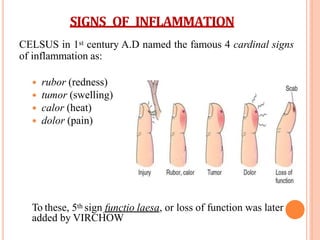
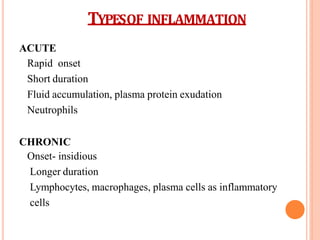
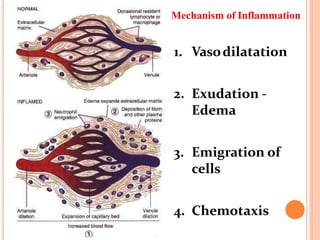
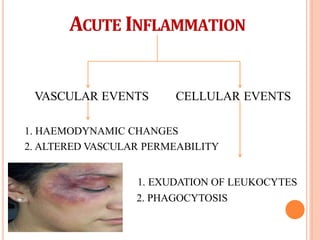
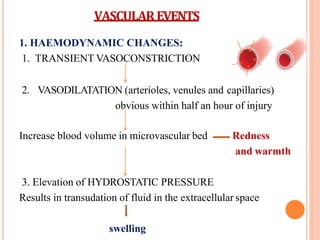
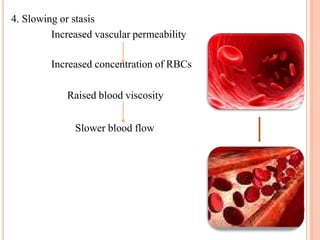
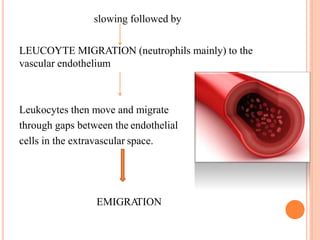
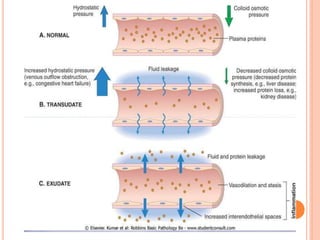
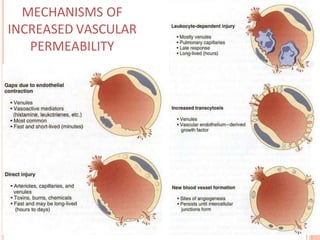
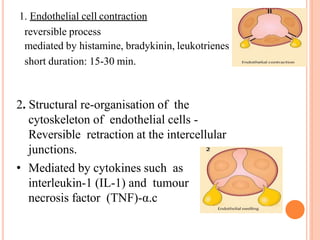
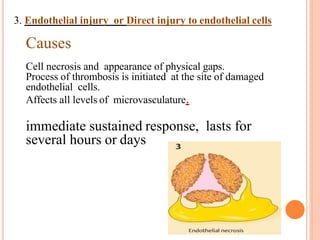
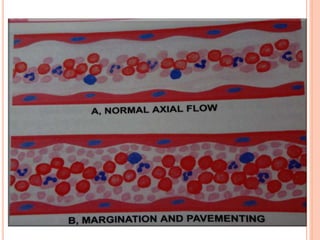
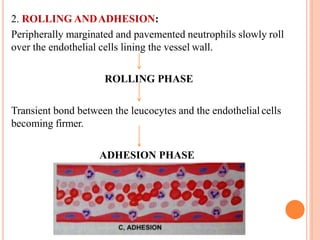
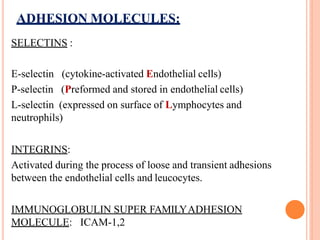
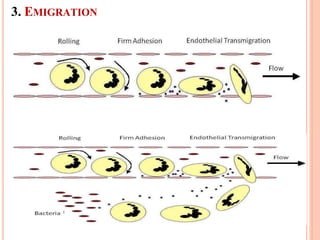
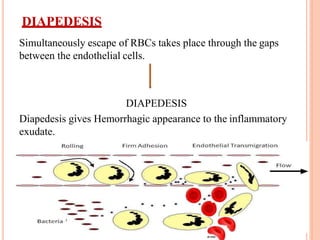
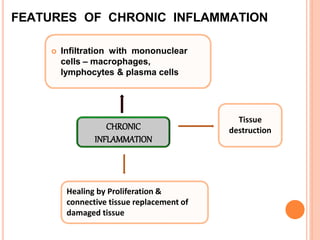
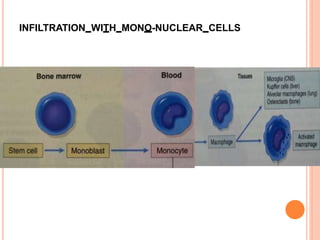
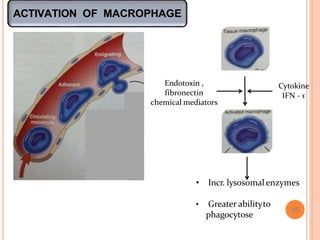
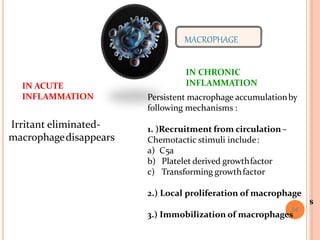
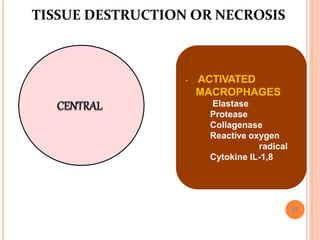
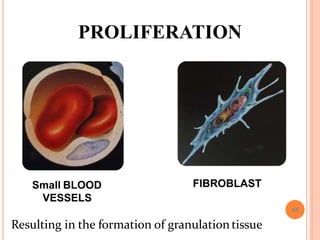
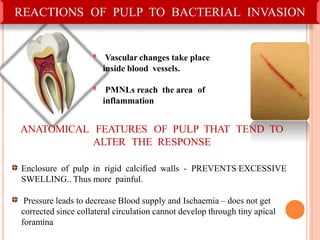
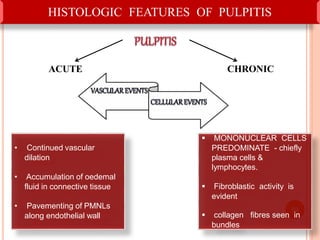
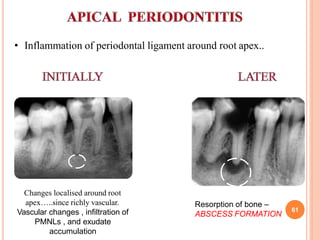
This document discusses inflammation and healing. It defines inflammation as the local response of living tissues to injury. The causes of inflammation can be exogenous, such as physical or chemical agents, or endogenous like circulation disorders or metabolic products. The classic signs of inflammation are redness, swelling, heat, and pain. Acute inflammation involves rapid onset and short duration, while chronic inflammation has insidious onset and longer duration. Acute inflammation is characterized by increased blood flow, vascular permeability, and leukocyte infiltration. Chronic inflammation features infiltration by mononuclear cells like macrophages and lymphocytes, along with simultaneous tissue destruction and healing.