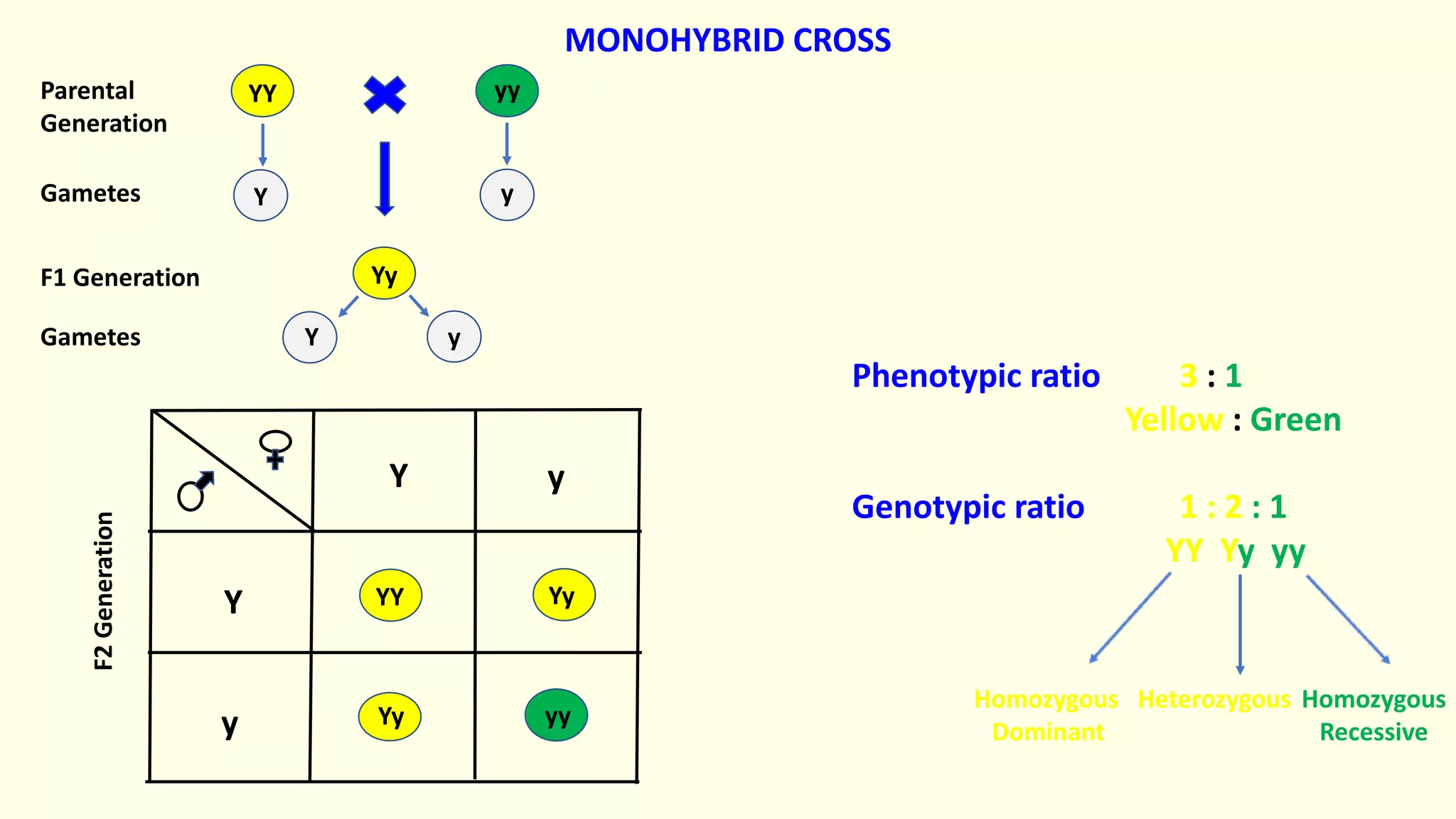
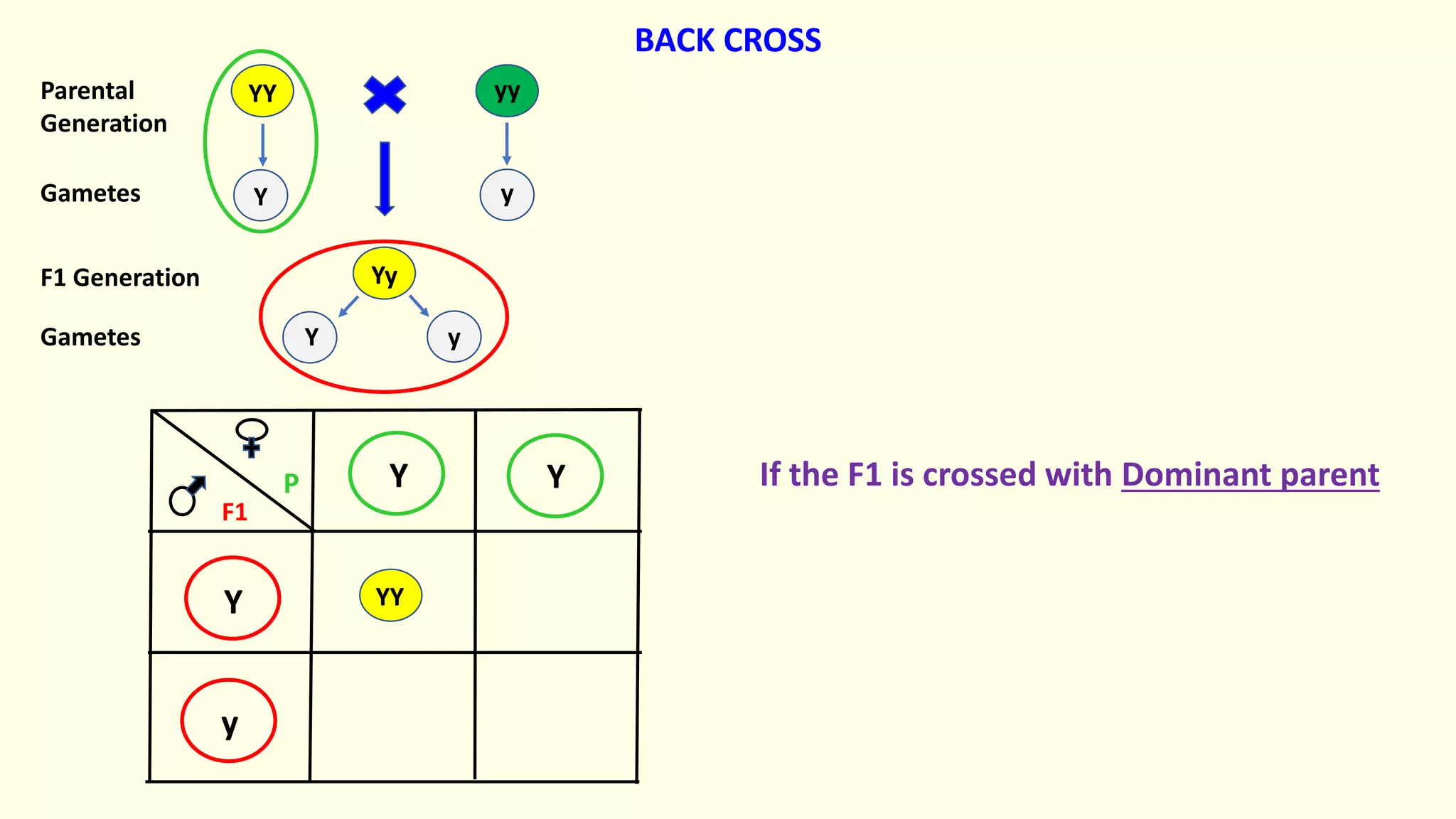
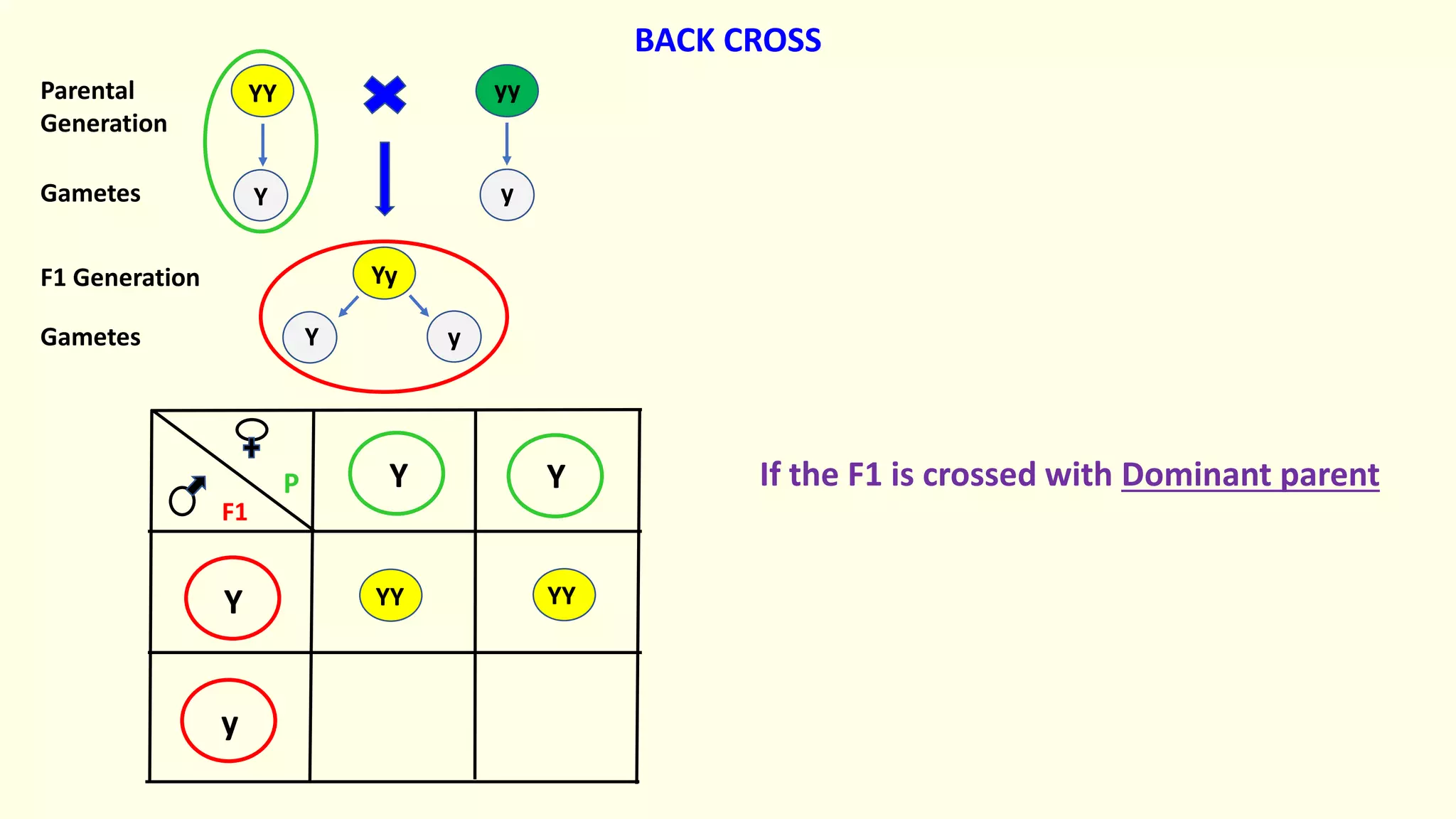
