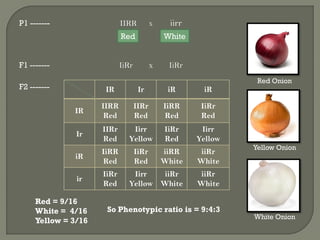
This document discusses epistasis, which is when the expression of one gene is affected by other independently inherited genes. It provides examples of different types of epistatic interactions including recessive epistasis. Recessive epistasis is when a recessive gene suppresses the expression of a non-allelic gene. The document uses pigmentation in onions as an example, where a recessive inhibitor gene (ii) causes white color regardless of other pigmentation genes when in the homozygous recessive state. A Punnett square is provided to show the expected phenotypic ratios in the F2 generation.

![What is Epistasis ?
Epistasis is a circumstance where the expression of one gene is affected by
the expression of one or more independently inherited genes.
Type of Epistasis :
1. Recessive Epistasis
2. Dominant Epistasis
3. Dominant [Inhibitory] Epistasis
4. Duplicate Recessive Epistasis
5. Duplicate Dominant Epistasis
6. Polymeric Gene Interaction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/epistasis-210203071803/85/Recessive-Epistasis-2-320.jpg)