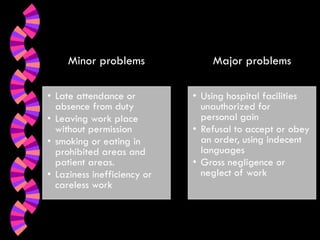
This document discusses discipline in the workplace. It defines discipline as promoting adherence to rules and procedures necessary for effective organizational functioning. Several definitions of discipline are provided that emphasize orderly conduct, submission to regulations, and ensuring compliance with objectives. The objectives, types, aspects, principles, and approaches of discipline are outlined. Self-discipline and factors influencing it are also explained. Indiscipline, its causes, and how to deal with problem employees are discussed. Effective strategies for absenteeism and impaired employees are presented.