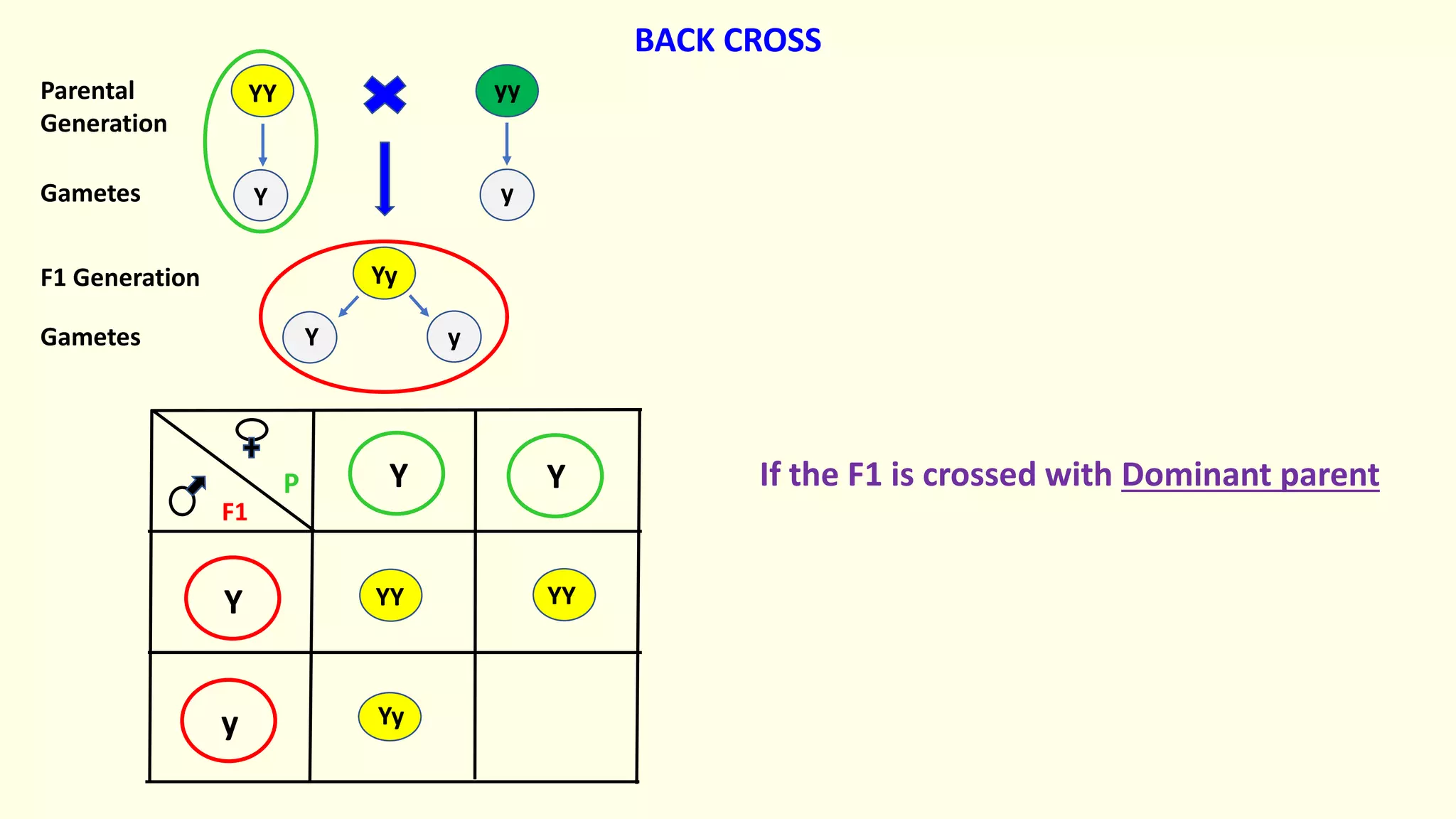
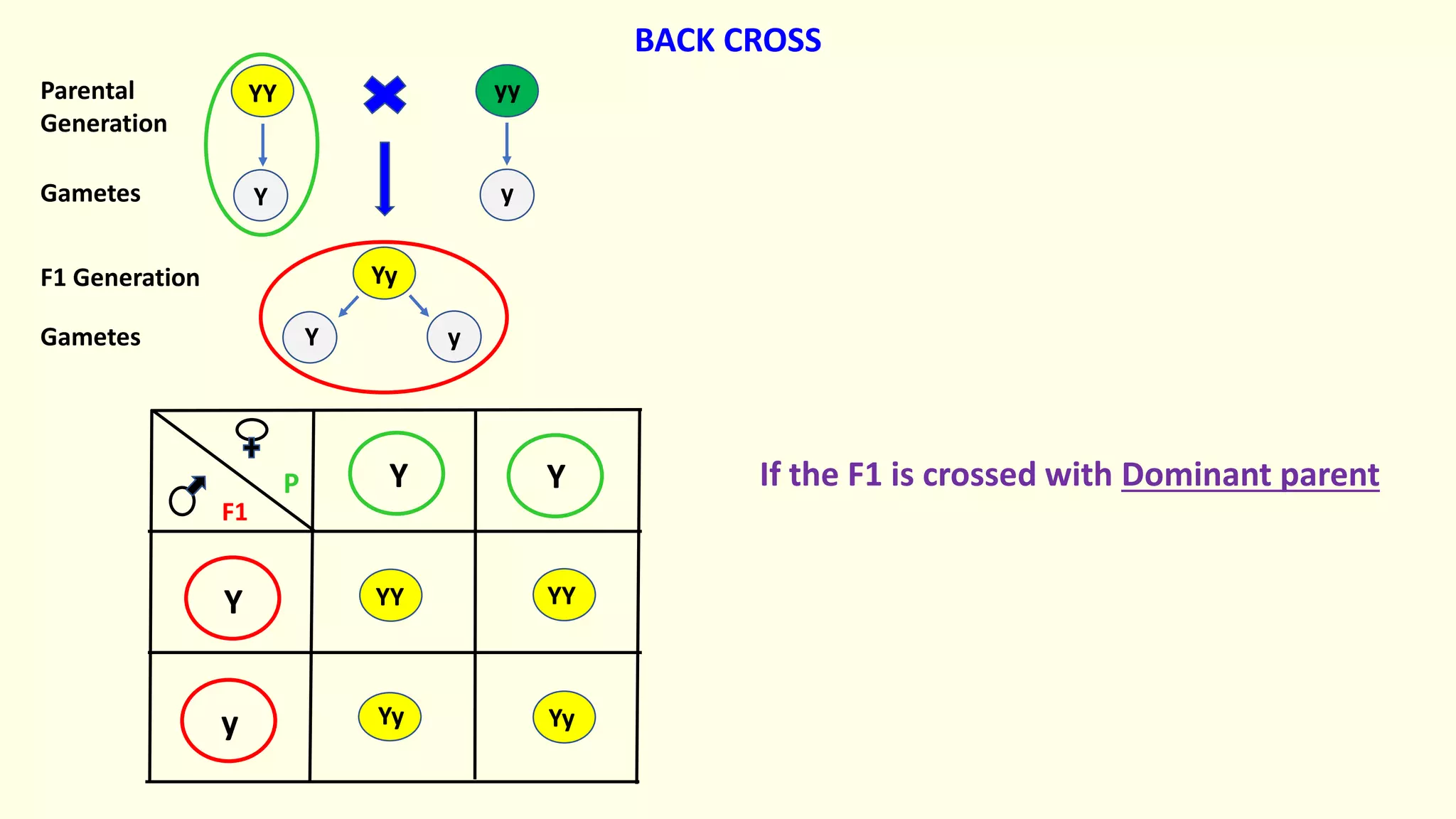
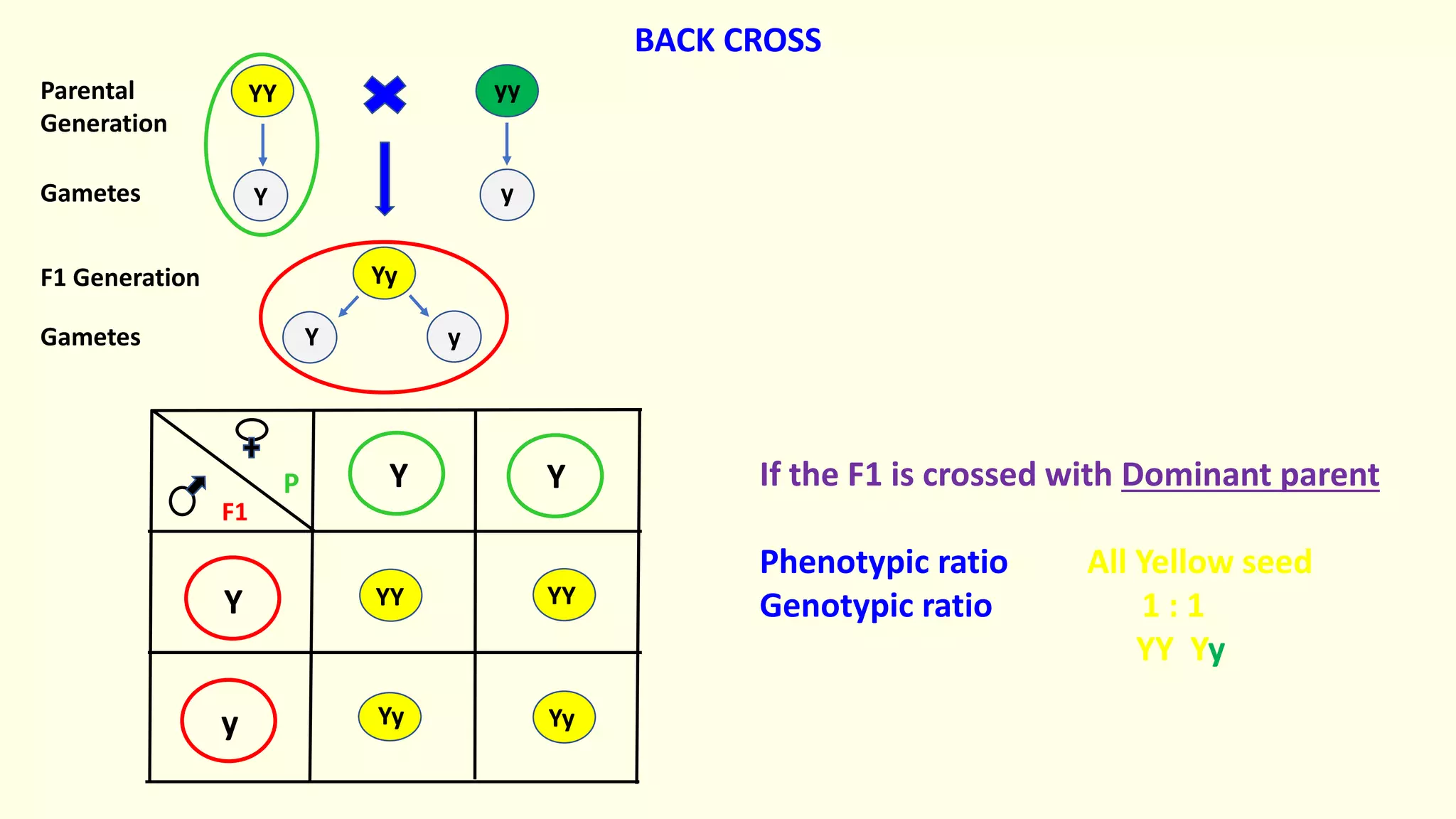
