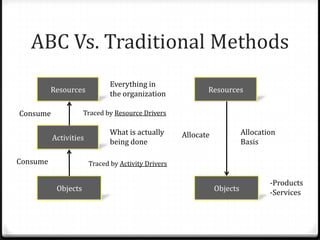
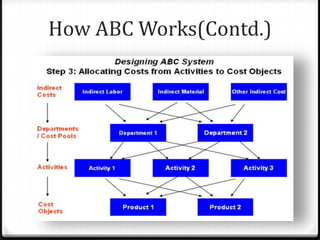
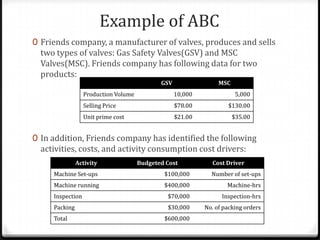
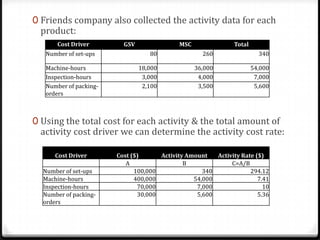
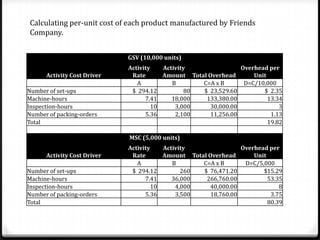
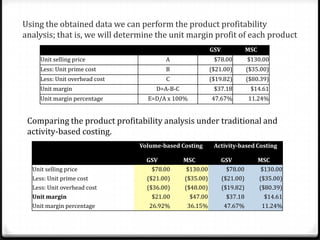
Activity based costing (ABC) is a management accounting approach that allocates direct and indirect costs to products and services based on the activities and resources required to produce them. It provides more accurate cost and profit information than traditional methods by tracing costs to activities and then to cost objects using activity drivers. The key steps in ABC are identifying activities and resources, assigning resource costs to activities, and assigning activity costs to cost objects using activity consumption drivers. This allows management to understand cost and profitability at a more granular level and improve decision making.