The document provides information about web browsers, email, and how they work. It discusses:
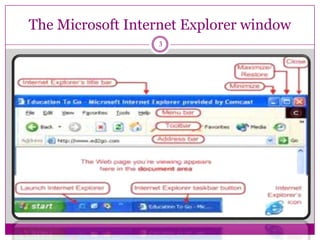
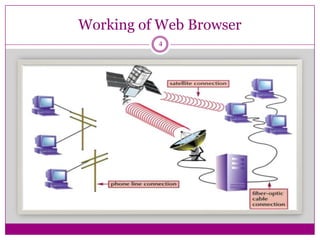
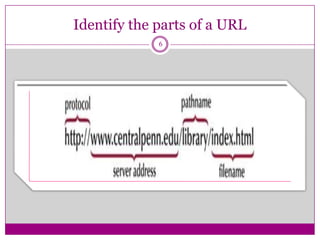
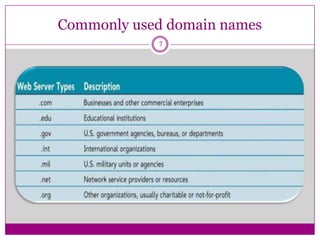
- How web browsers connect to web servers to access web pages coded in HTML and display them, with hyperlinks allowing navigation between pages.
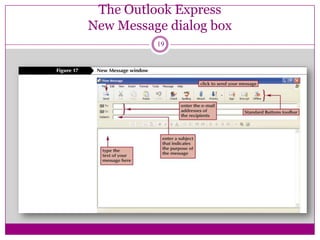
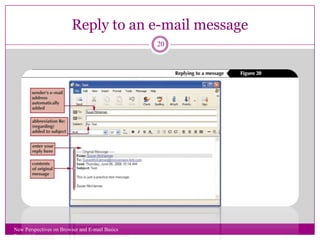
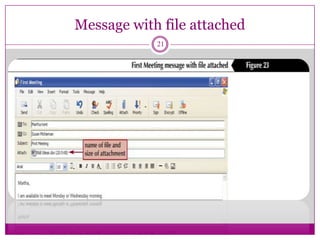
- The basics of email, how it works by sending messages between users through email servers, and some common functions like compose, reply, forward, and attach files.
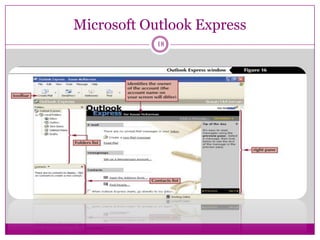
- Two common ways for users to access their email - through a webmail interface or by using email software like Outlook Express to download messages from the server to their computer.