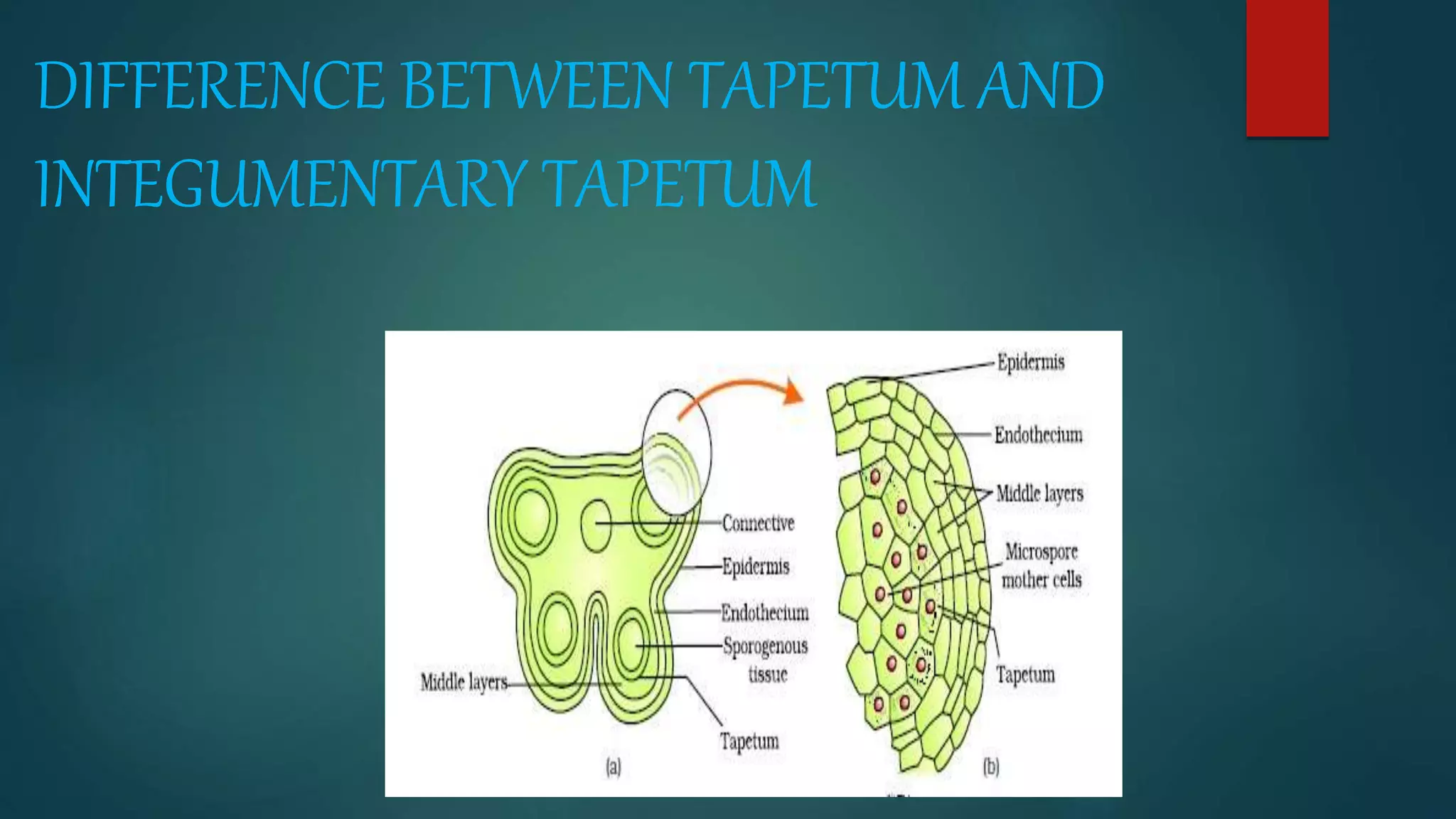
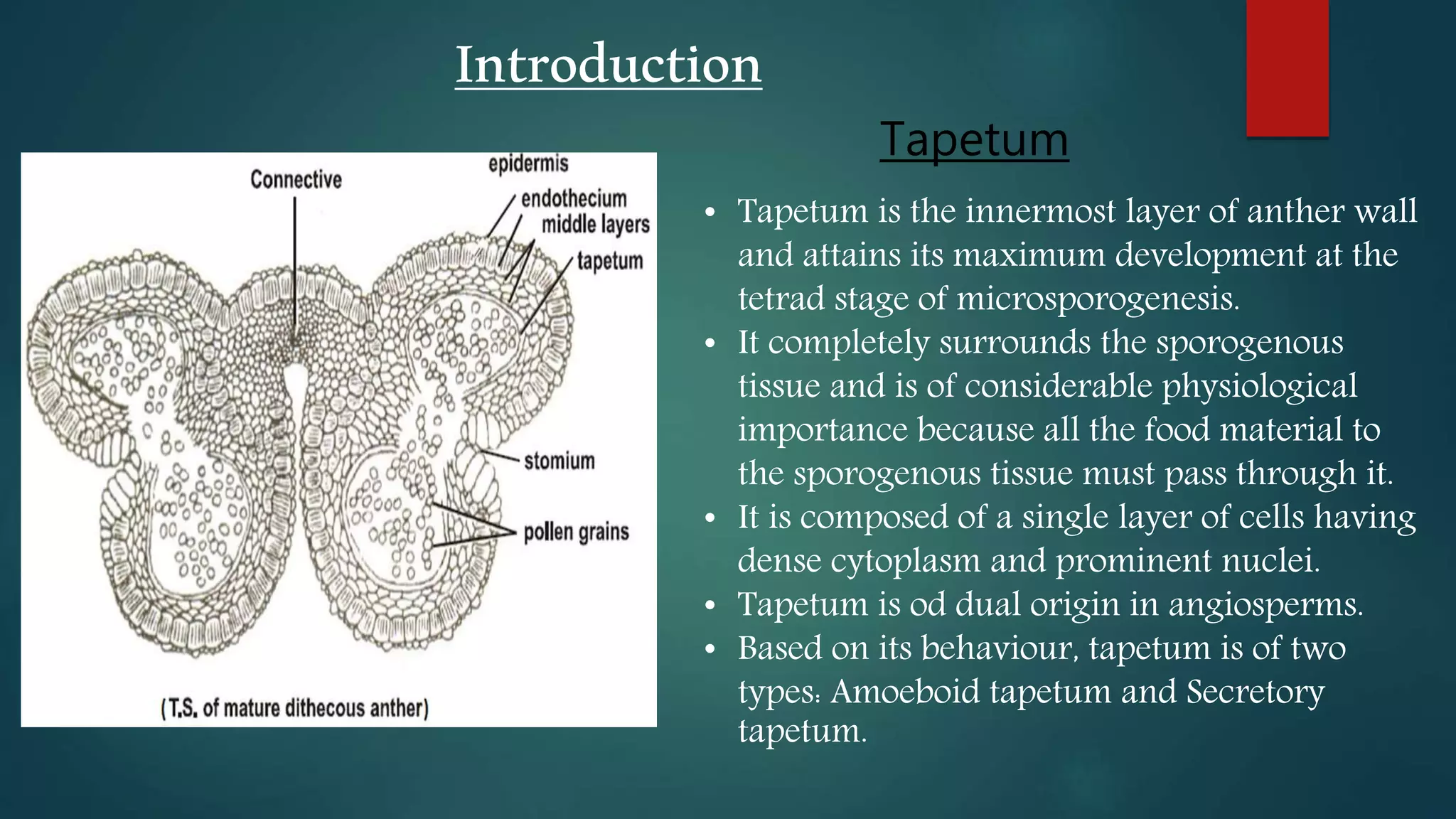
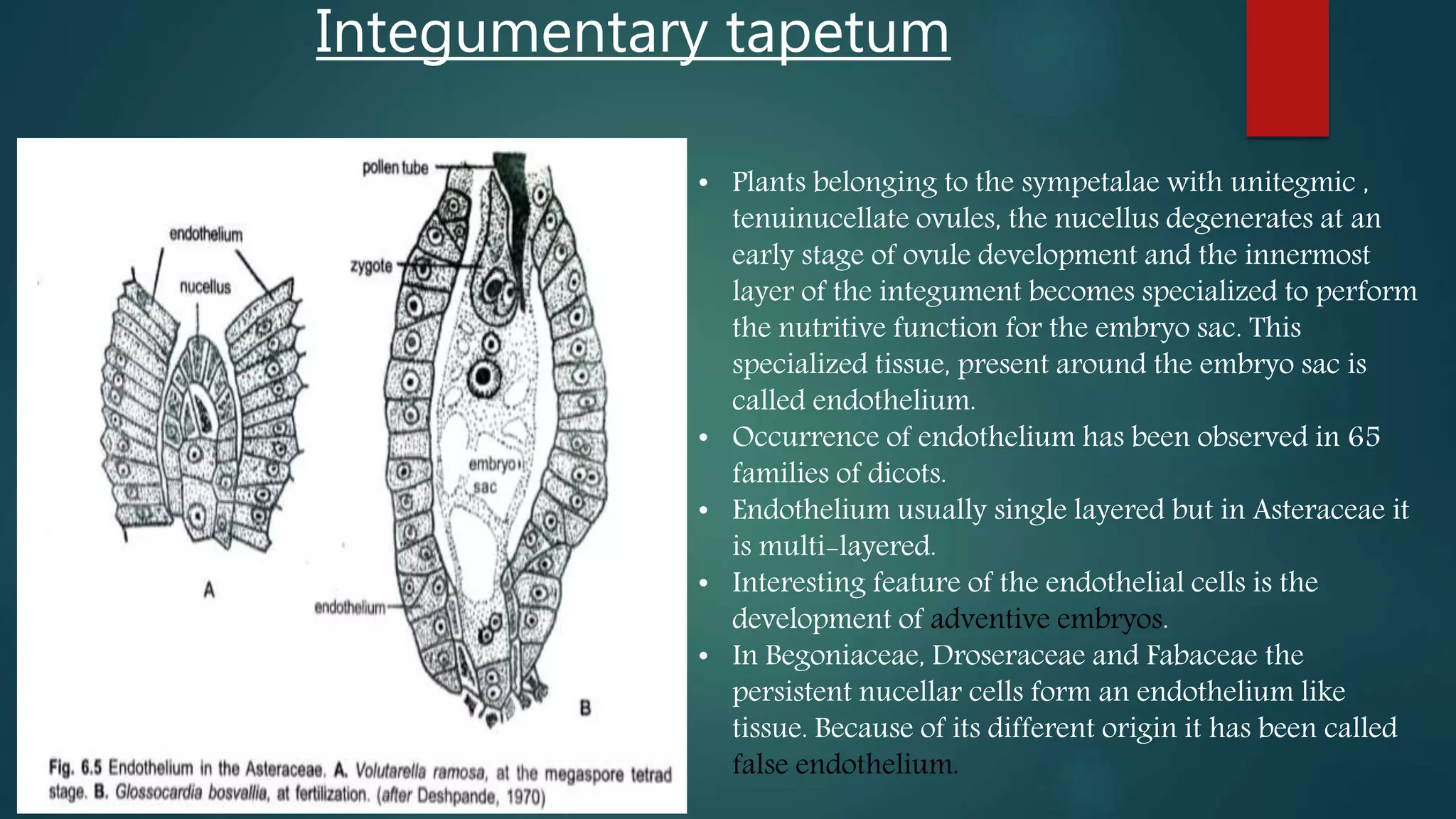
