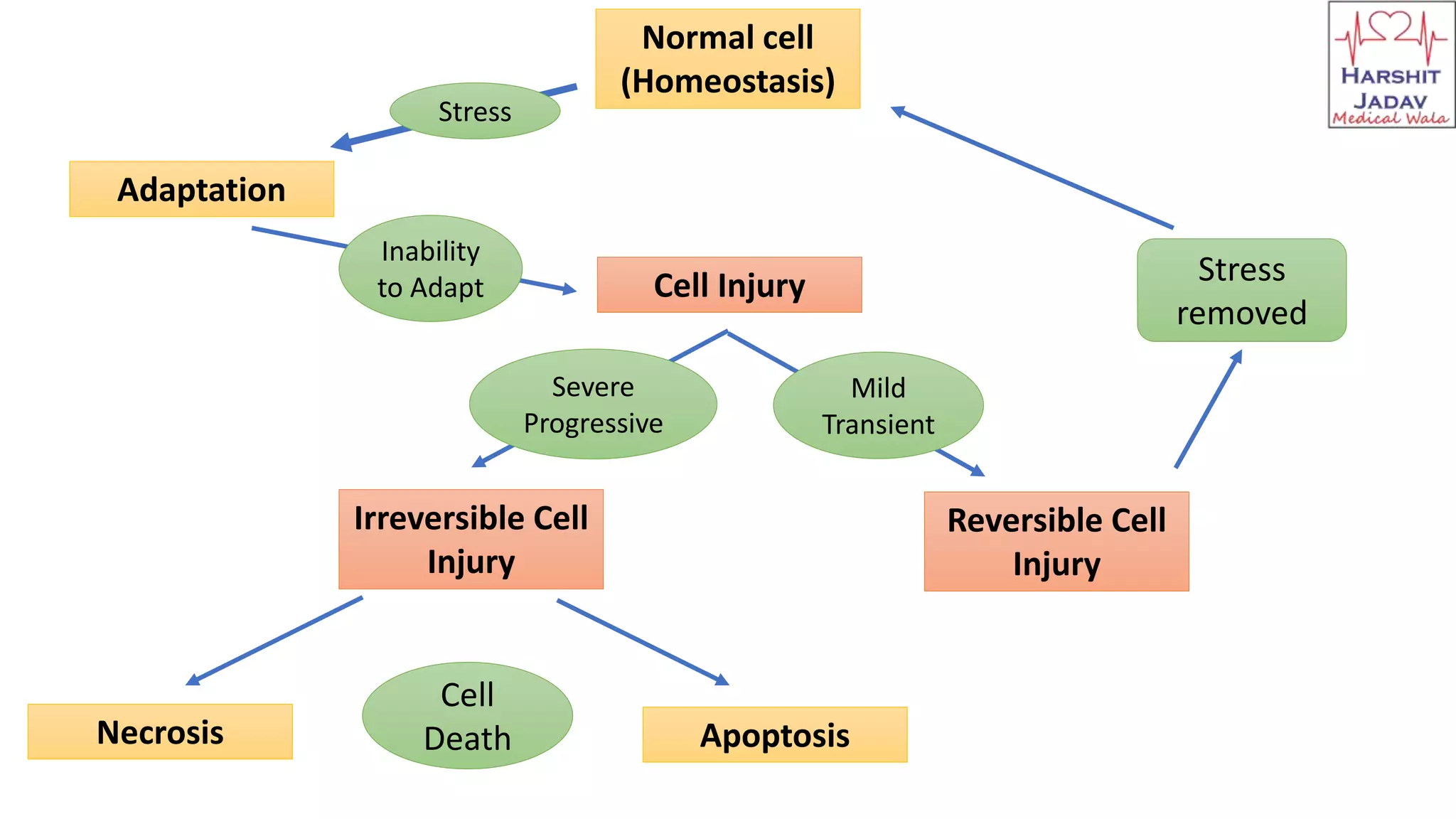
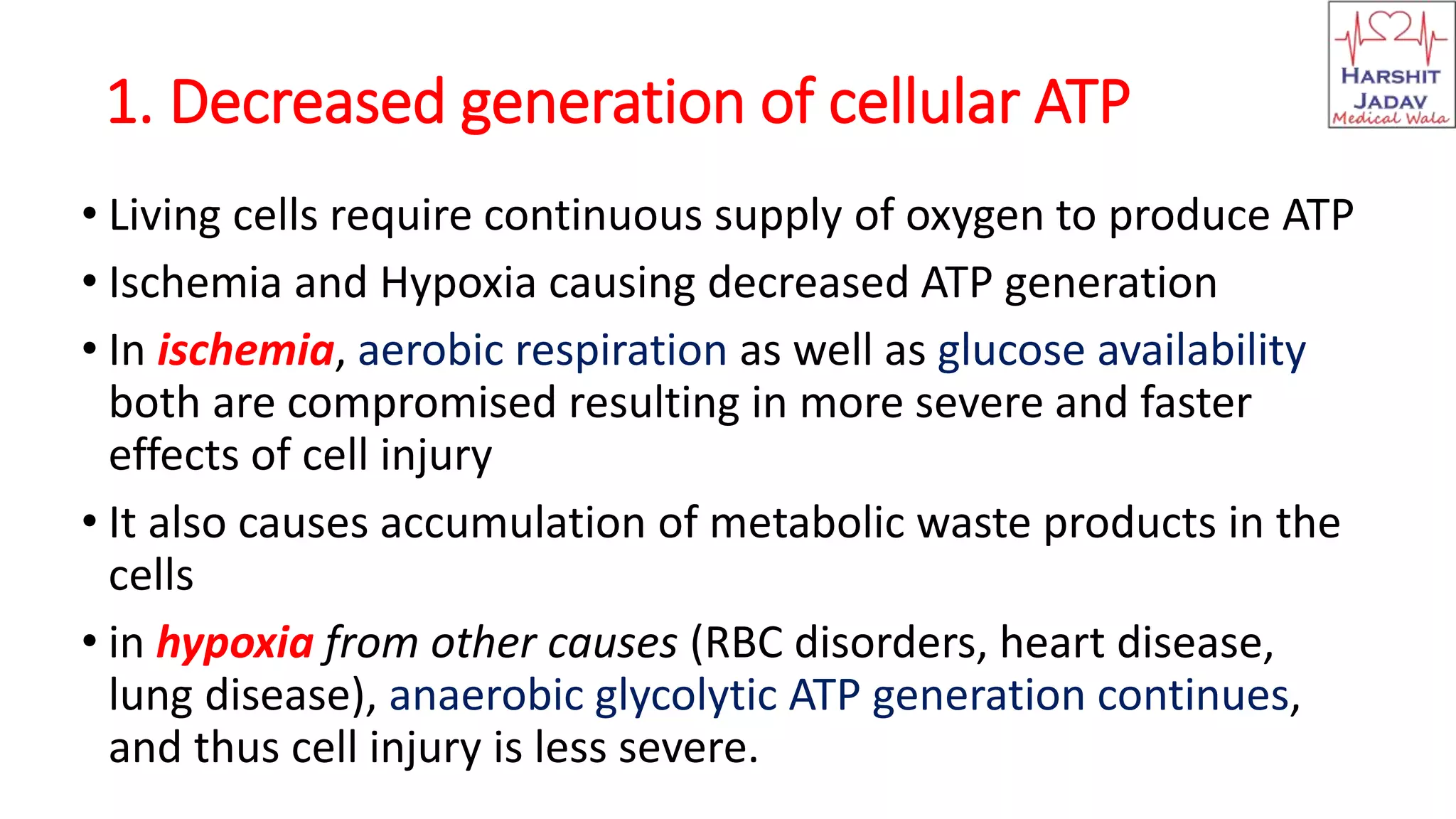
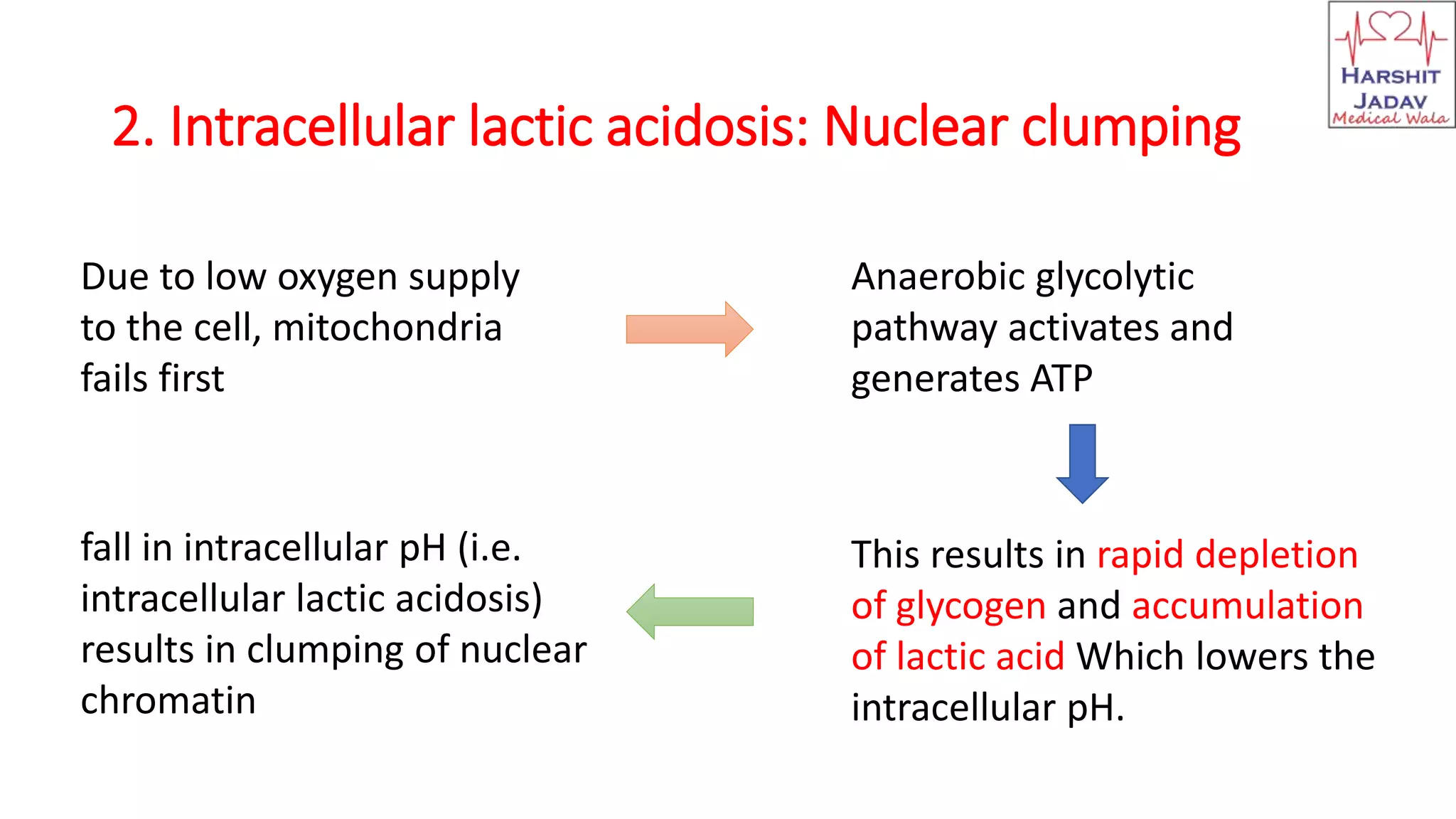
