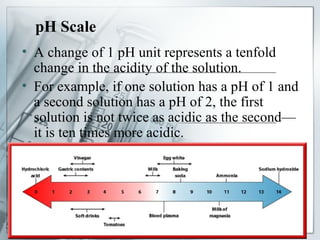
This document provides an overview of acids and bases. It begins with a brief history of acids and bases according to Arrhenius' theory. Key points include that acids produce H+ ions and bases produce OH- ions in water. The document then discusses the properties, uses, and pH scale of acids and bases. It explains that acids have a pH below 7 while bases have a pH above 7. The document concludes by noting that the reaction between an acid and base is called neutralization.