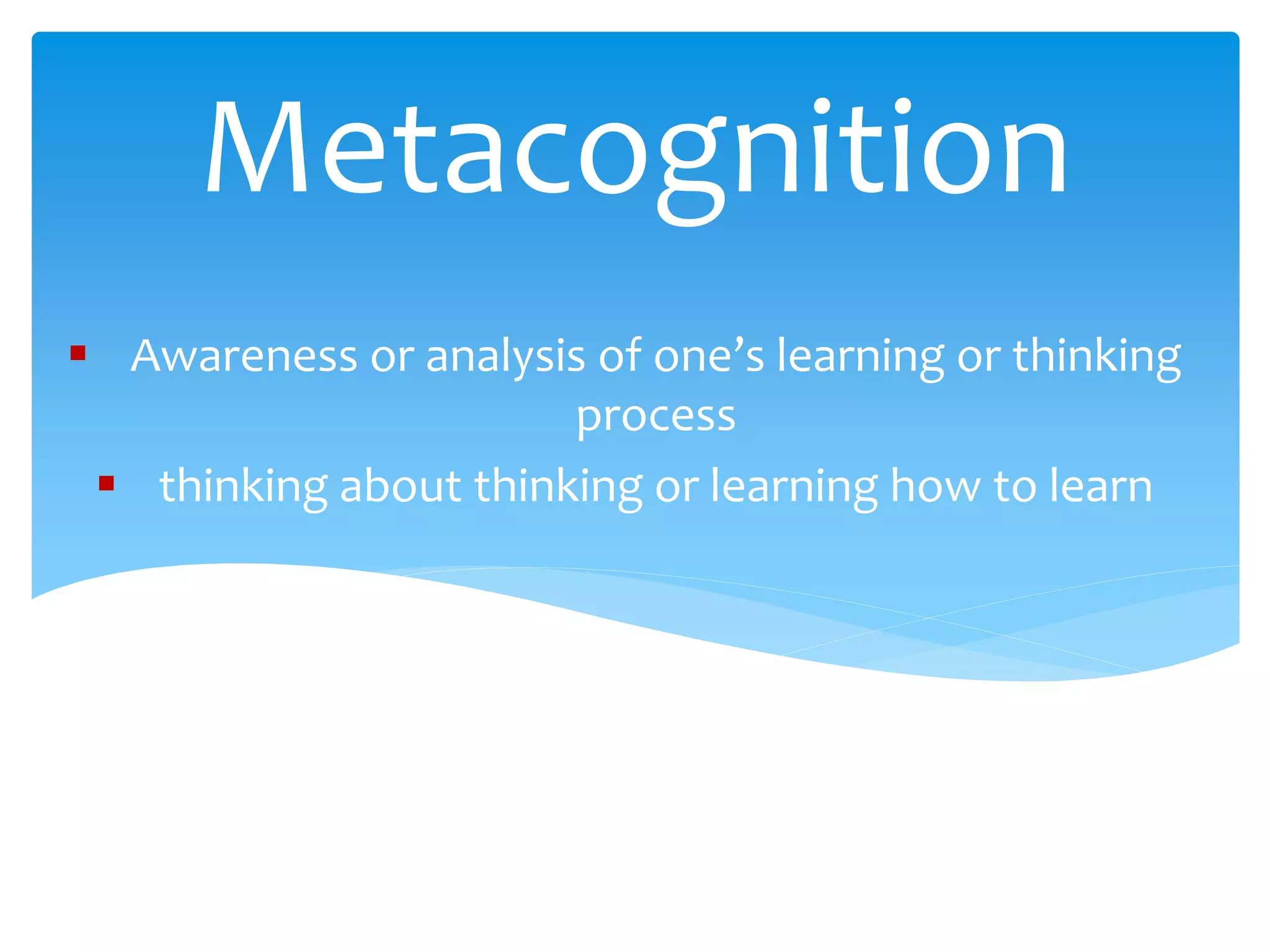
Techniques and strategies for teaching ethnically diverse classrooms are discussed. Key points include appreciating student diversity, building relationships, using various instructional strategies that consider student culture and language, facilitating independent thinking, and providing feedback. Teaching styles include directing, discussing, and delegating. Metacognition and strategies like TQLR and PQ4R are presented to help novice learners become expert through monitoring learning. Student diversity is influenced by socioeconomic status, thinking styles, and exceptionalities.