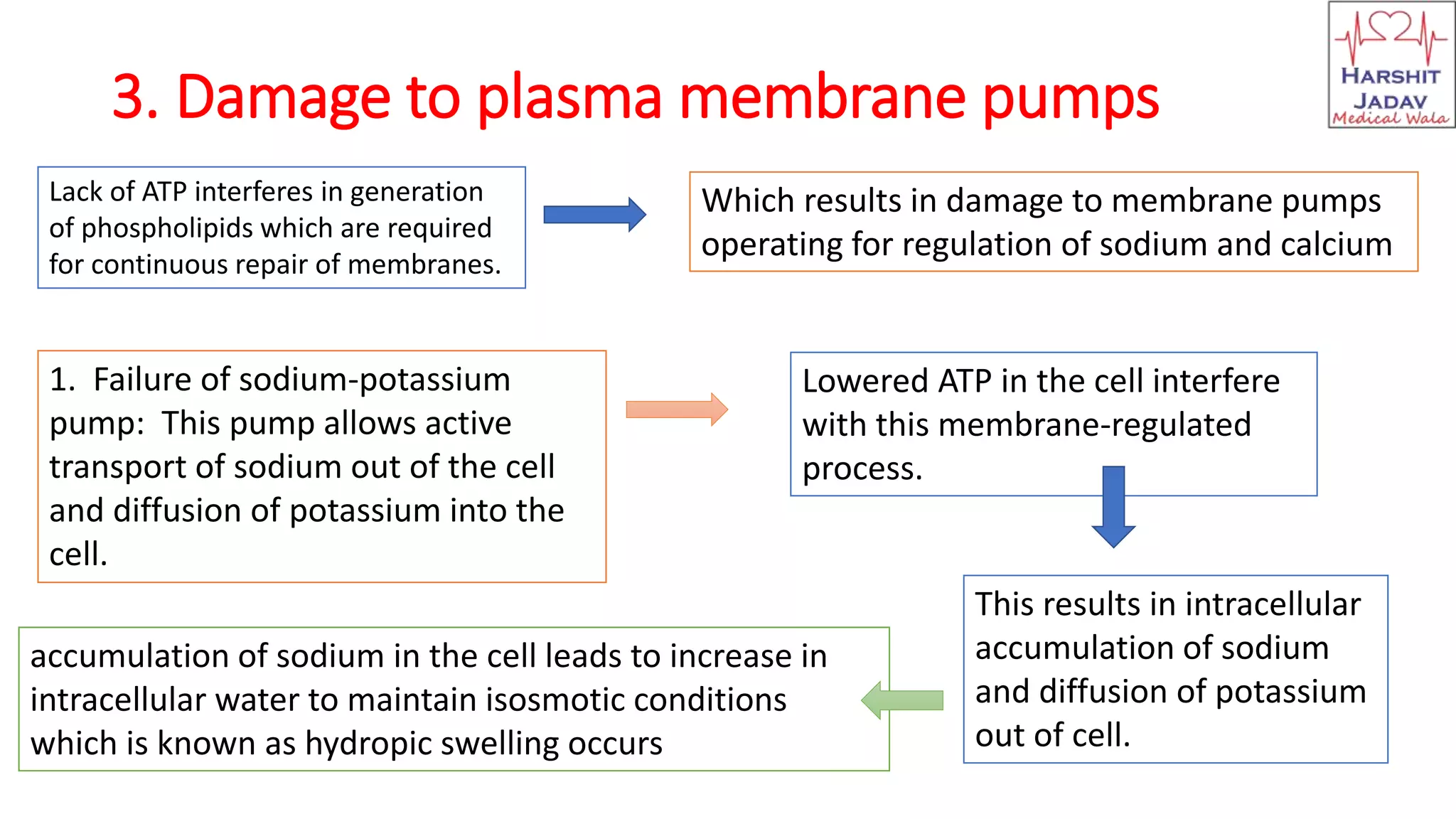
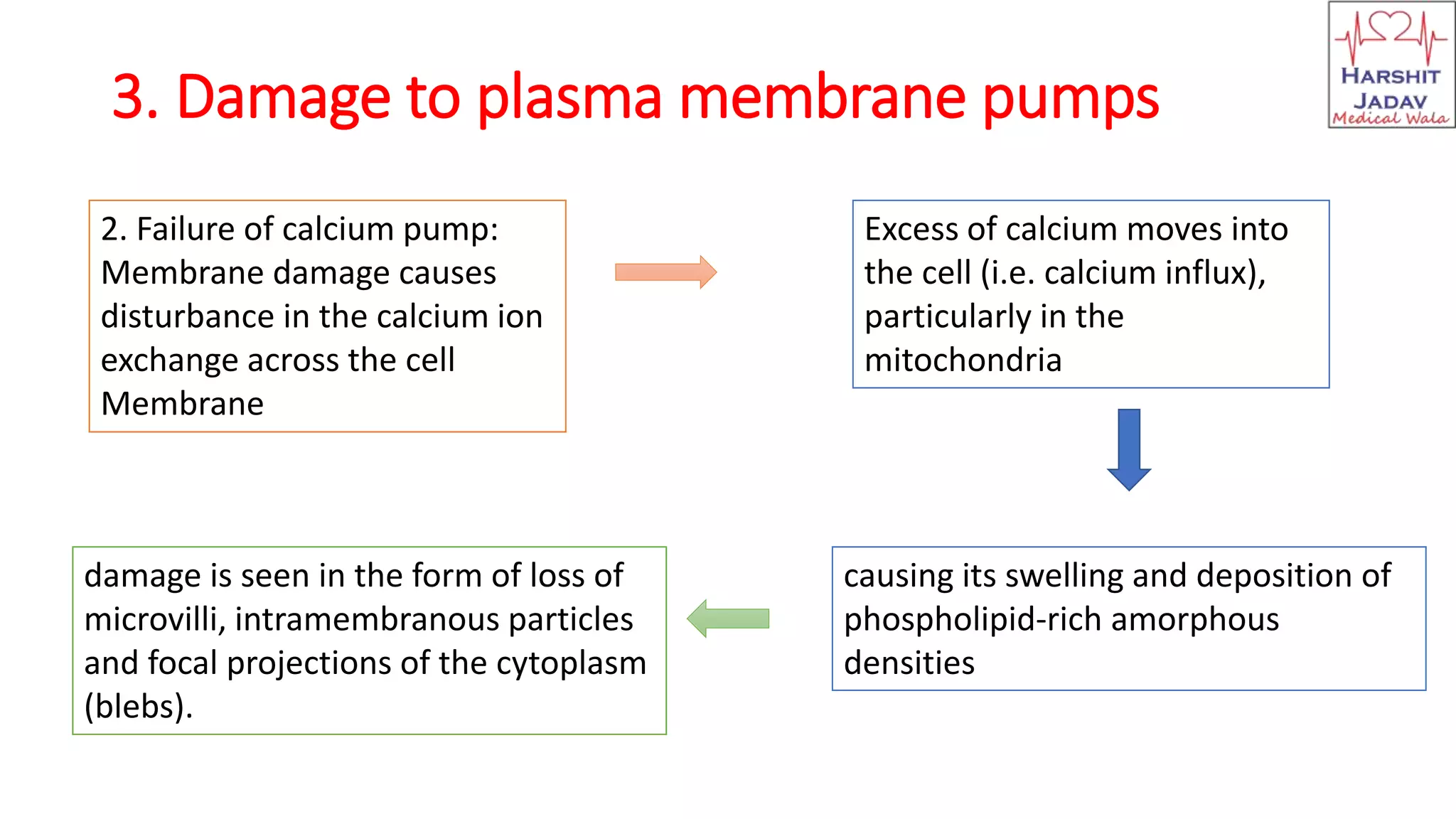
