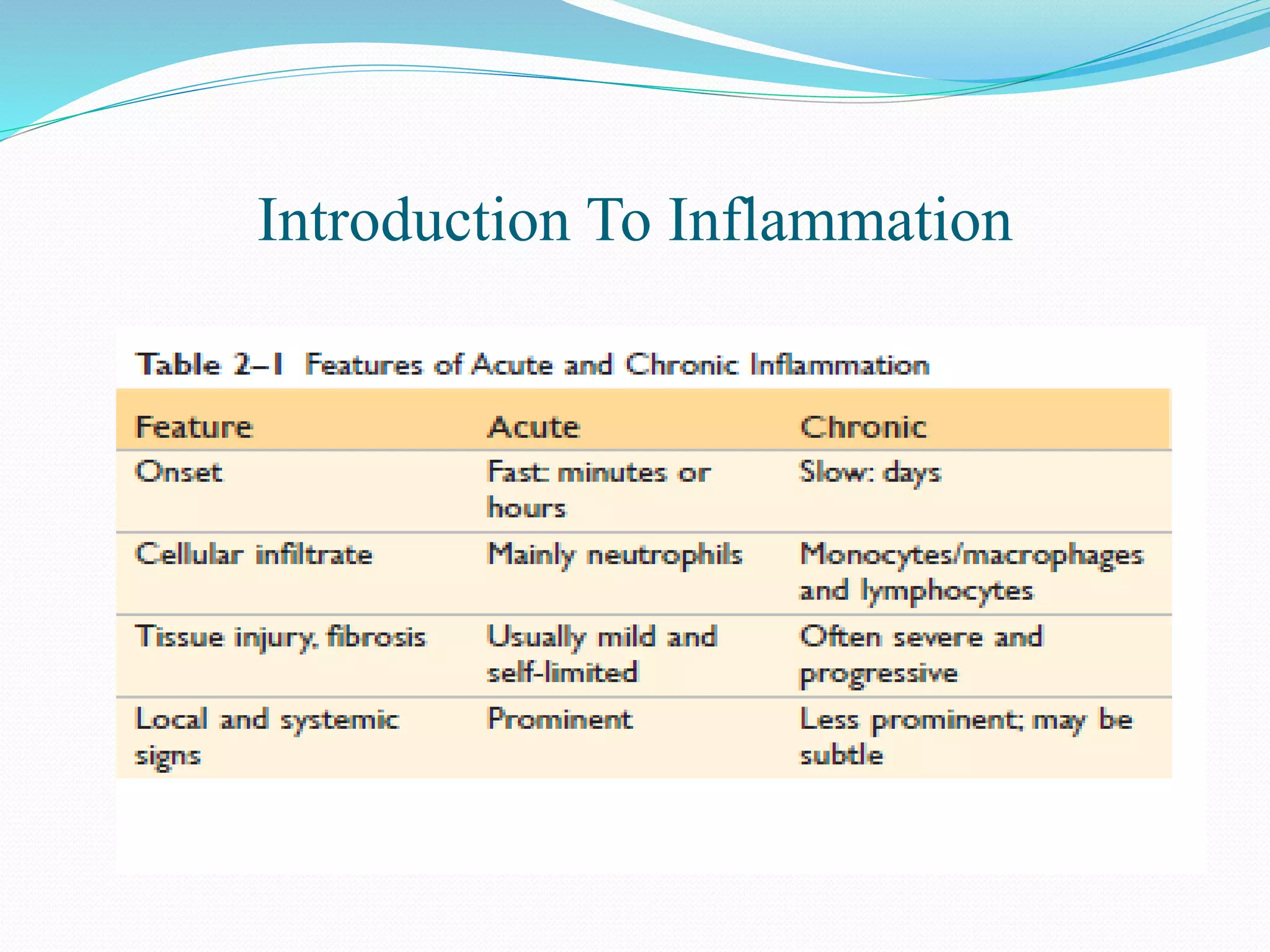
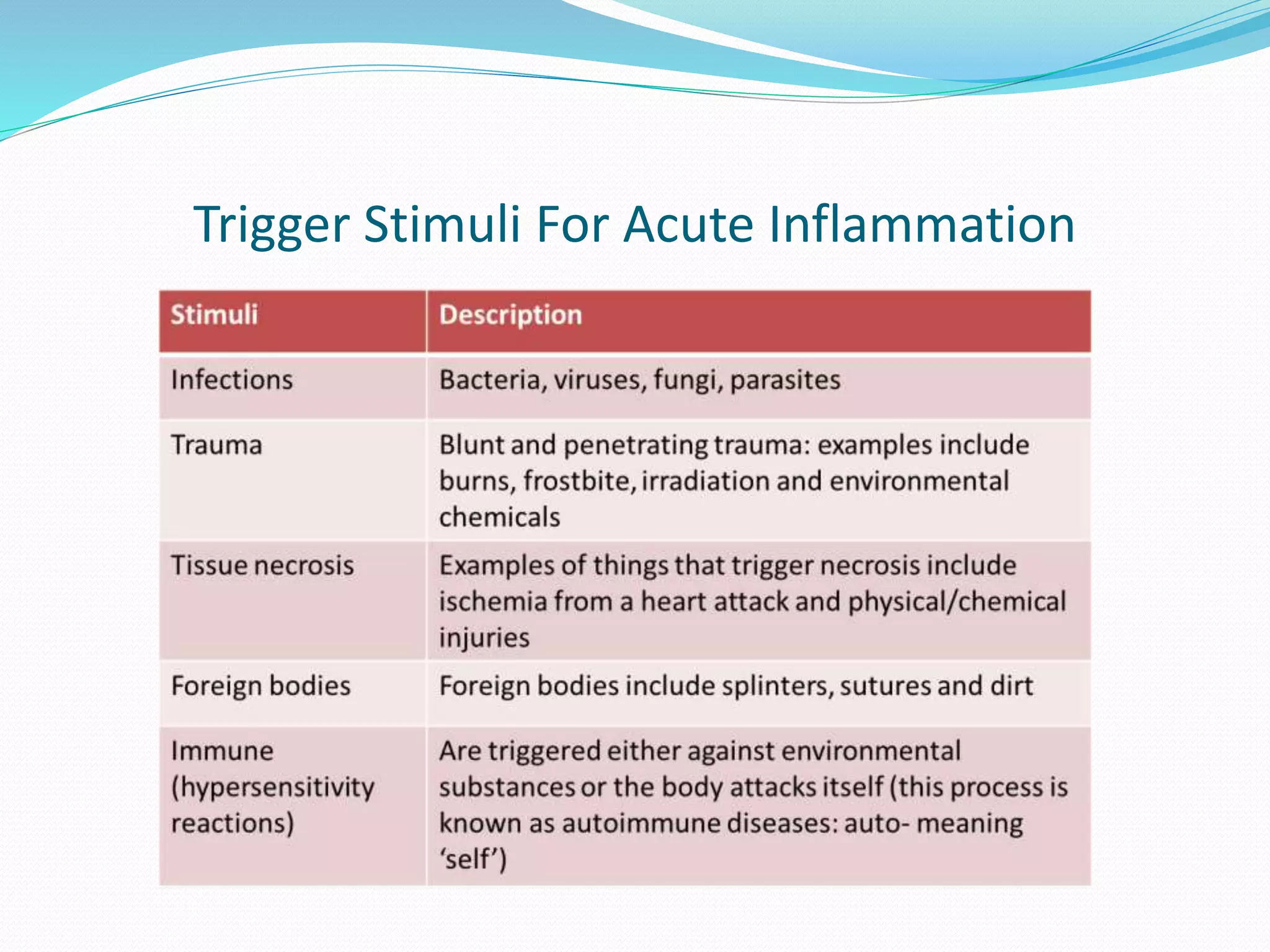
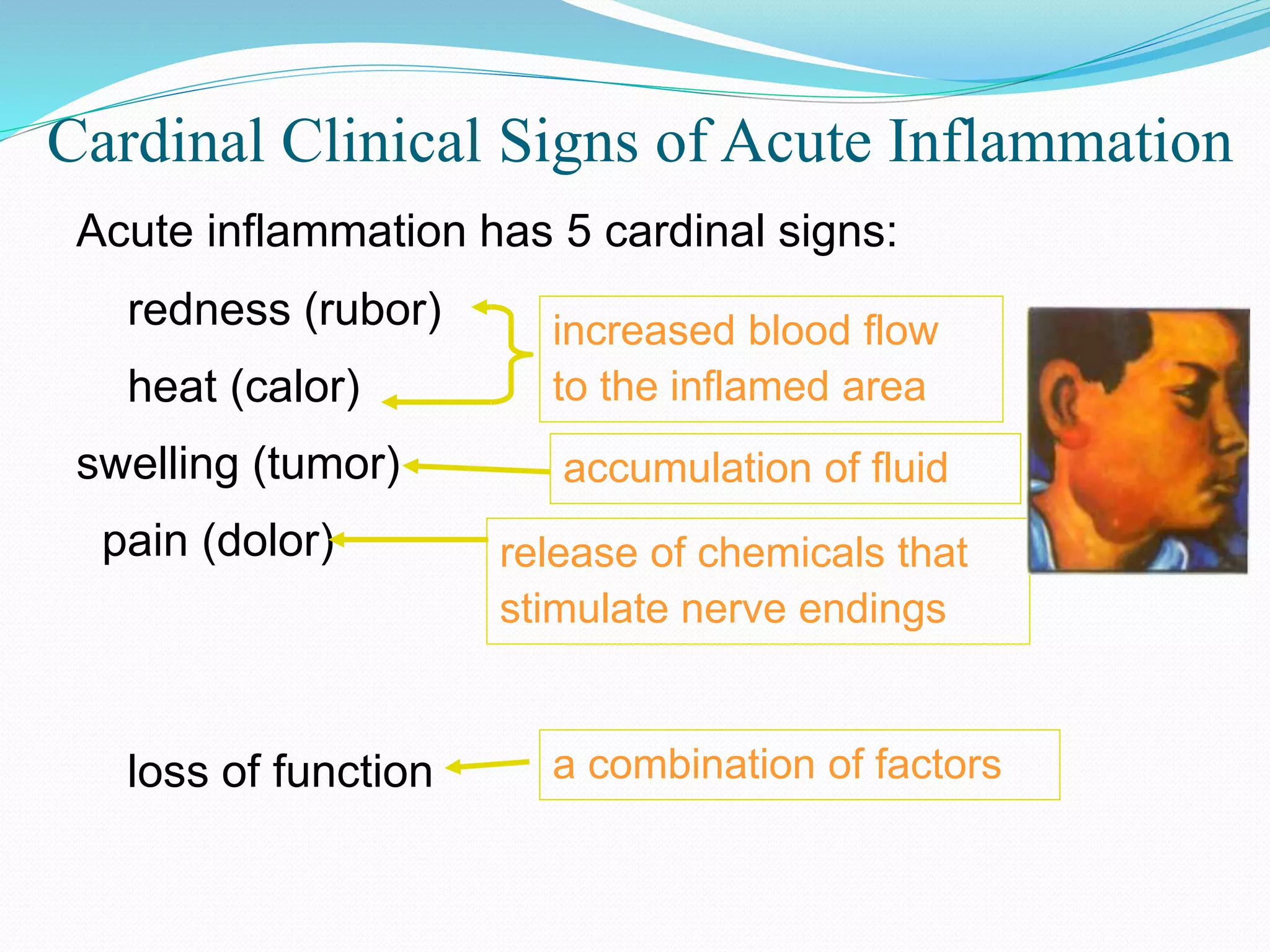