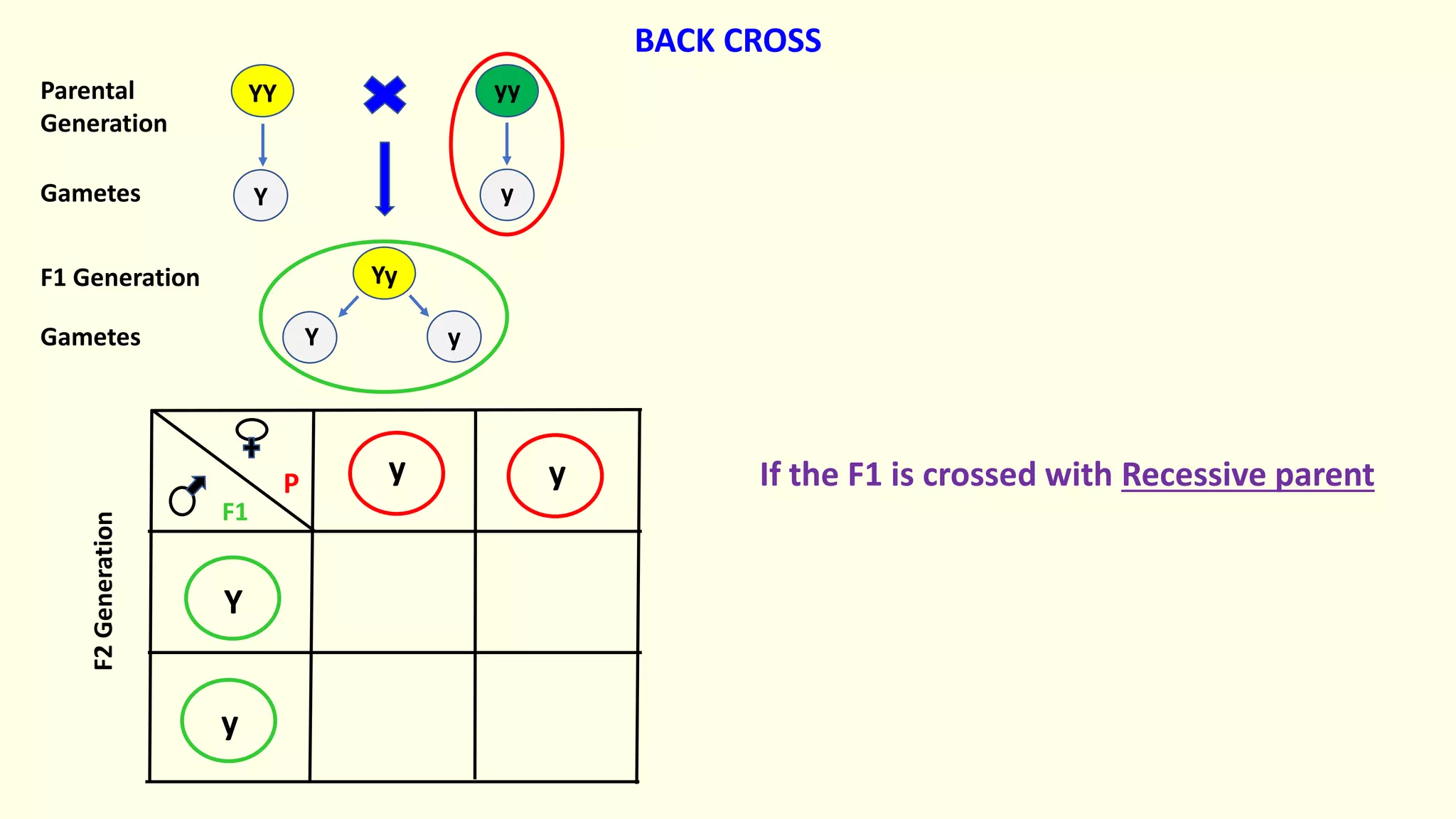
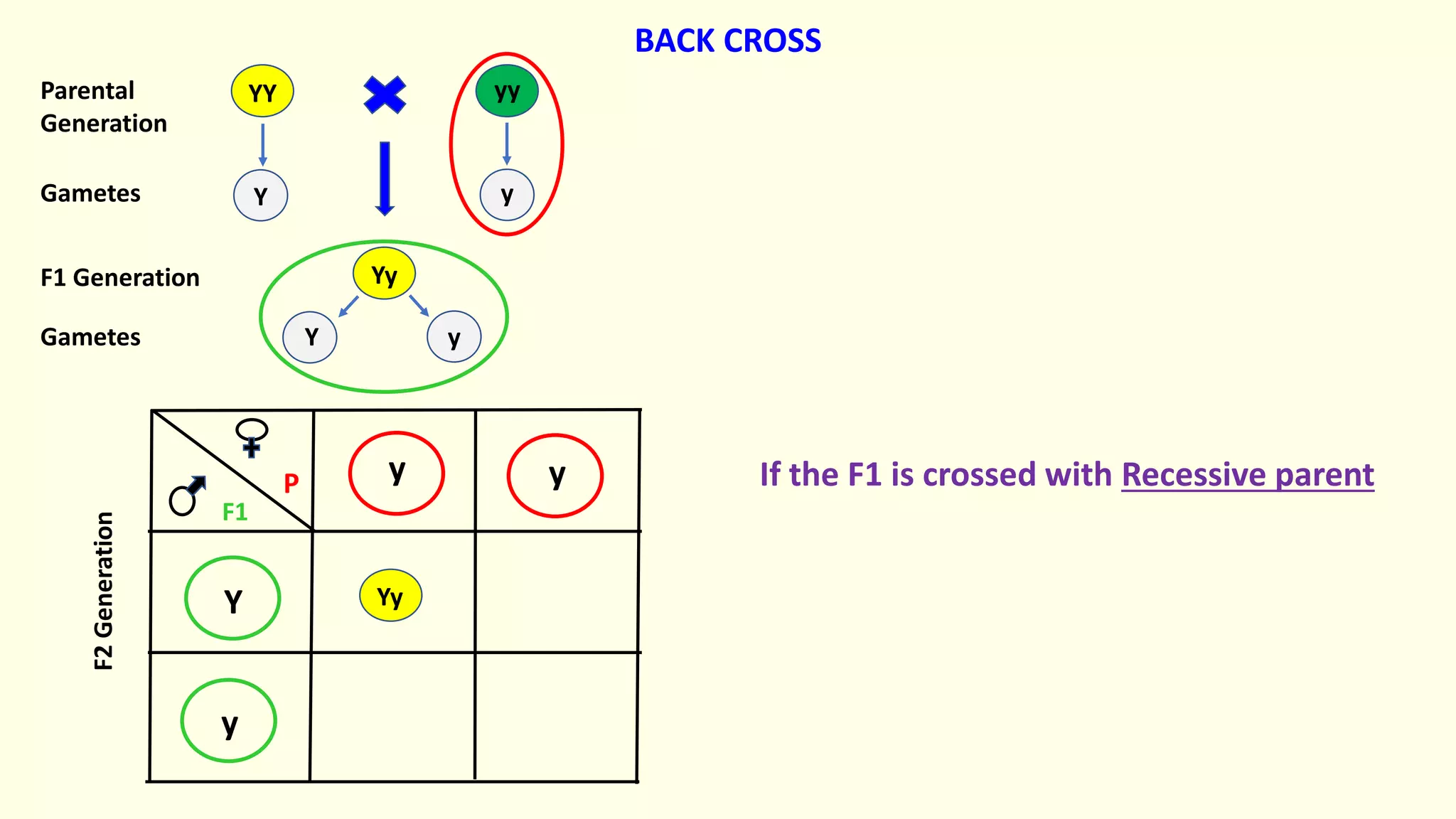
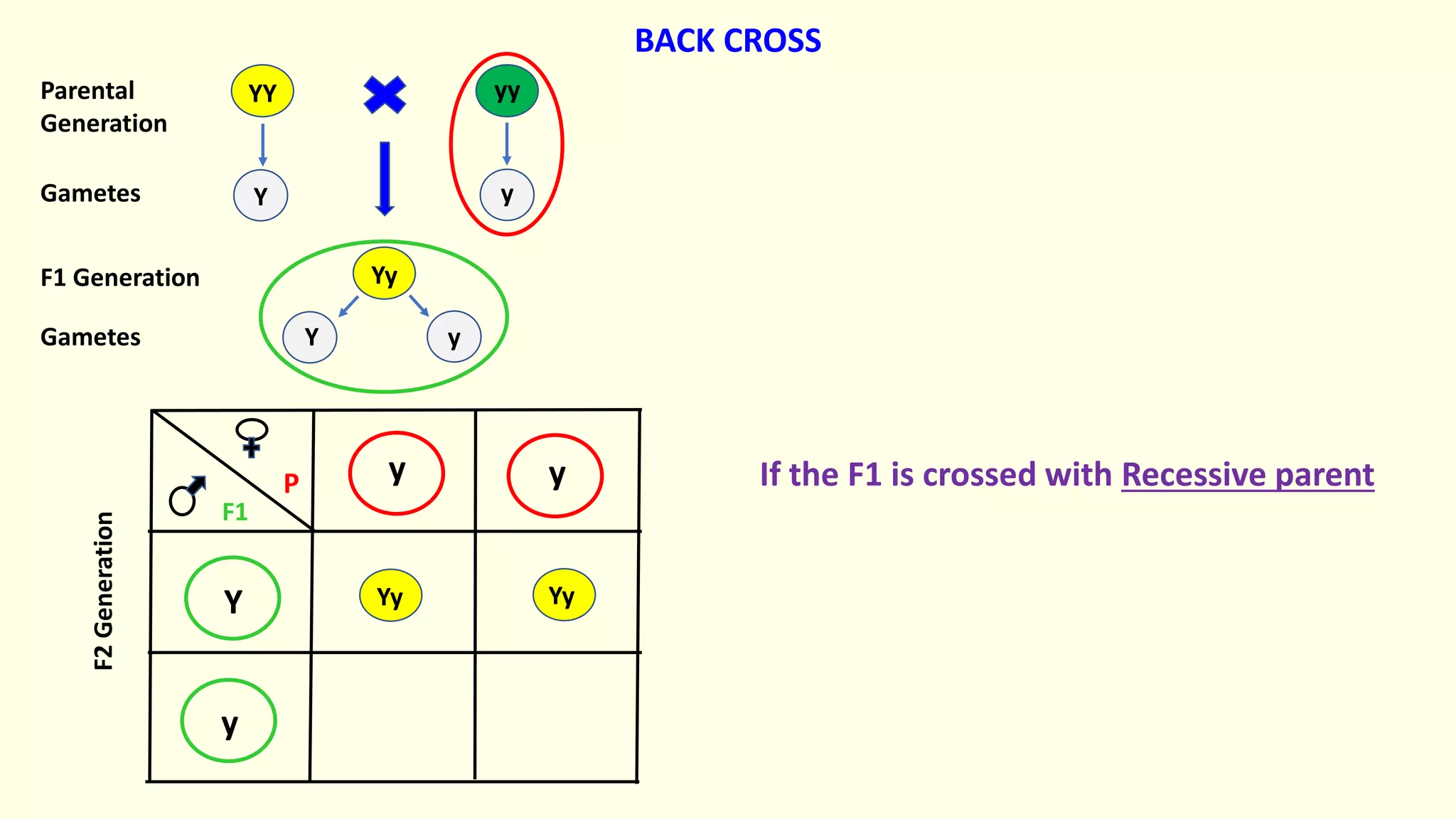
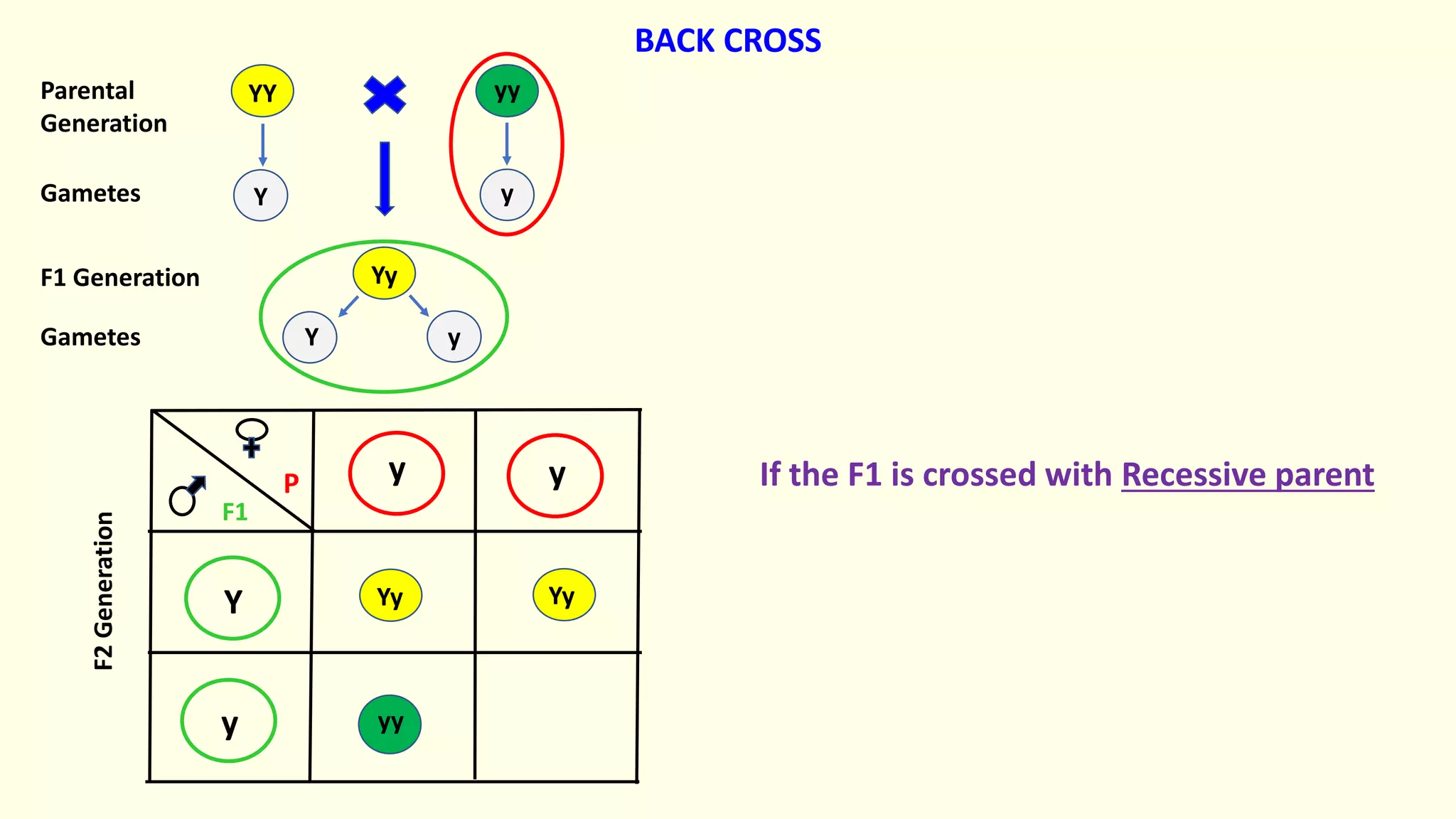
