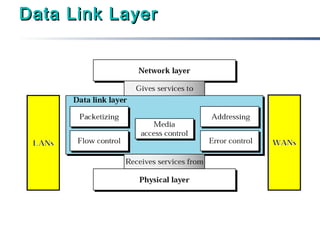
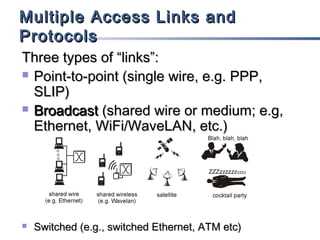
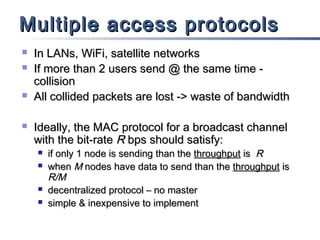
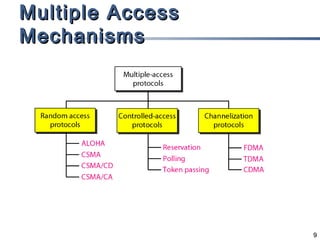
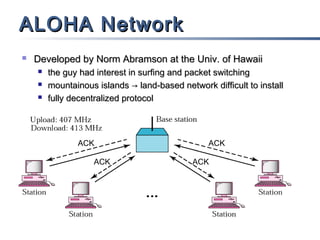
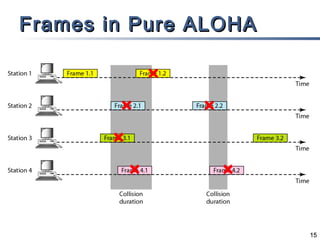
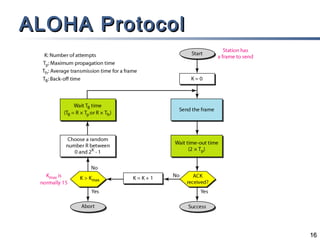
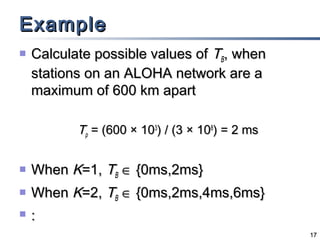
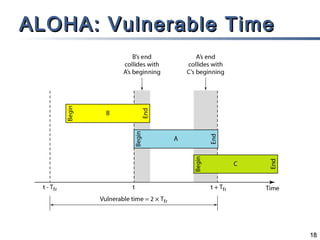
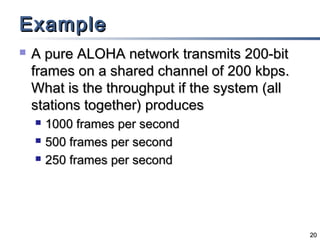
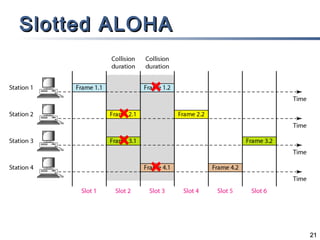
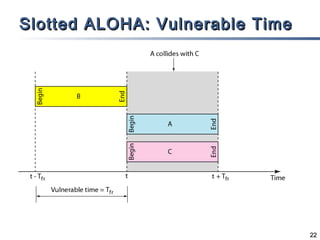
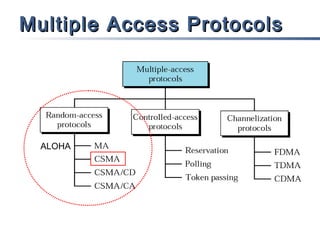
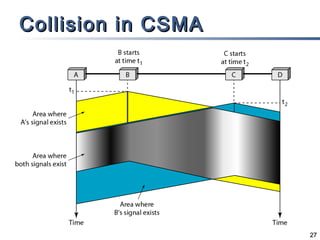
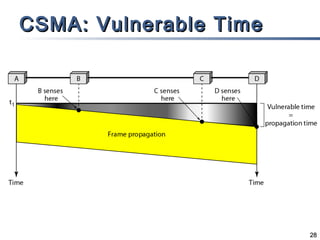
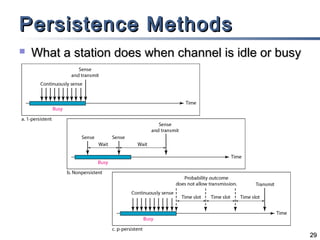
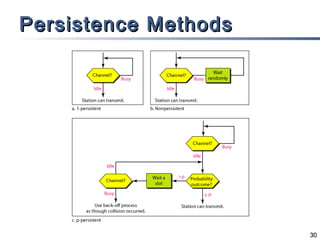
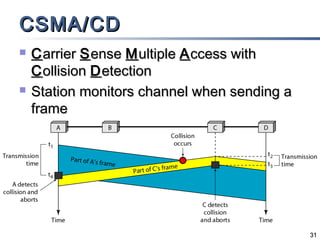
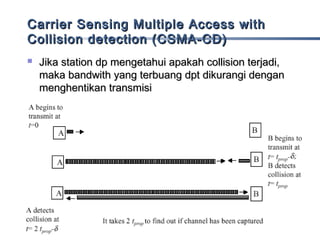
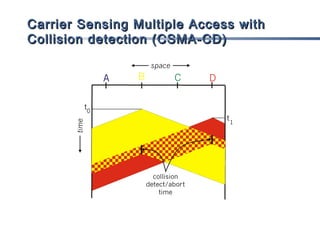
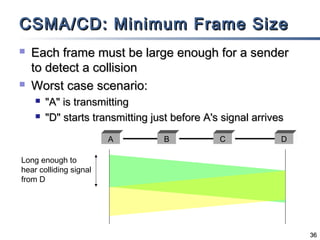
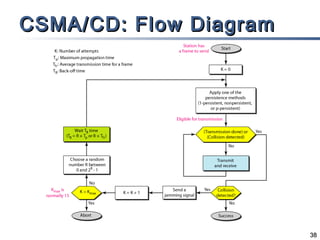