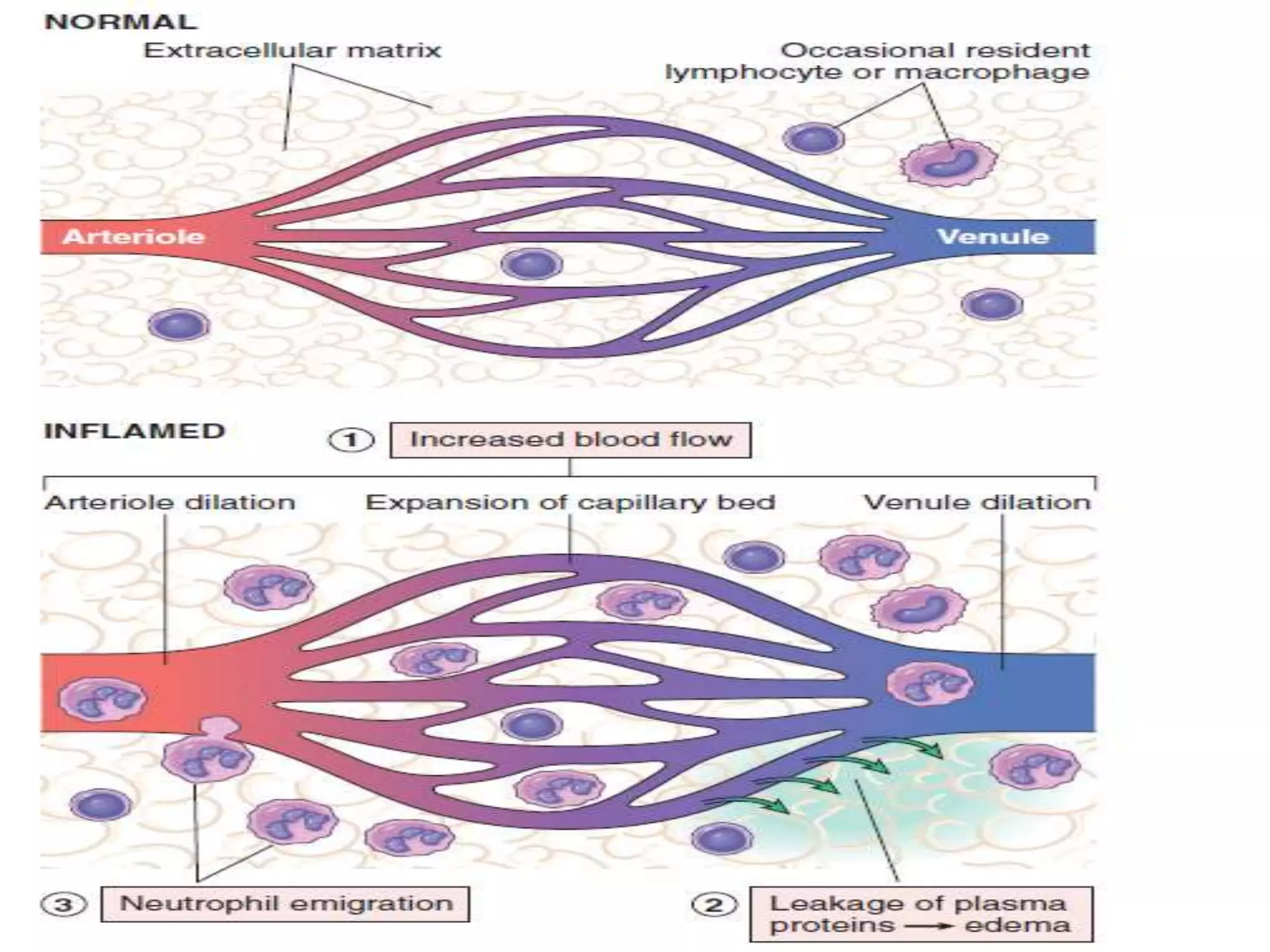
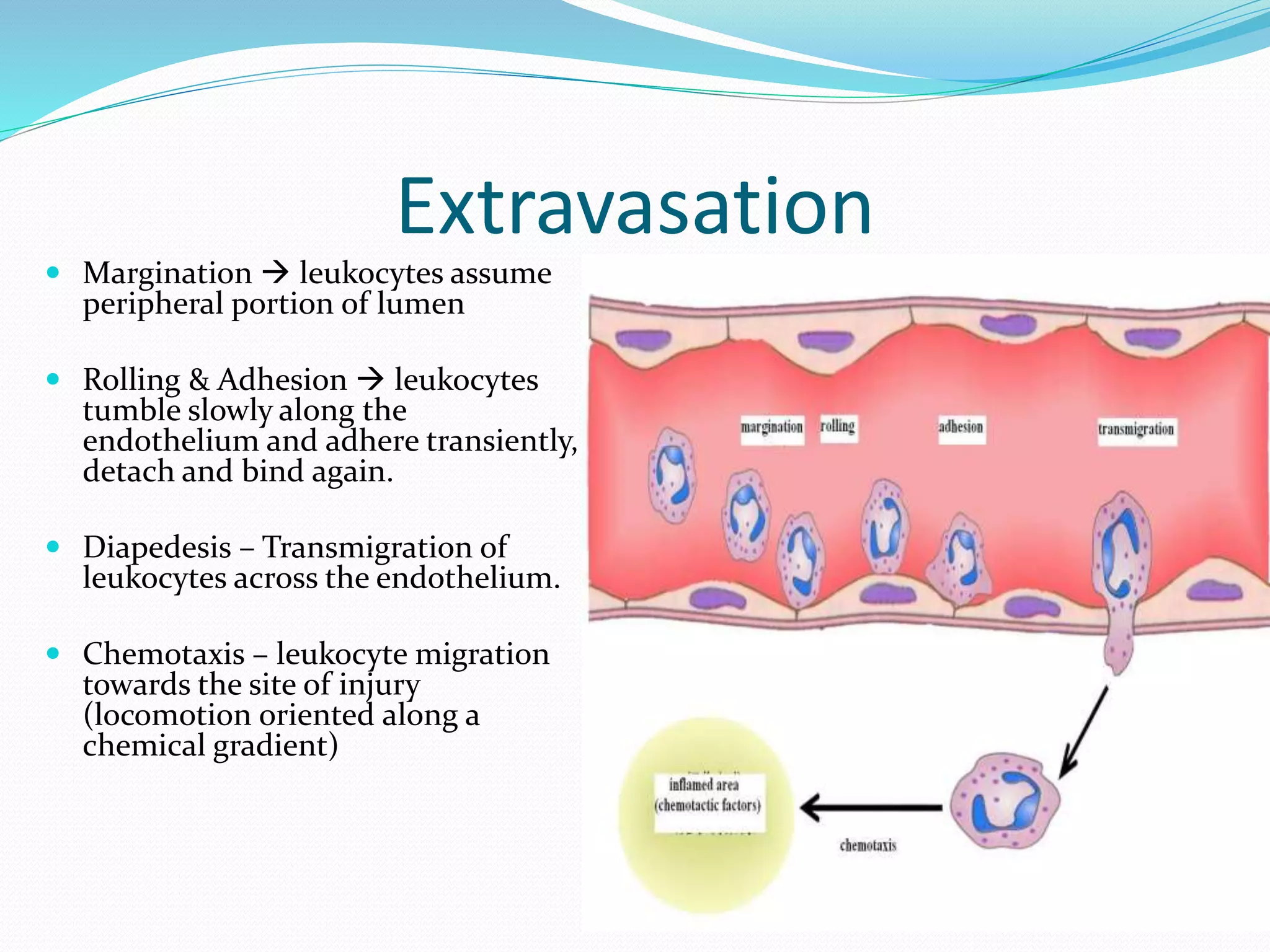
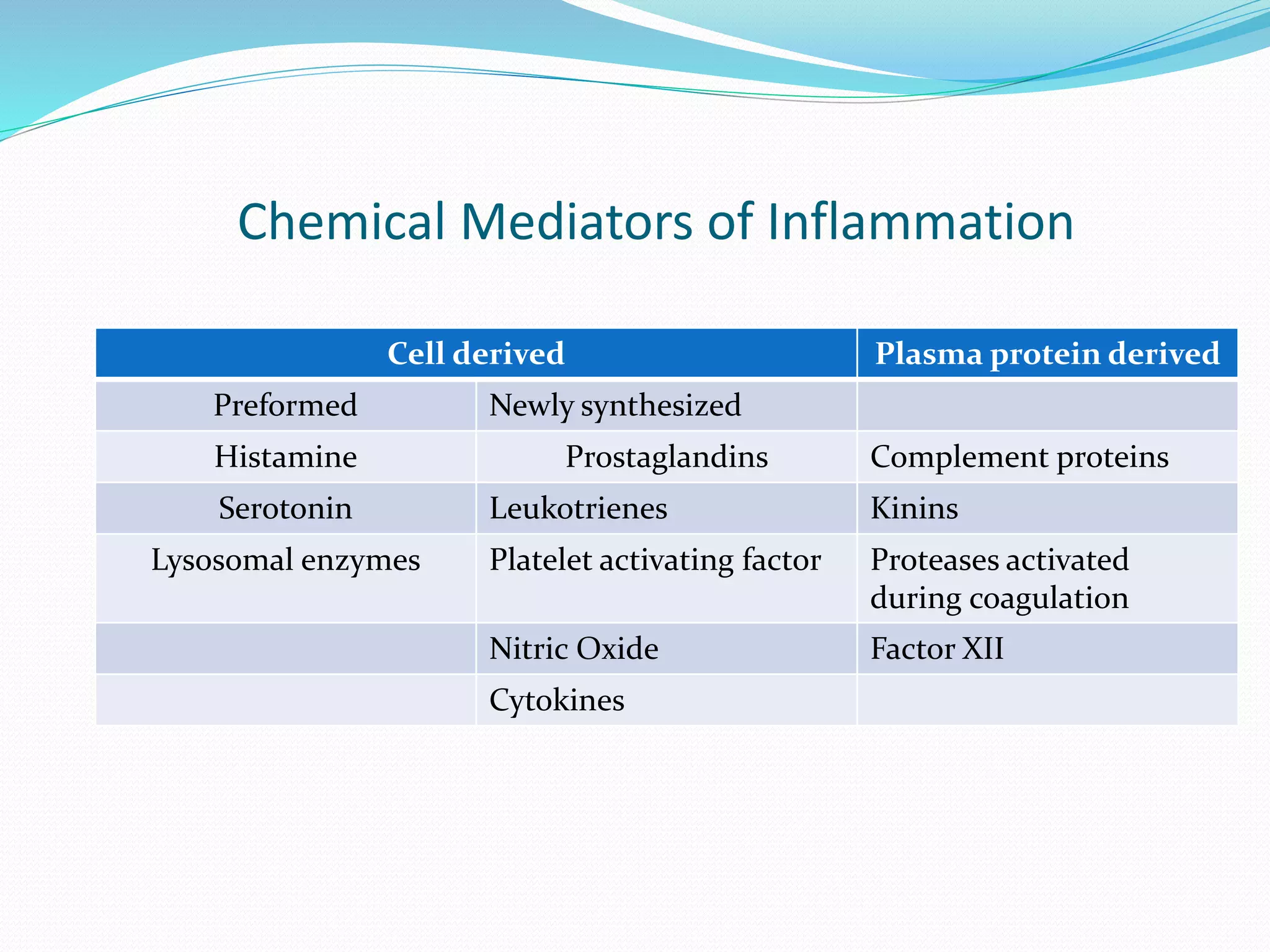
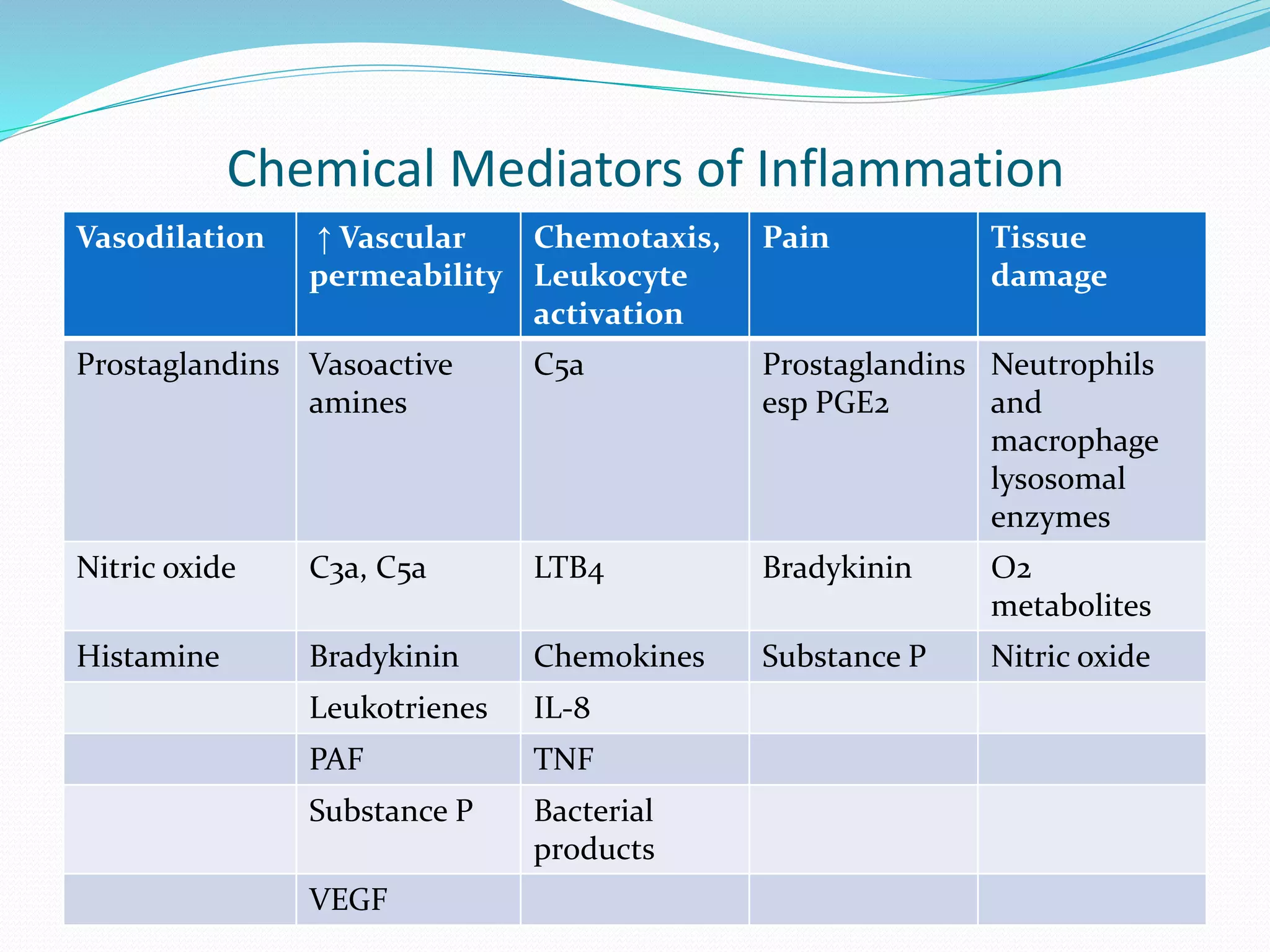
