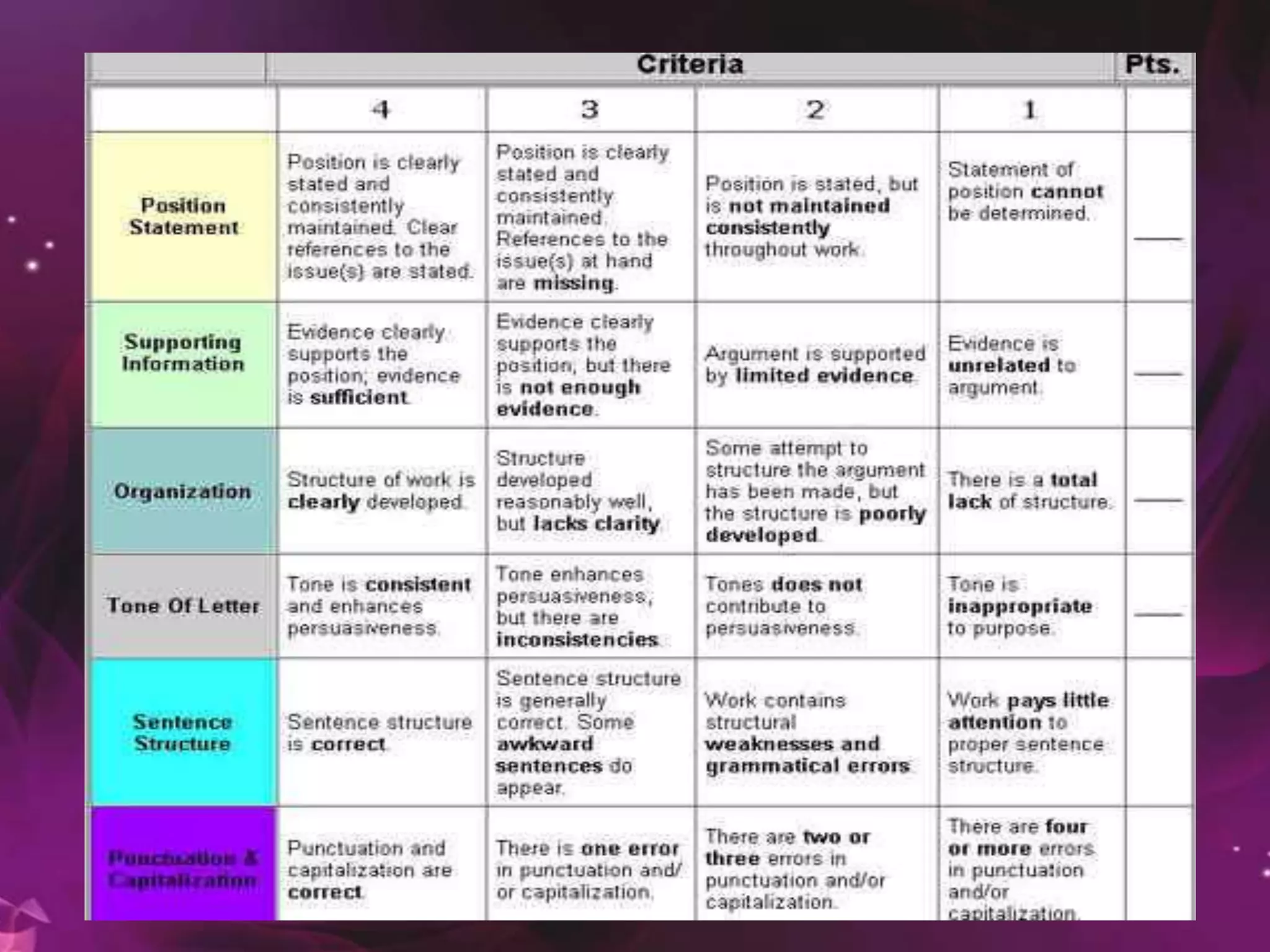
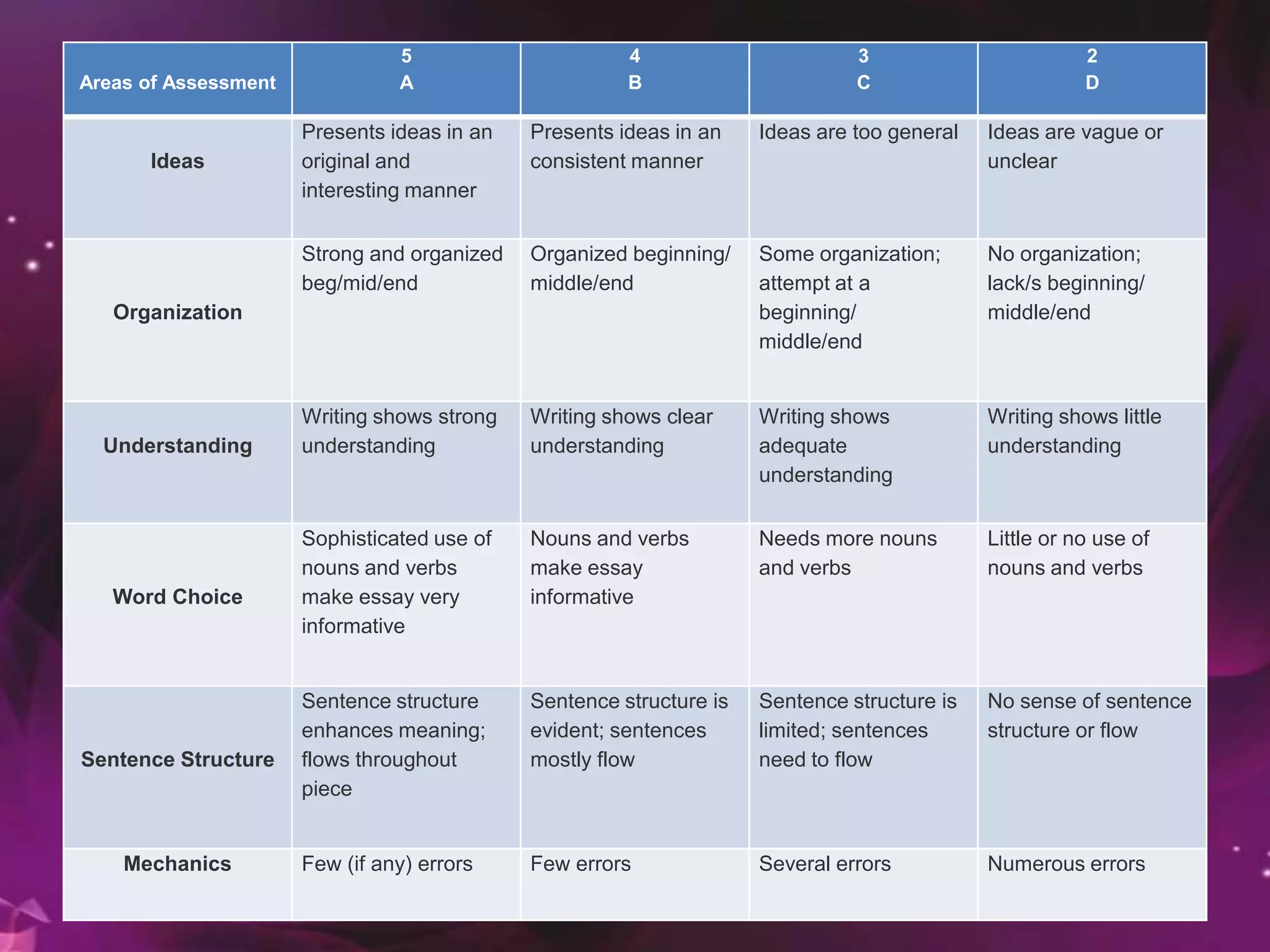
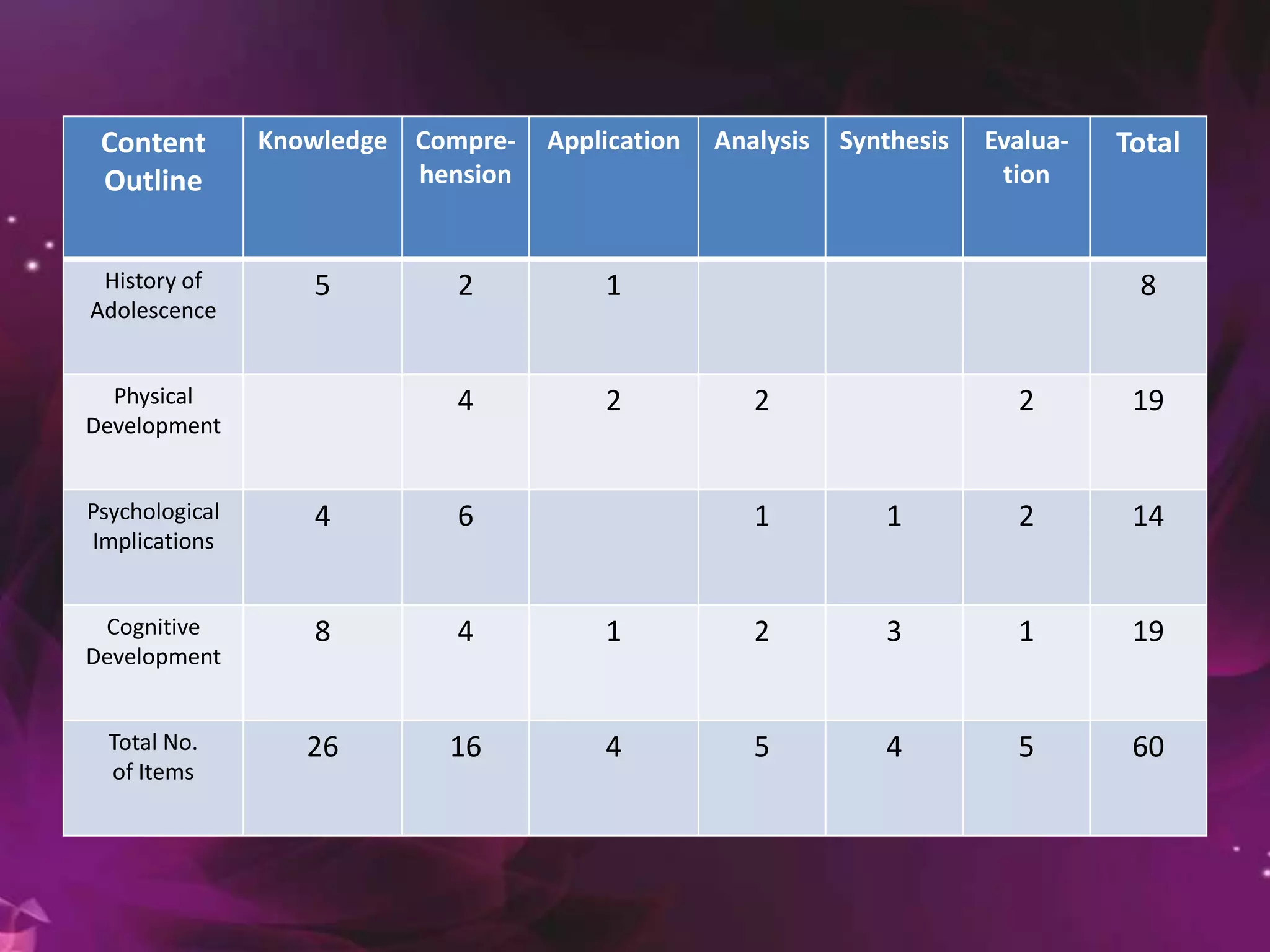
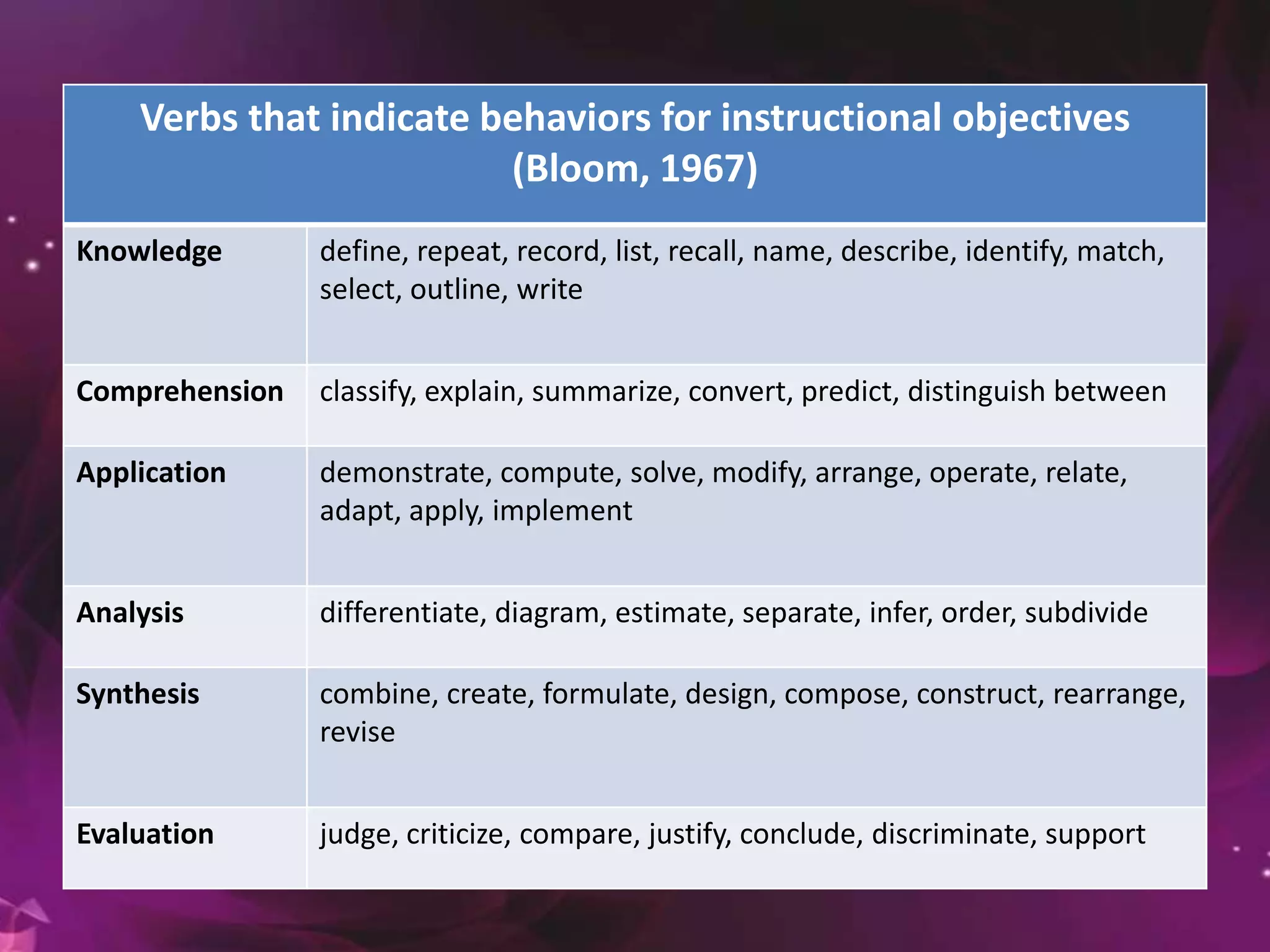
This document provides guidelines for constructing effective tests. It discusses the purposes of tests and different types of test items, including multiple choice, true/false, matching, essay, and performance-based questions. It emphasizes the importance of aligning test items with learning objectives through a table of specifications. Guidelines are provided for writing, selecting, editing, arranging and scoring test items to ensure validity, reliability and fair assessment of students. The document stresses considering difficulty, independence of items, and coverage of content when developing tests.