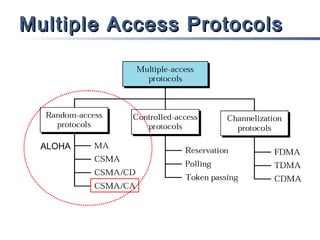
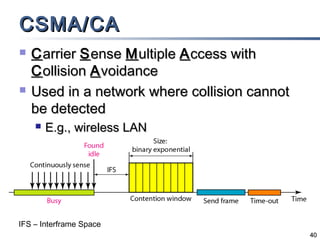
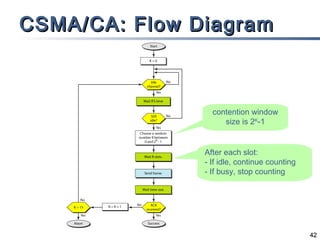
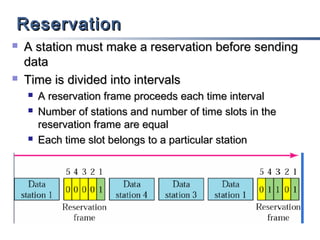
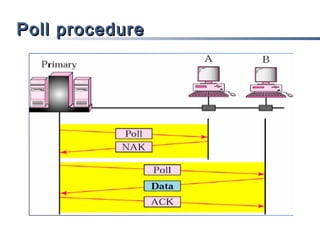
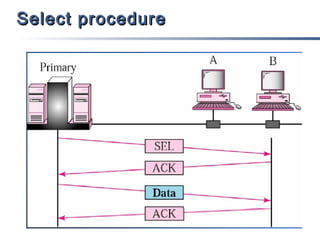
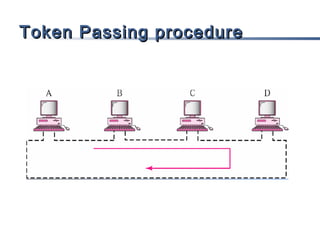
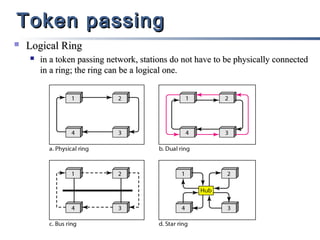
This document discusses multiple access mechanisms for communication networks. It describes three main types of multiple access protocols: random access, controlled access, and channelization. Random access protocols like ALOHA and CSMA allow nodes to access the channel randomly and risk collisions. Controlled access protocols like polling, token passing, and reservation assign channel access in a coordinated fashion to avoid collisions. Channelization techniques partition the channel by frequency (FDMA), time (TDMA), or code (CDMA) to enable multiple simultaneous transmissions.