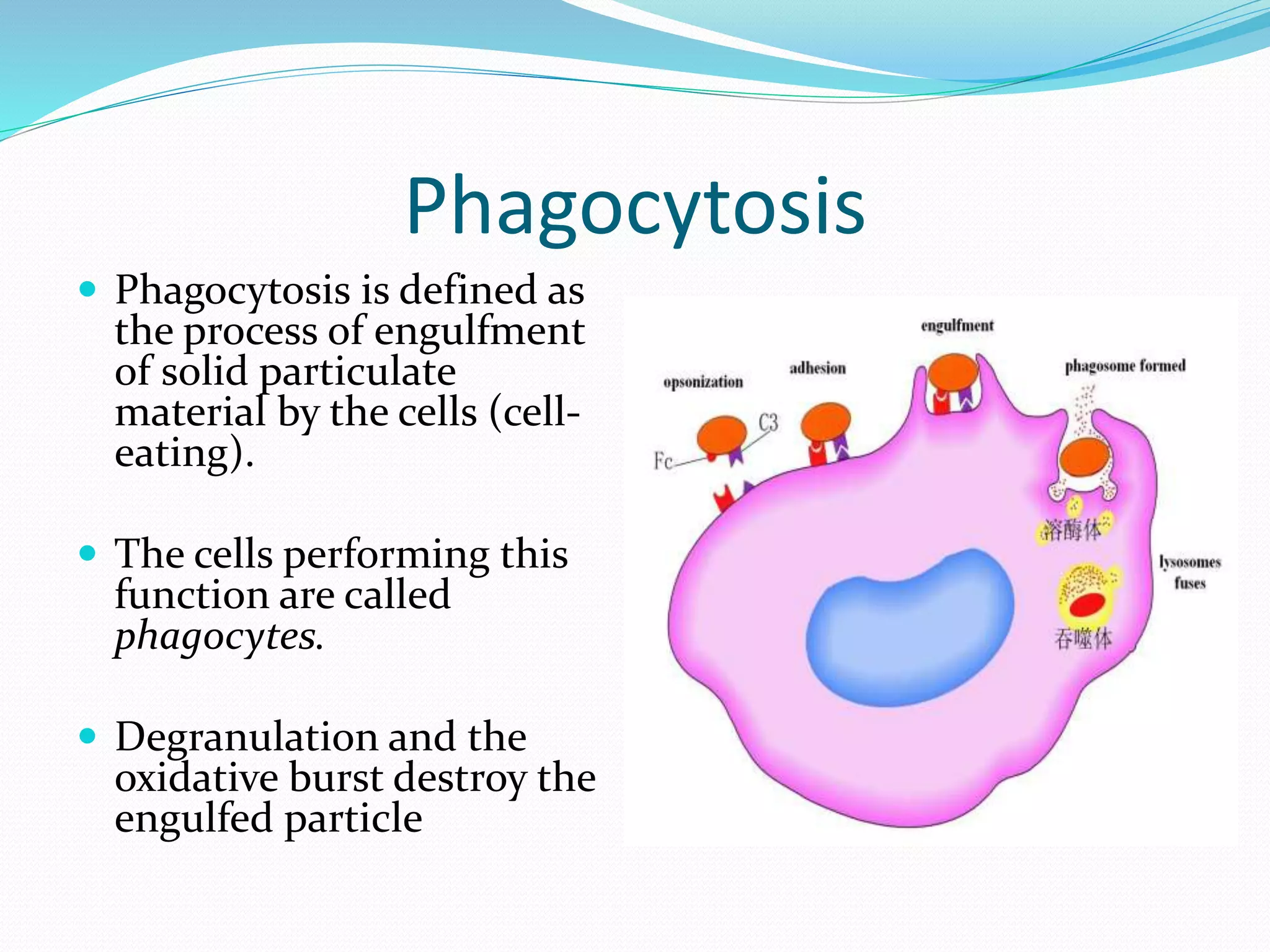
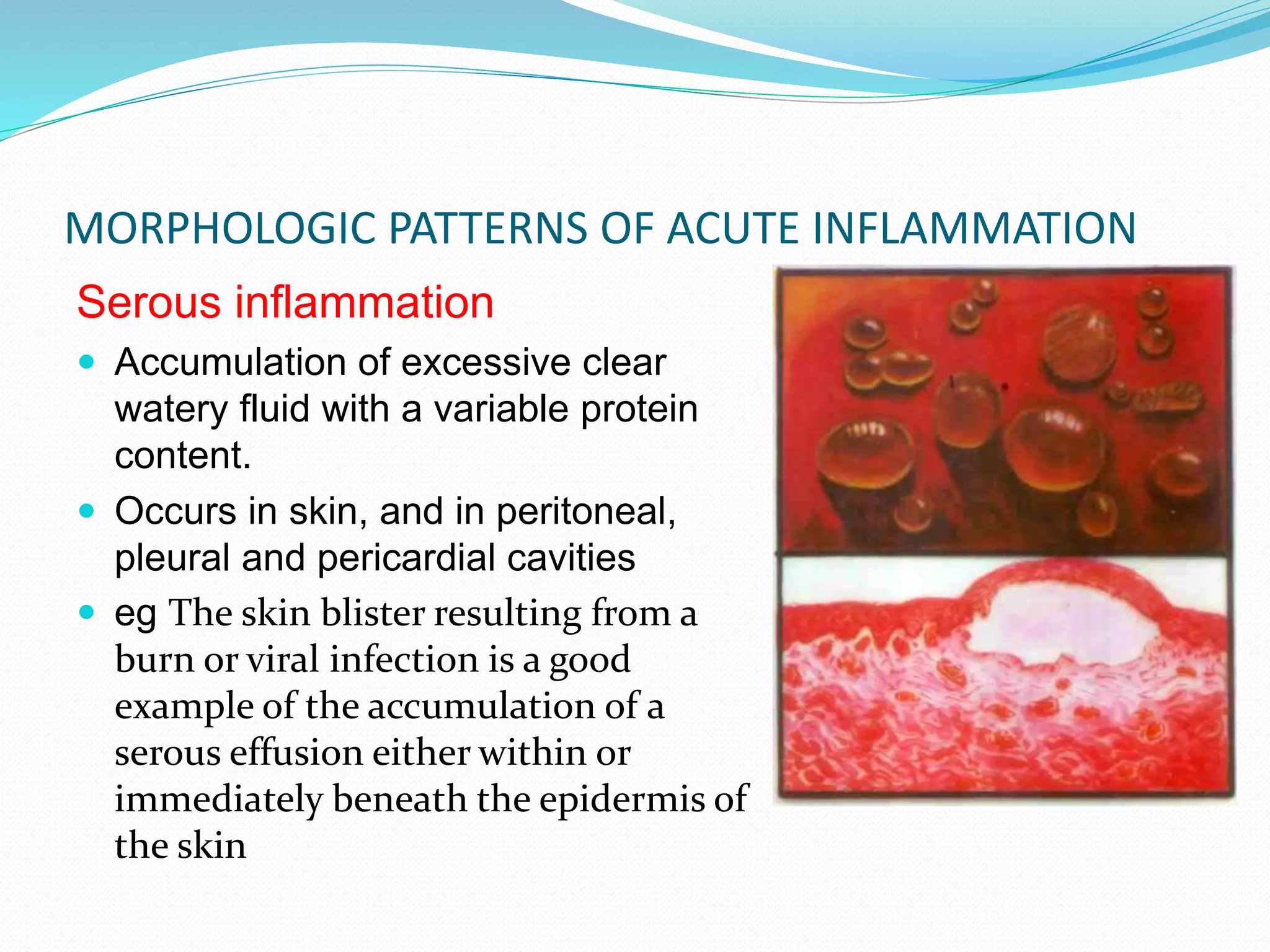
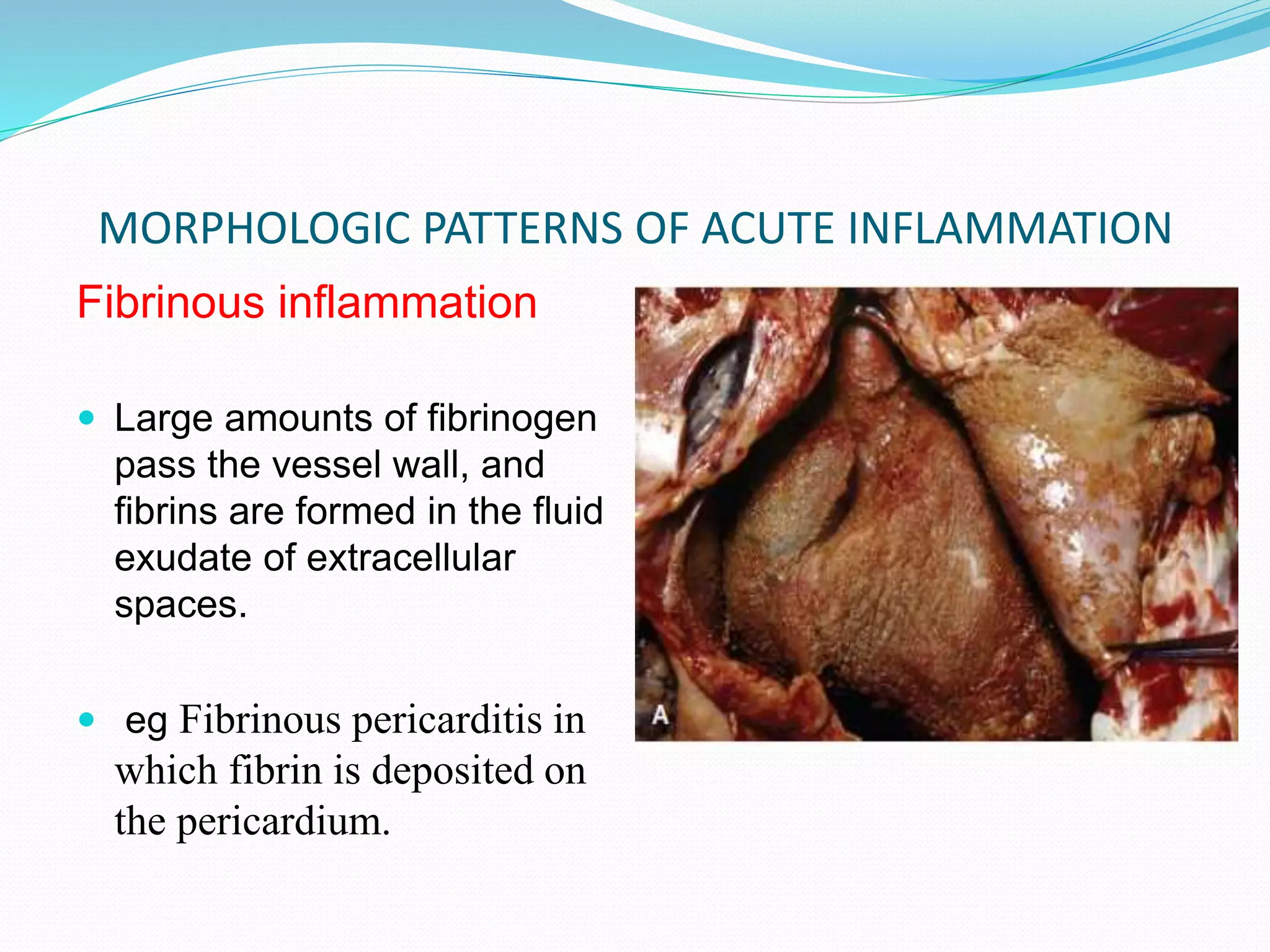