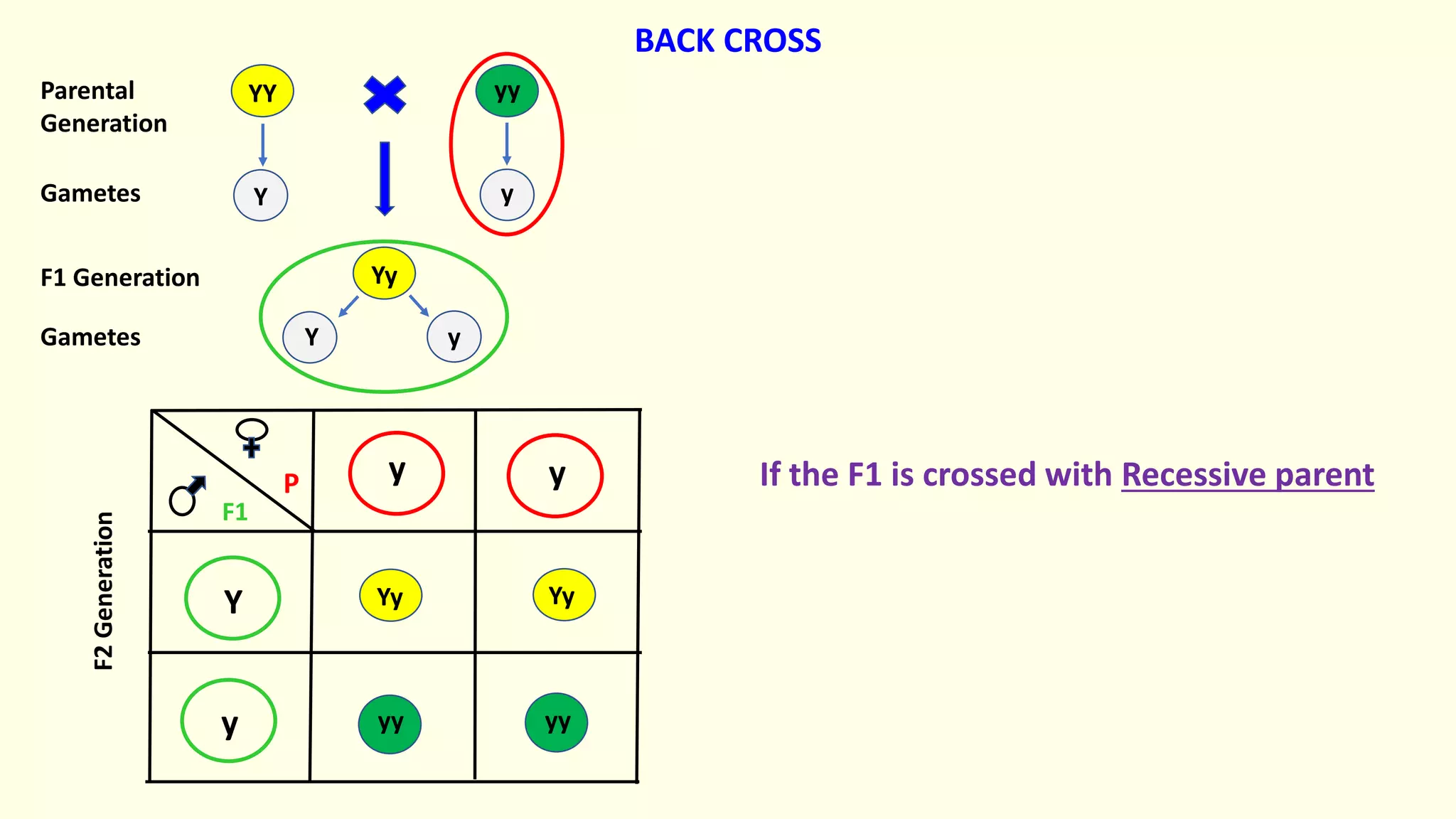
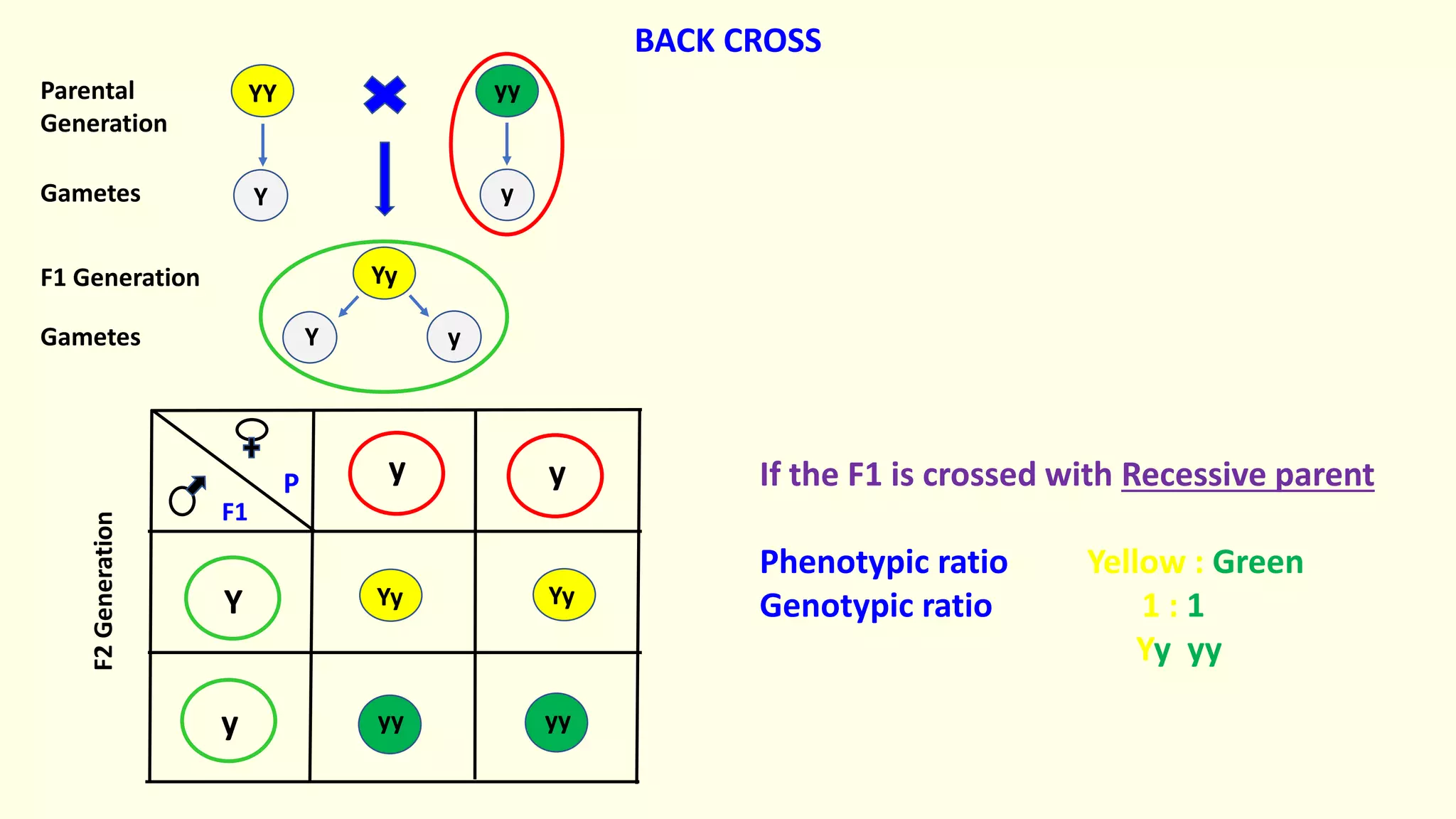
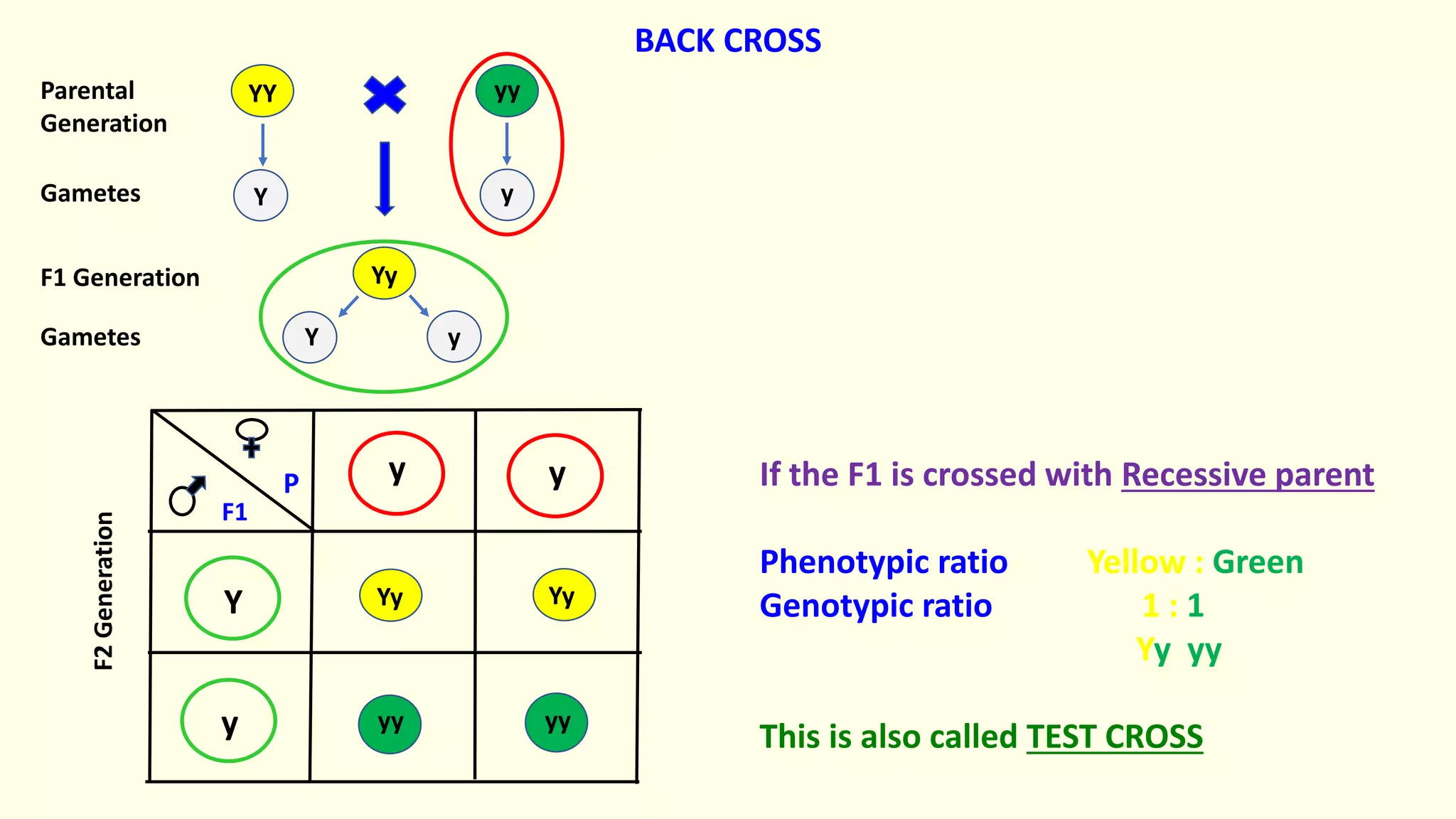
Backcrossing involves crossing a hybrid with one of its parents to produce offspring that are genetically more similar to the parent. It is used in plant and animal breeding to transfer desired traits from a hybrid back into a parent's genetic background. A backcross can be described as BC1, BC2, etc depending on how many times the hybrid has been backcrossed. Backcrossing with the dominant parent will result in all dominant phenotype offspring, while backcrossing with the recessive parent will result in a 1:1 phenotypic ratio.