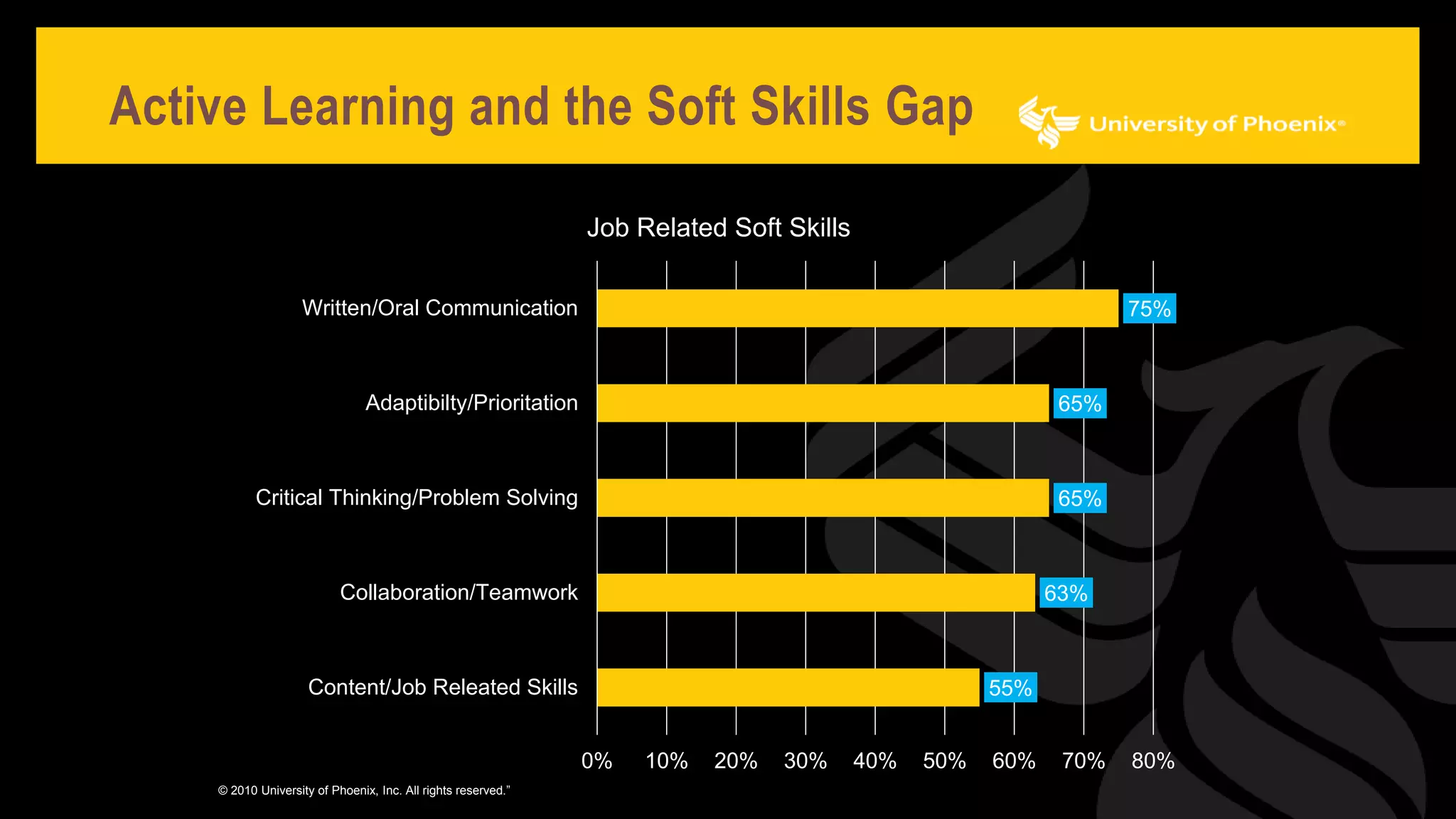
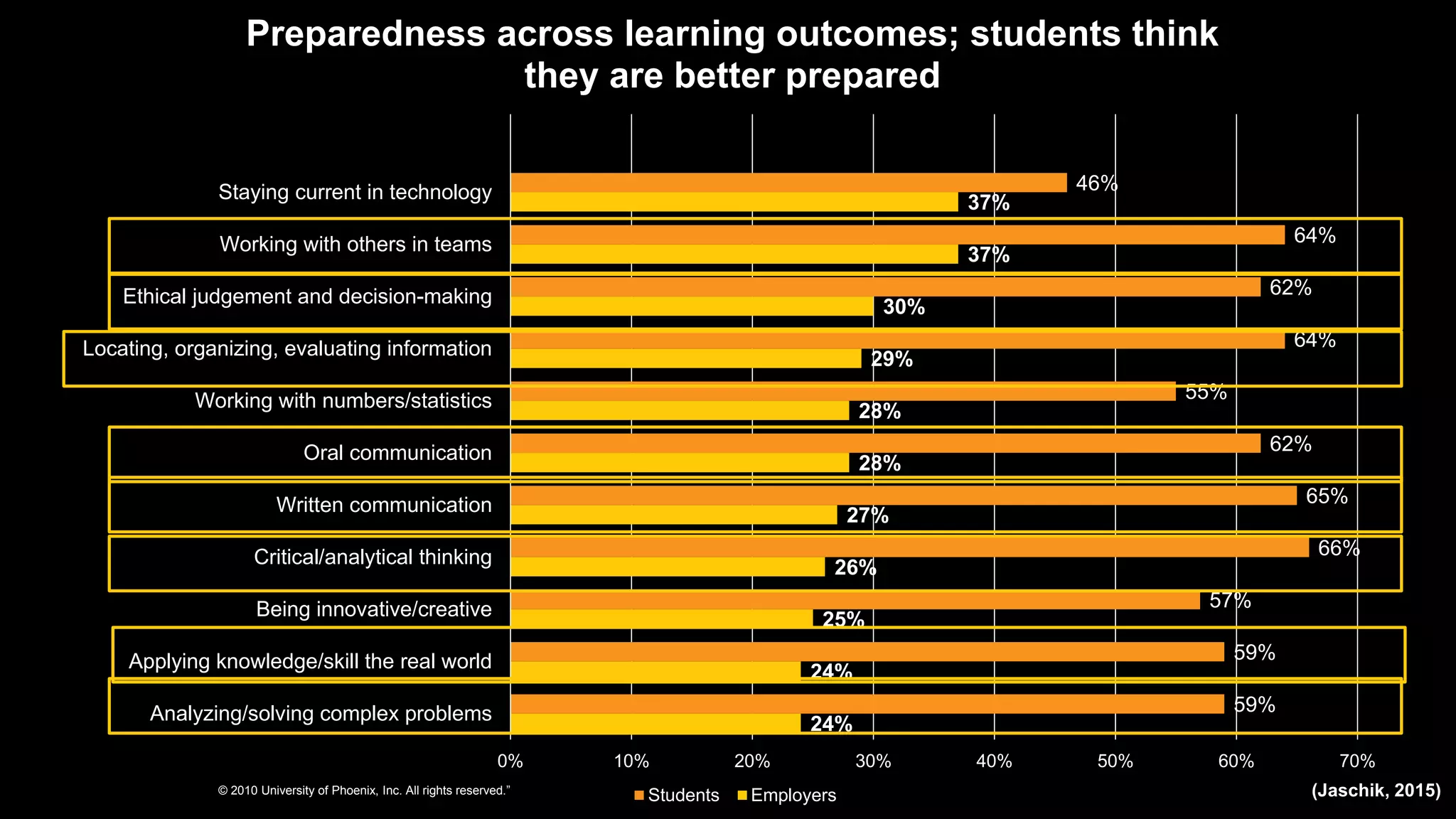
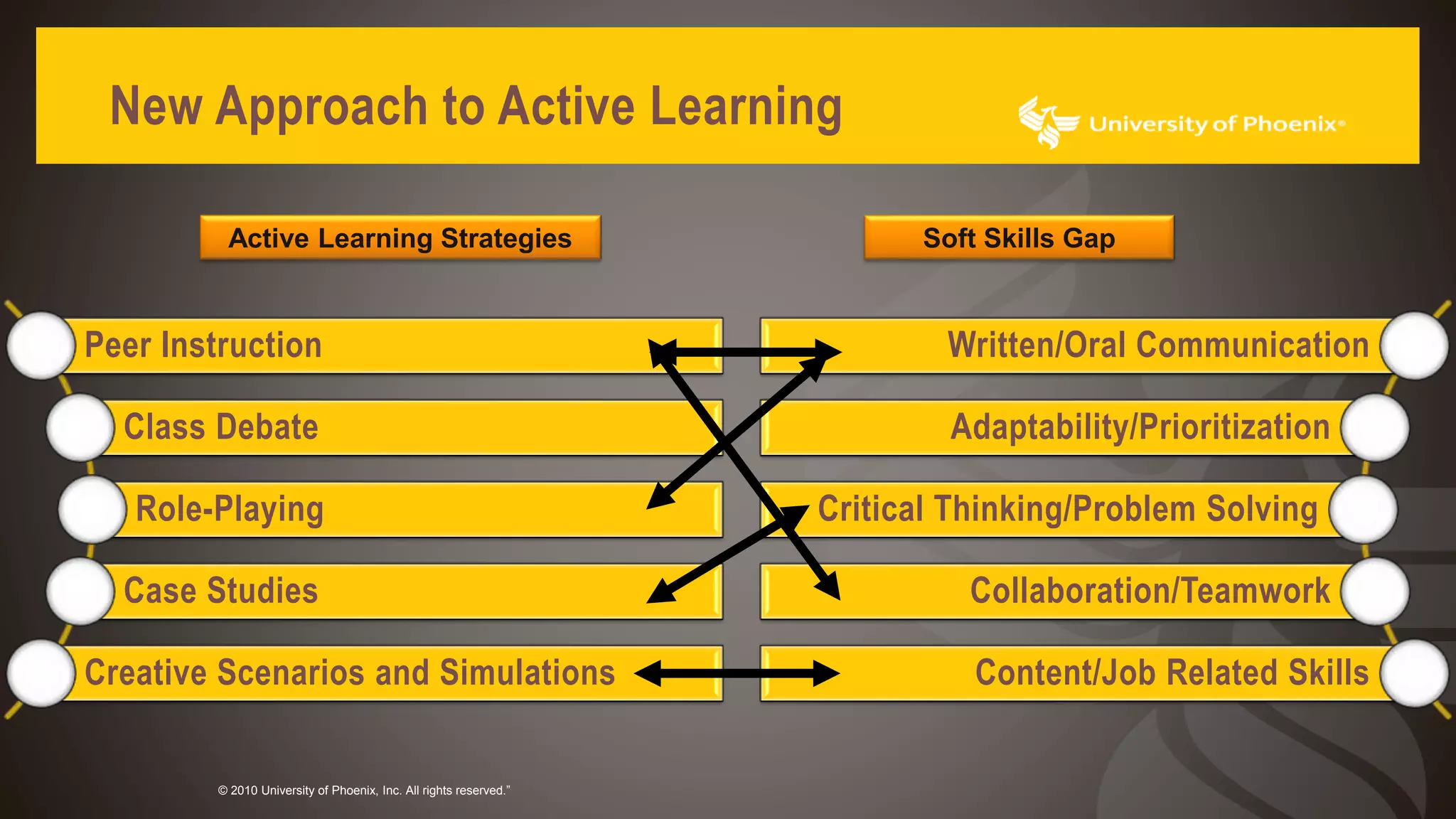
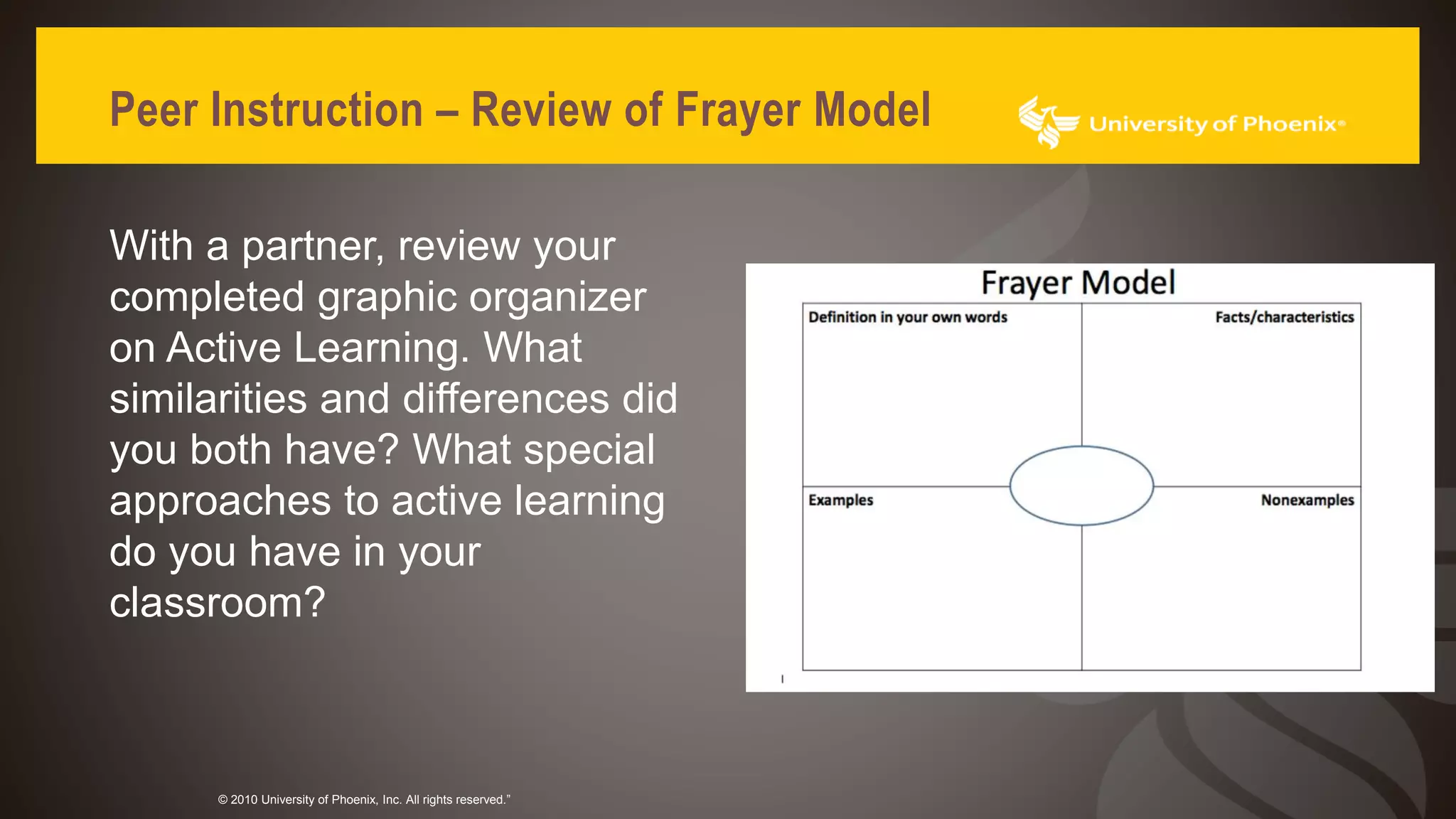
The document discusses promoting active learning in K-12 classrooms. It defines active learning as student-centered approaches involving activities like discussions, debates and role-playing. Research shows active learning improves memory retention and ability to apply knowledge. It also helps develop soft skills employers prioritize like communication, collaboration and problem-solving, helping reduce the skills gap. The document proposes strategies for teachers including peer instruction, debates, case studies and role-playing. It provides guidance on planning active learning activities and using them to review concepts.