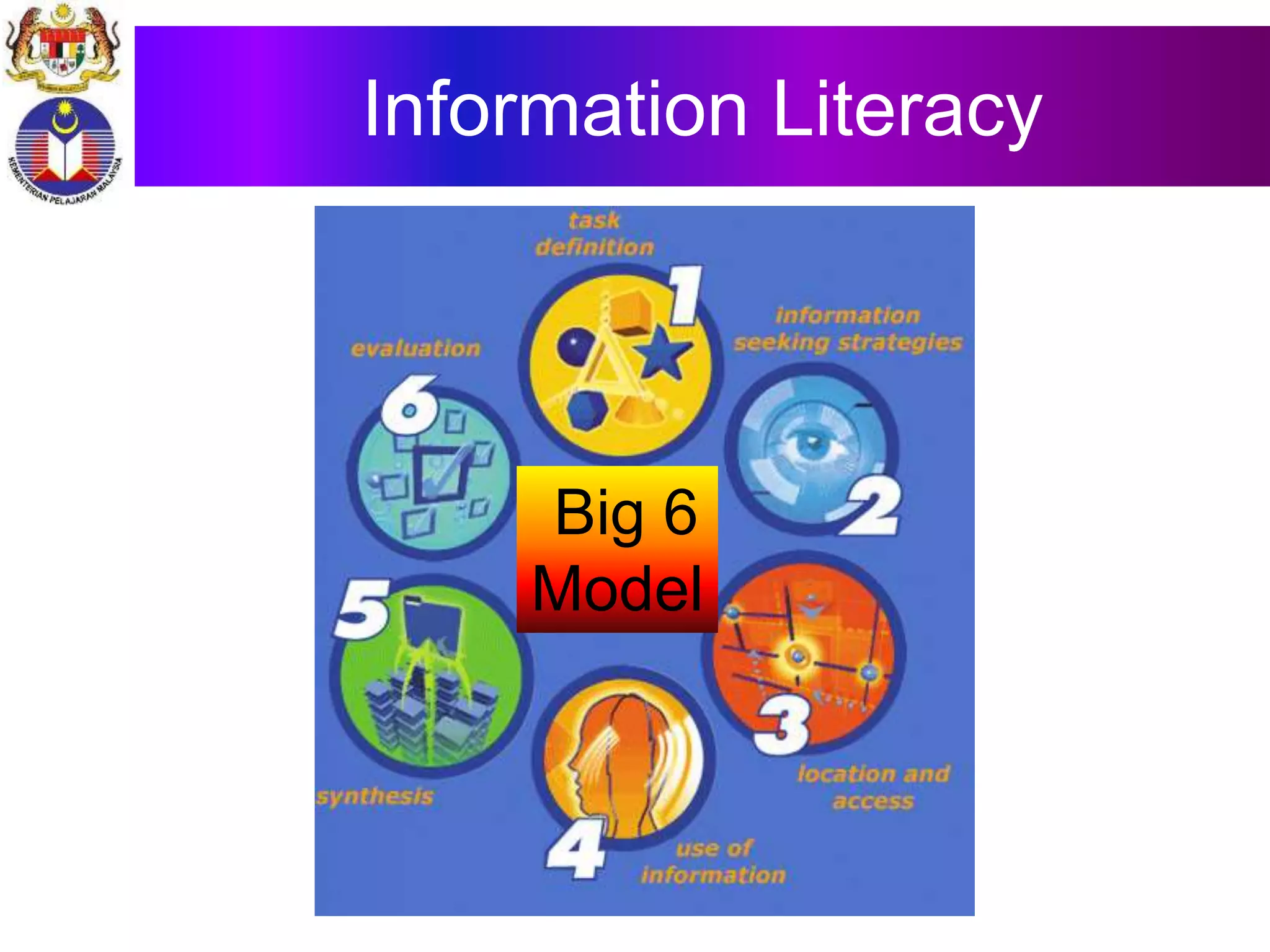
This document discusses 21st century education and the role of technology in Malaysian schools. It begins by defining the 21st century and education. It then discusses how students today are digital natives and teachers are often digital immigrants. It outlines some key technology trends like the internet, web 2.0, and new media. The document also provides statistics on the Malaysian education system and literacy rates. It discusses initiatives to improve ICT infrastructure in schools and training for teachers. Challenges and the path forward to ubiquitous learning are also mentioned.