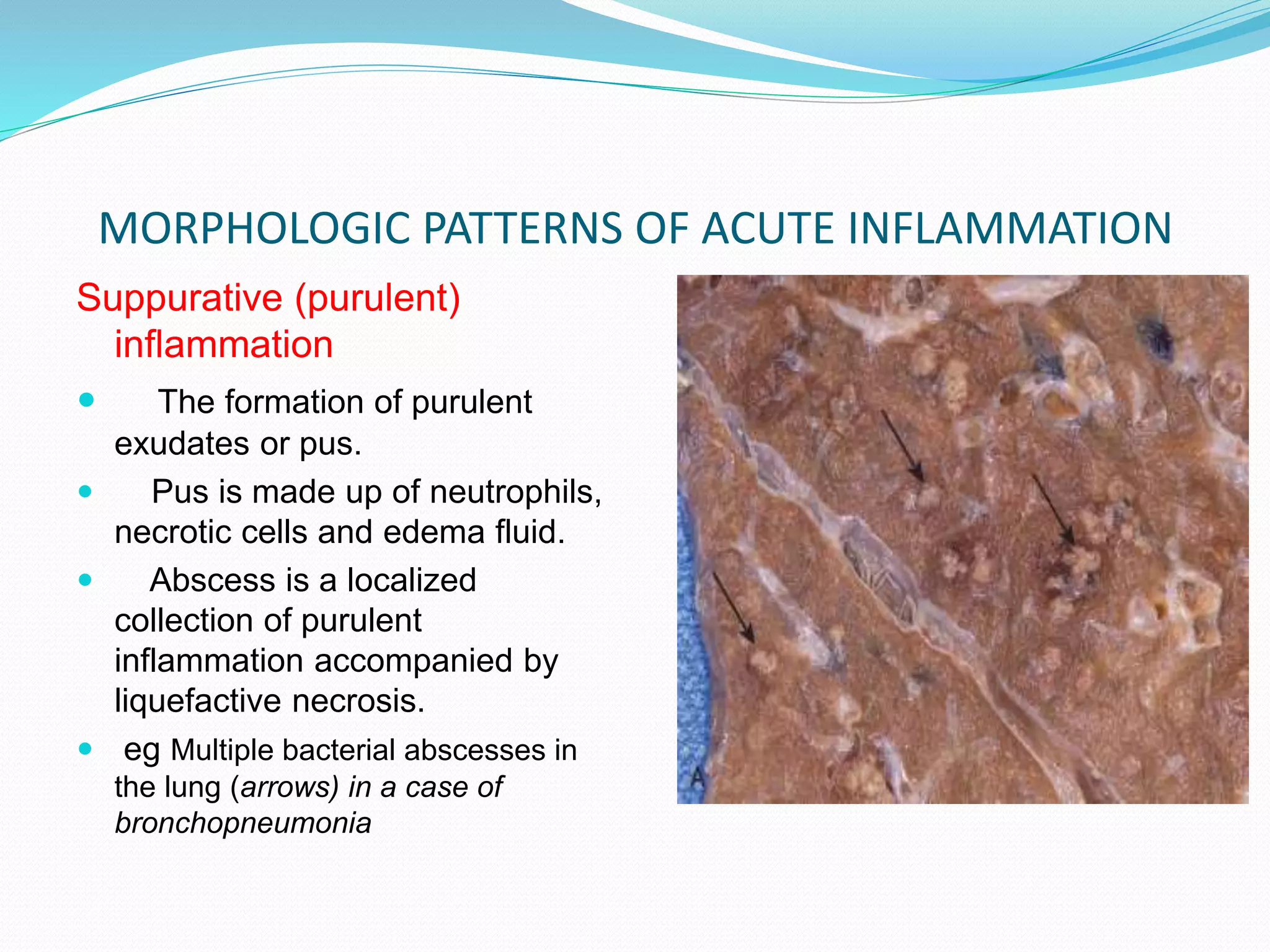
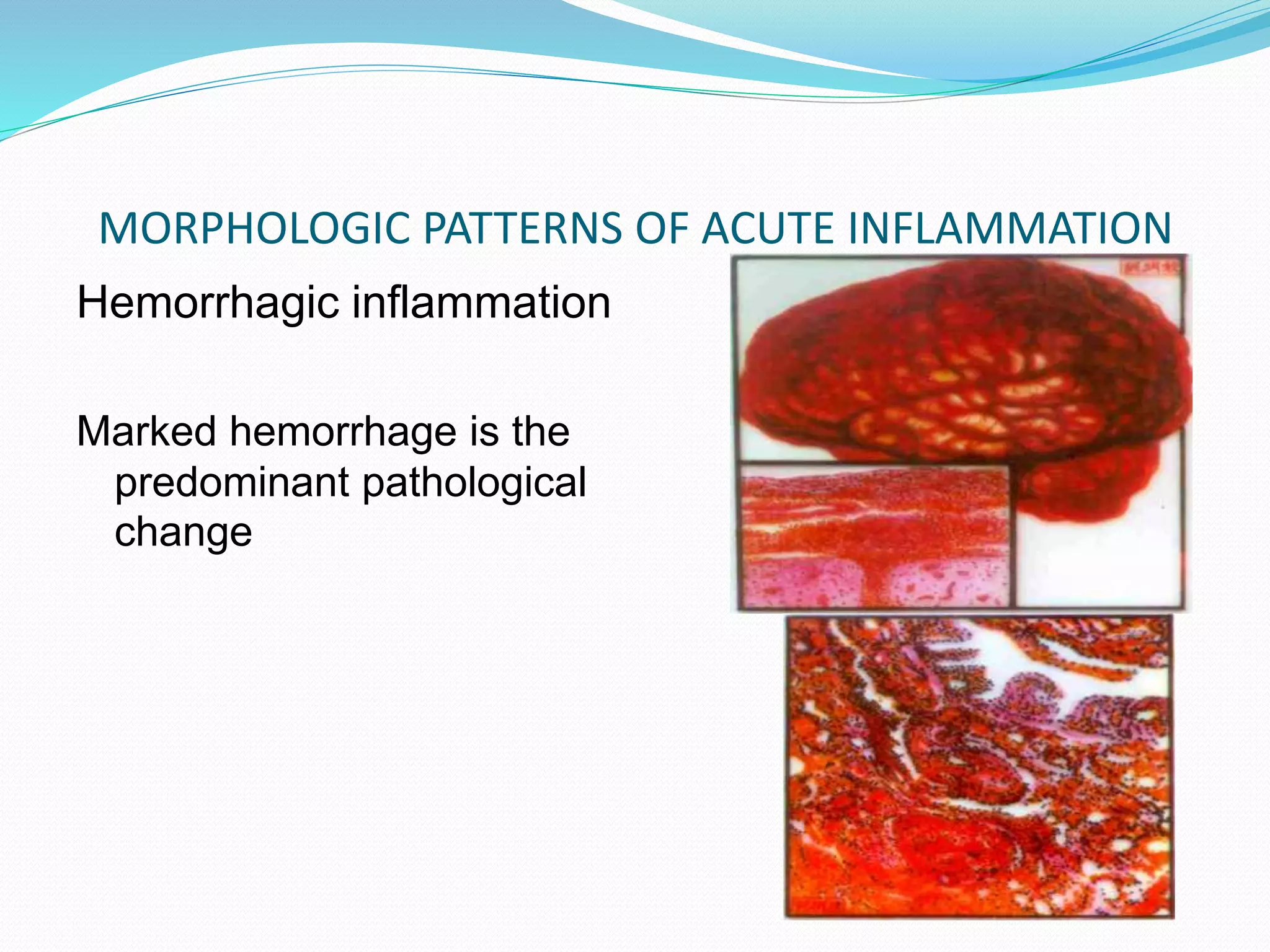
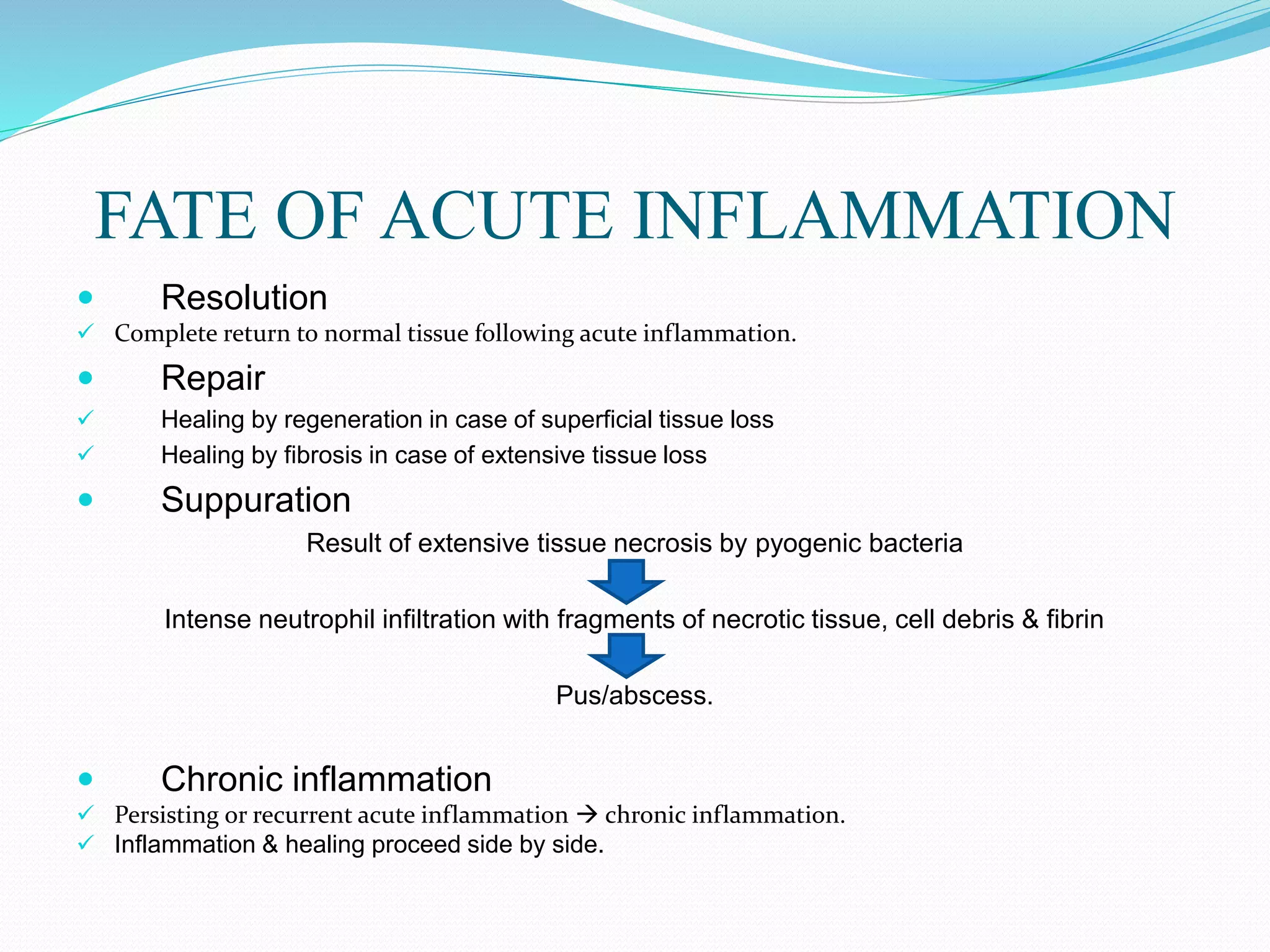
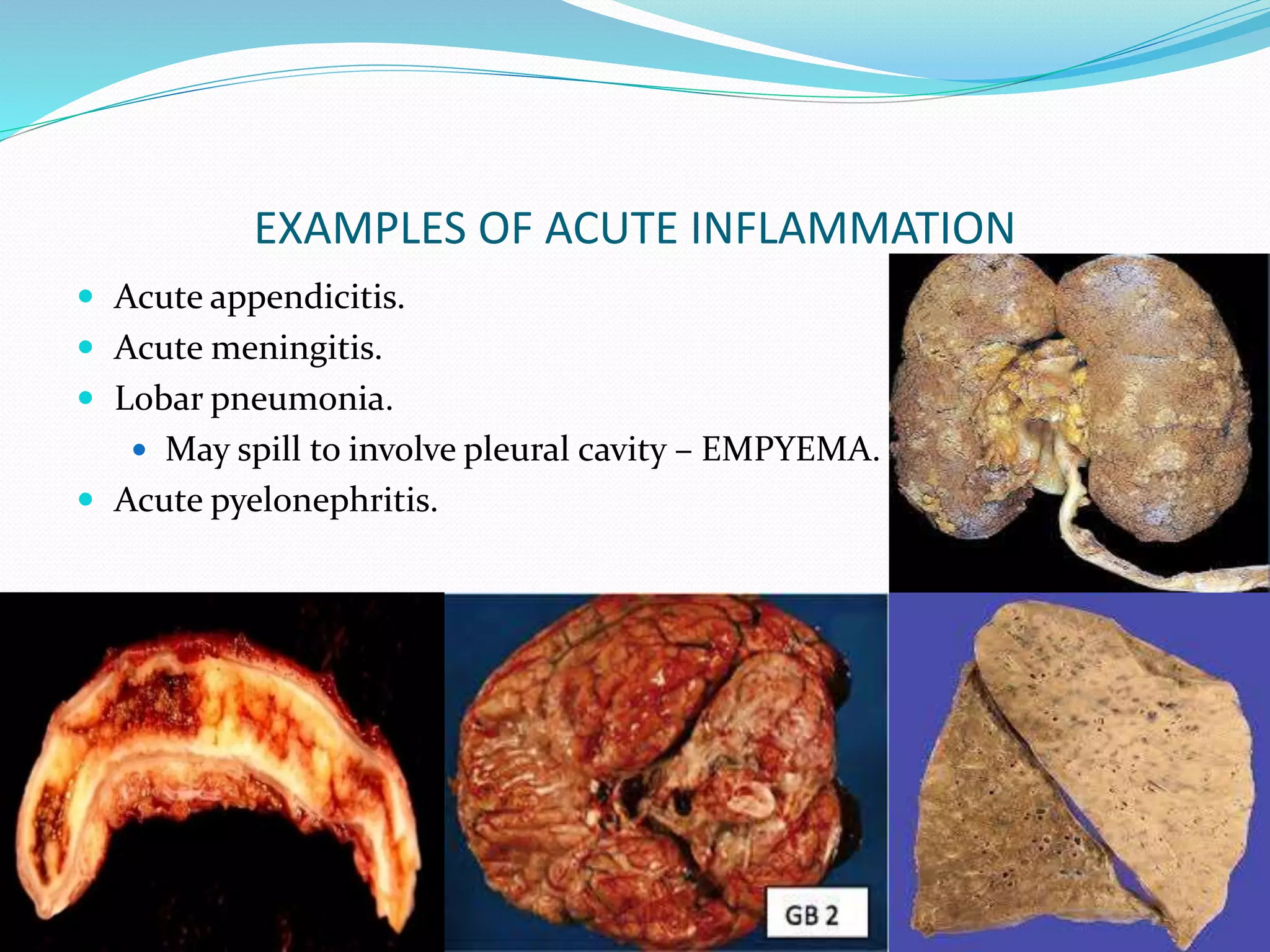
Acute inflammation is characterized by five signs: redness, heat, swelling, pain, and loss of function. The main events of acute inflammation are vascular events like vasodilation and increased permeability, and cellular events involving leukocyte recruitment and activation. This results in an inflammatory cell-rich exudate. Acute inflammation can resolve, repair through regeneration or fibrosis, lead to suppuration or pus formation, or progress to chronic inflammation. Examples include acute appendicitis, meningitis, and pneumonia.