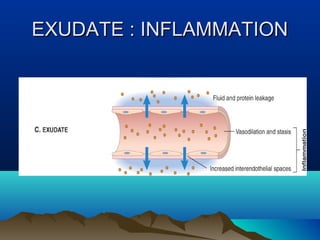
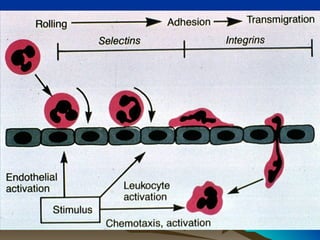
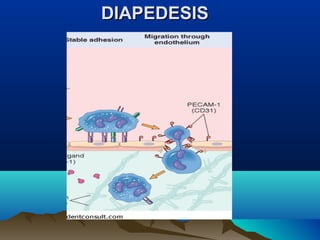
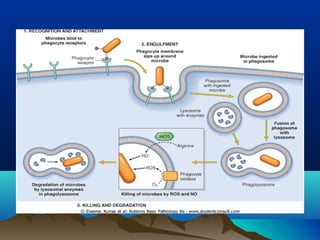
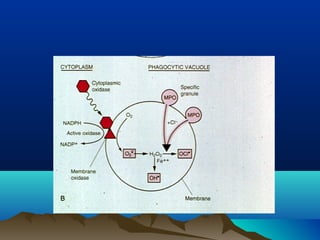
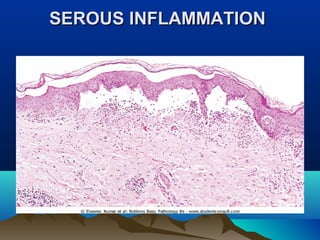
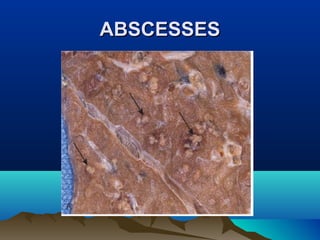
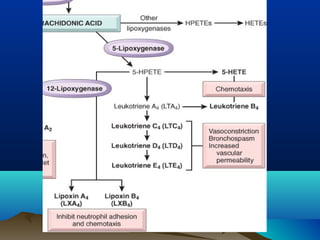
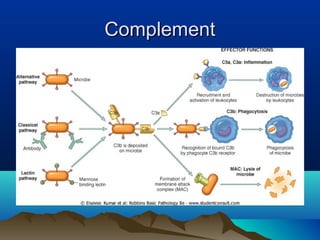
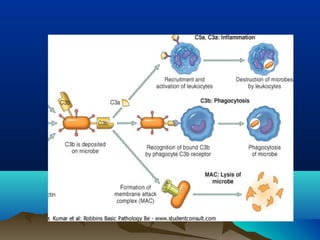
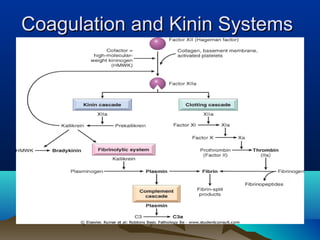
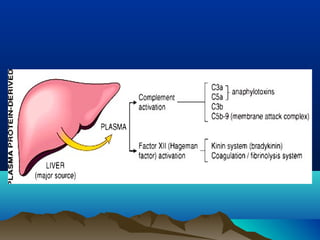
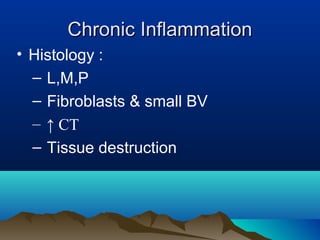
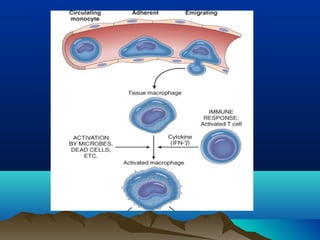
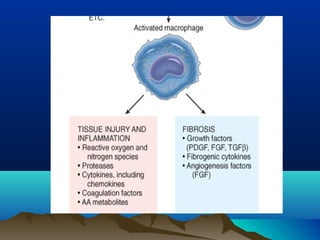
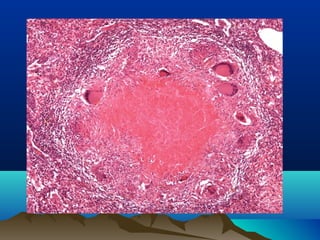
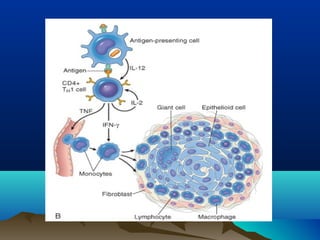
Inflammation is the body's protective response to injury or infection. The document discusses the key components of acute and chronic inflammation. Acute inflammation is characterized by rapid onset, short duration, and features like fluid exudation and neutrophil accumulation. Chronic inflammation lasts longer and involves lymphocytes, macrophages and plasma cells. The inflammatory response involves vascular changes like vasodilation and increased permeability, as well as cellular events like leukocyte recruitment and activation through processes such as chemotaxis and phagocytosis. Chemical mediators released include histamine, prostaglandins, leukotrienes and cytokines which regulate the inflammatory response.