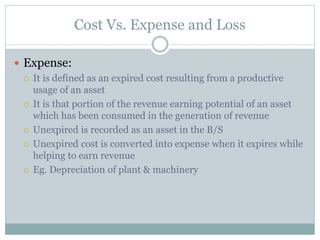
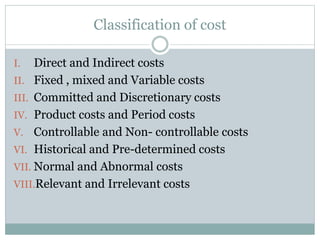
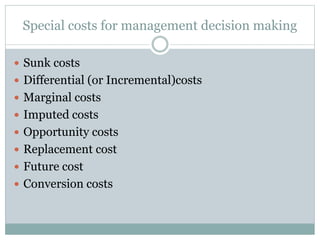
This document defines key cost concepts and classifications. It explains that cost is the monetary measure of resources used for production or services. Expenses are expired costs that helped generate revenue, while losses are expired costs with no benefit. Cost centers and cost units are defined as sections or units for which costs can be measured and used for control. Costs are classified in various ways such as direct/indirect, fixed/variable, and product/period costs to aid management decision making. Special costs like sunk, differential and marginal costs are also discussed.