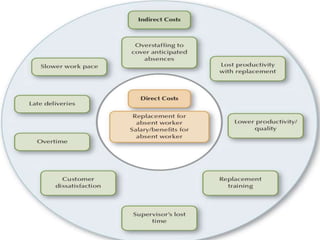
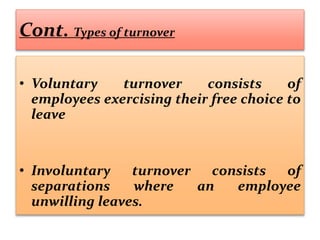
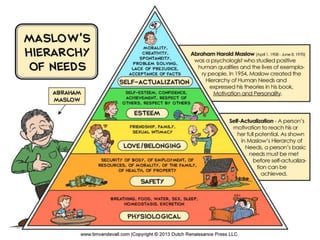
This document discusses absenteeism and turnover among nursing staff. It defines key terms like absenteeism, turnover, and retention. It outlines various types of absenteeism and turnover. The document also examines theories of absenteeism and identifies common causes of absenteeism and turnover among nurses. Finally, it proposes several methods that can be used to reduce absenteeism and turnover rates, such as accurate record keeping, counseling, health programs, safety initiatives, and flexible staffing policies.