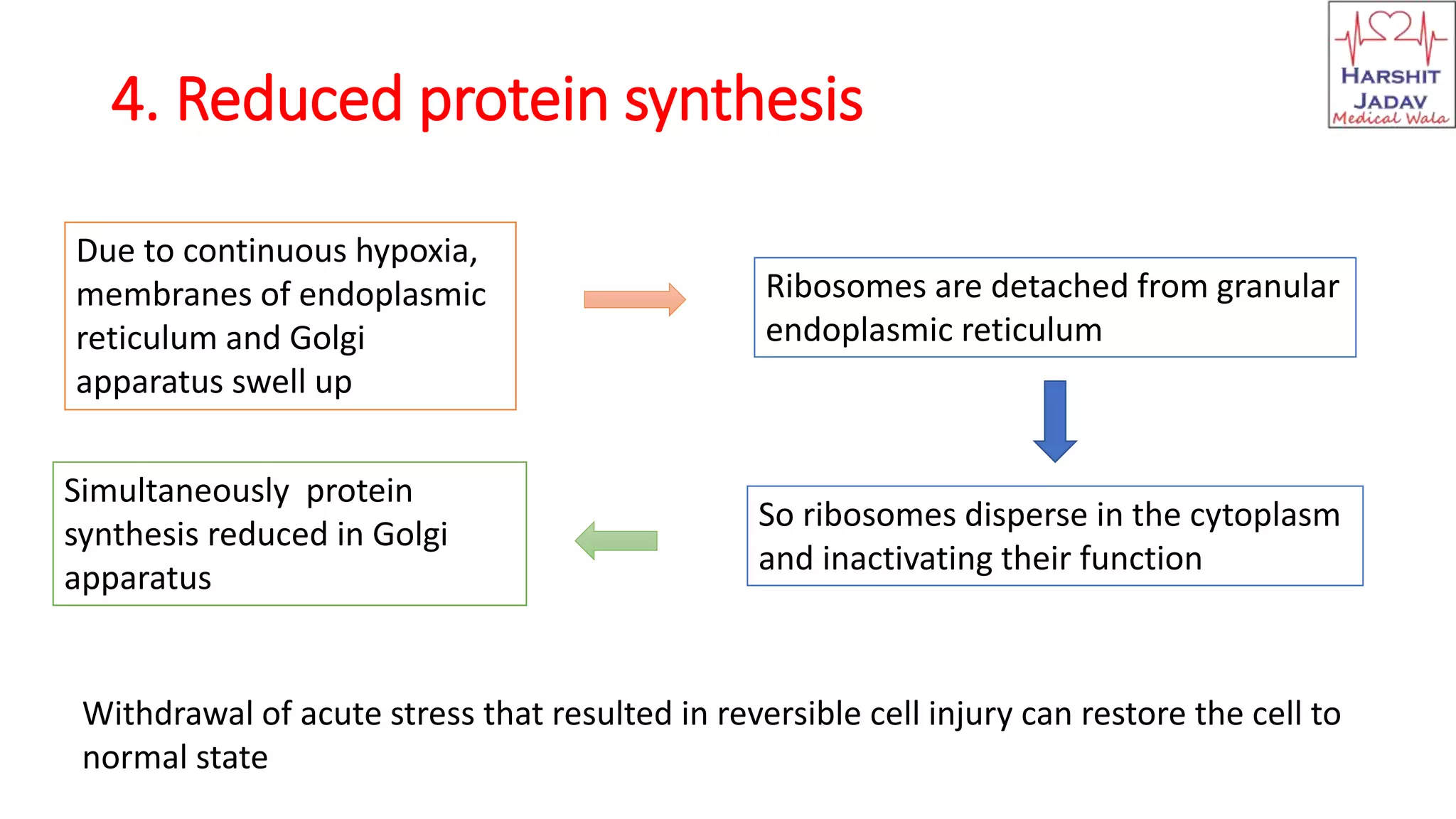
Reversible cell injury occurs when cells are exposed to a brief period of ischemia or hypoxia. This causes 1) decreased ATP generation, 2) intracellular lactic acidosis and nuclear clumping, 3) damage to plasma membrane pumps causing sodium accumulation and calcium influx, and 4) reduced protein synthesis. If the stressor is removed quickly, the cell injury may be reversible and the cell can return to normal functioning.