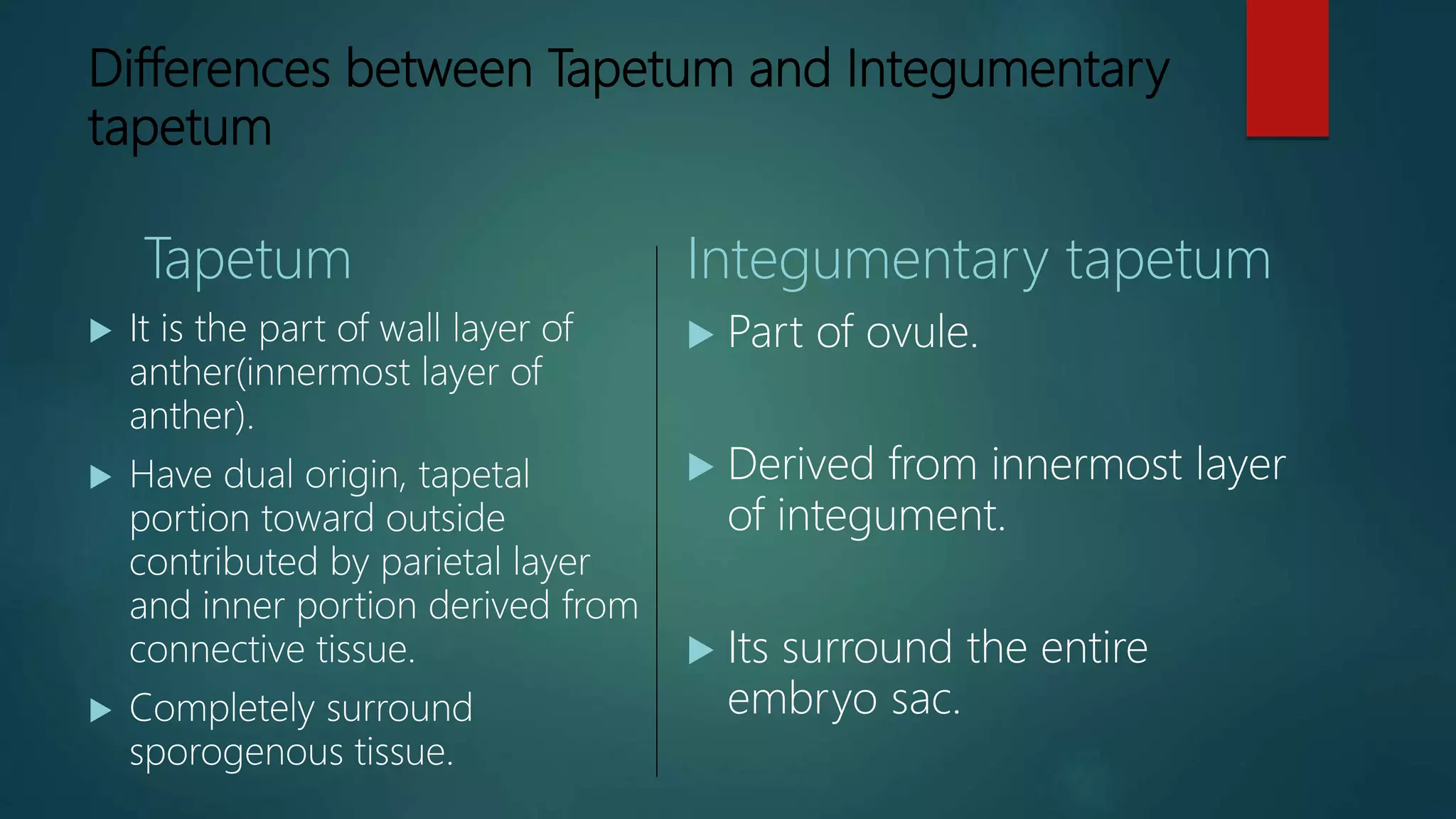
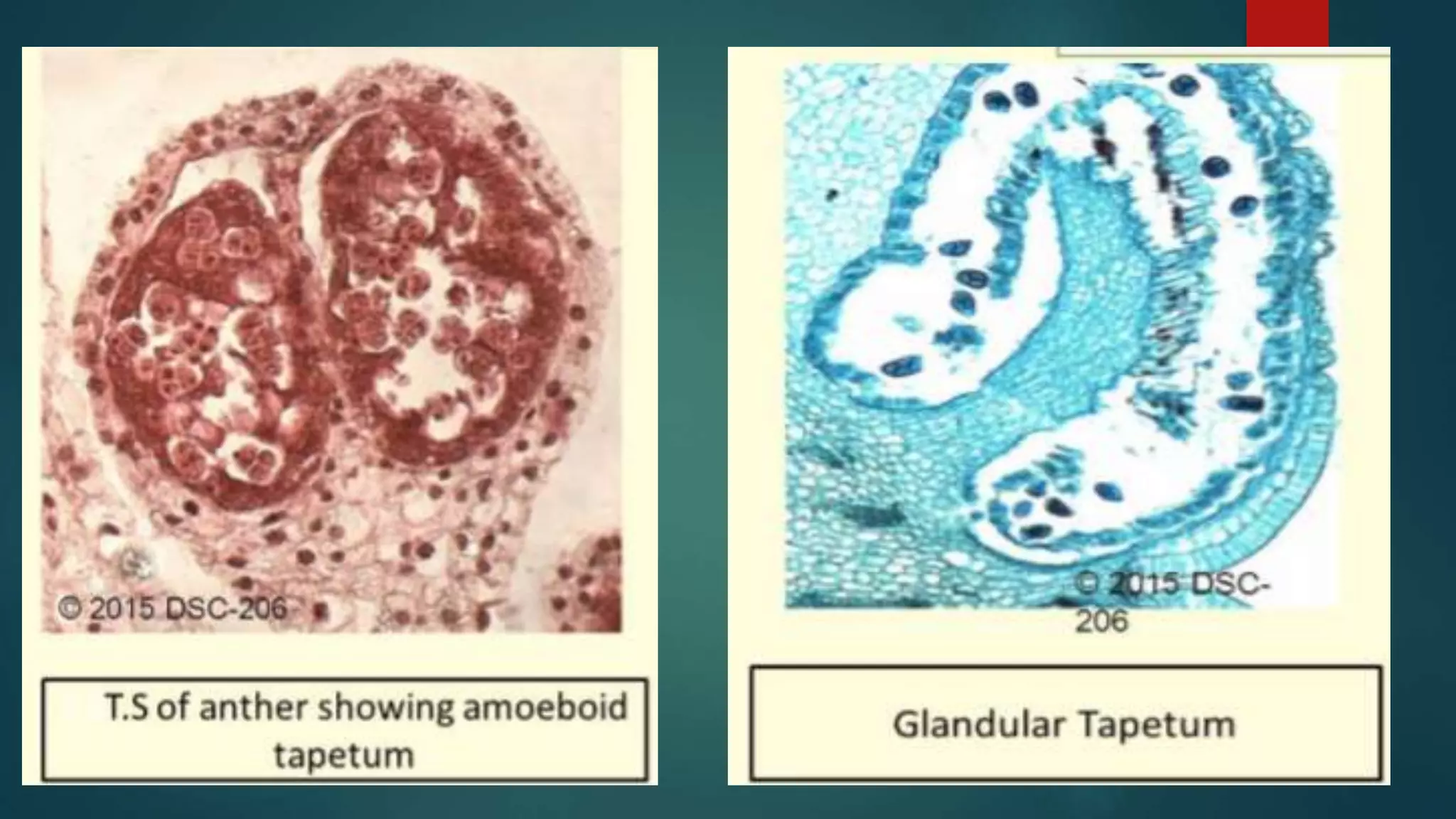
The document discusses the differences between tapetum and integumentary tapetum in plants, highlighting their roles and origins. Tapetum is the innermost layer of the anther, essential for nutrient transfer during microsporogenesis, while integumentary tapetum, also known as endothelium, derives from the innermost layer of the integument and surrounds the embryo sac. Both structures have unique characteristics and may vary in layering and morphology across different plant families.