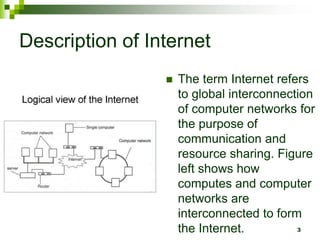
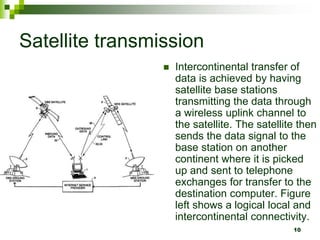
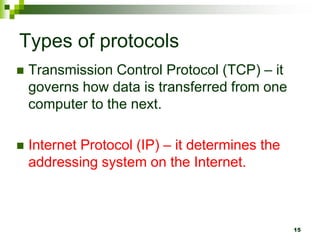
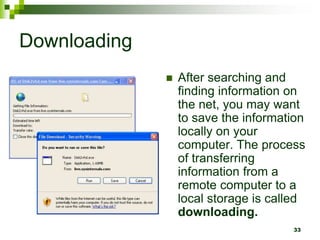
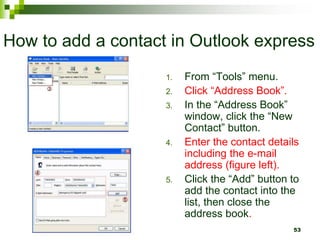
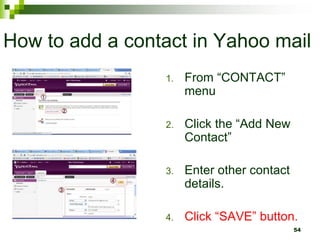
The document provides an overview of the internet and email. It discusses the development of the internet from 1969 when ARPANET was created, allowing universities to share information. By 1994, 3 million computers were connected to the internet. The document also describes how computers connect to the internet through telecommunication facilities, satellites, modems, wireless technologies, internet service providers, and internet software/protocols. Users can access the internet through web browsers and use features like bookmarks, hyperlinks, search engines, downloading, and printing web pages. The document concludes by explaining electronic mail including email software, facilities like sending/receiving mail with attachments, and managing contacts.