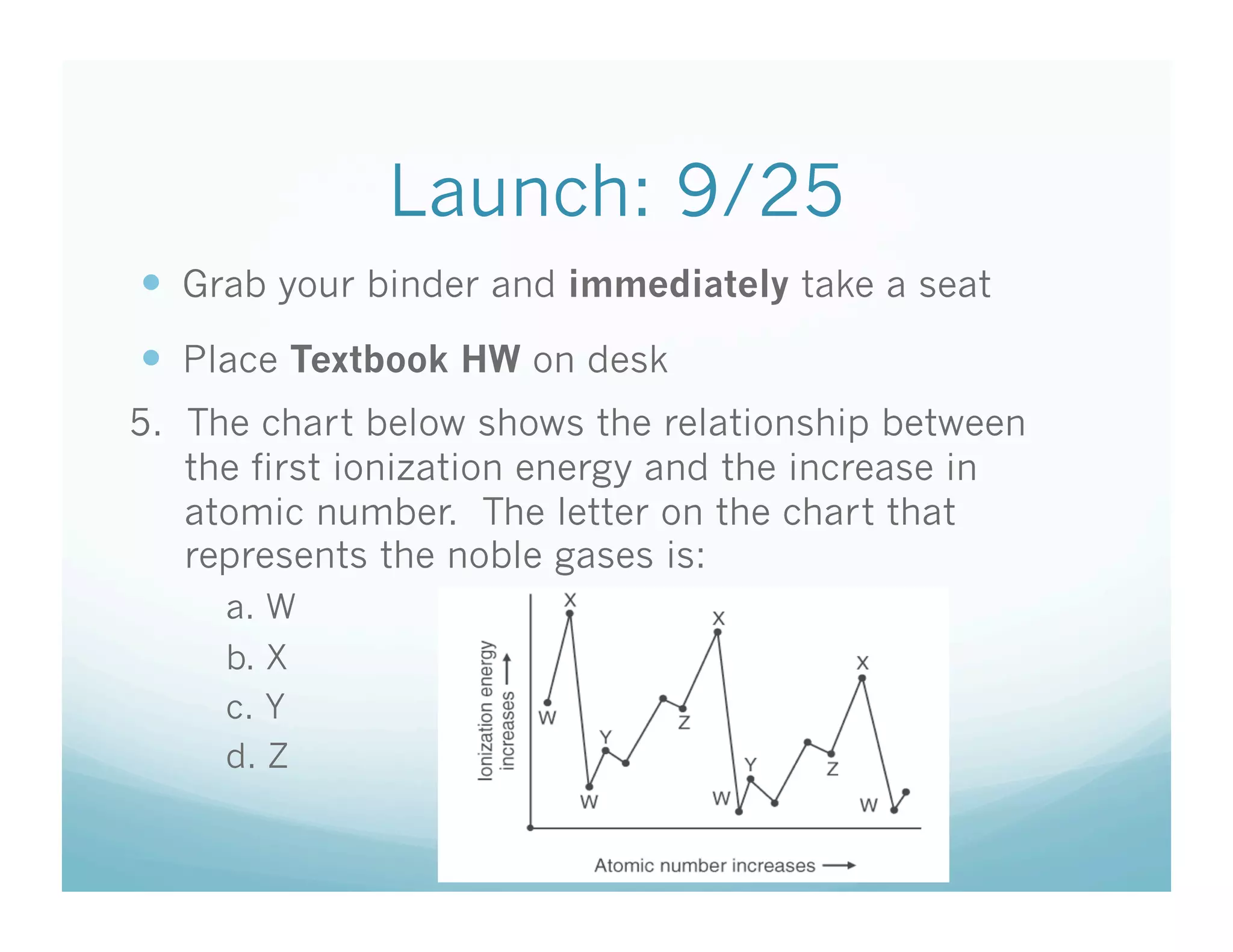
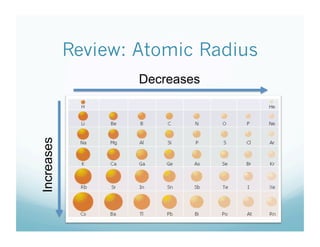
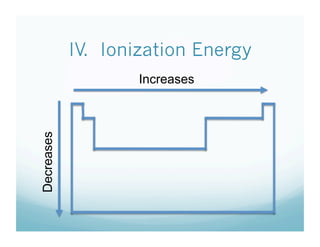
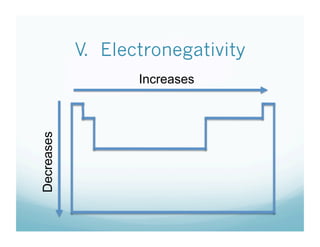
The document is a chemistry class lecture on trends in the periodic table, specifically electronegativity. It defines electronegativity as an atom's ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond. It then explains that electronegativity increases from left to right across periods due to more protons, but decreases down groups because more electron shells shield the nucleus from outer electrons. Practice problems are assigned for students to study these trends.