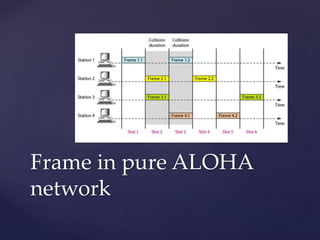
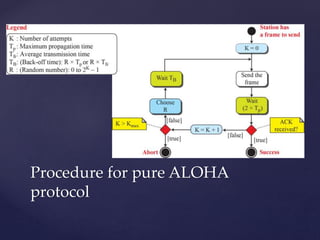
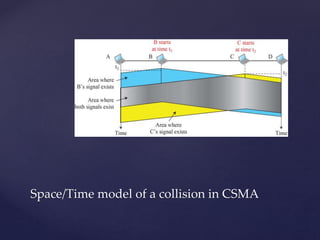
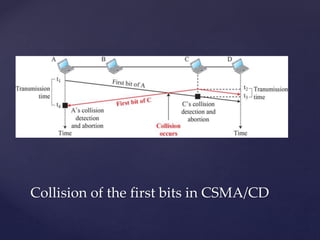
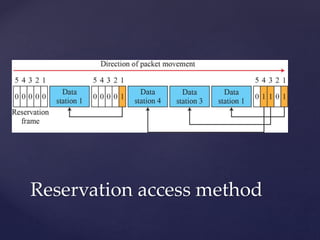
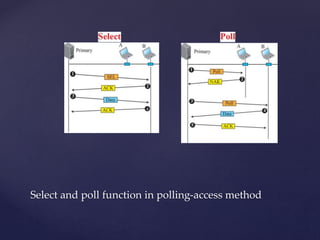
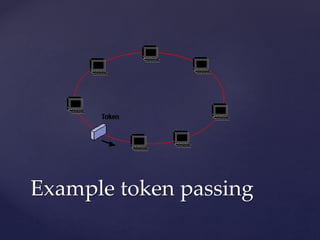
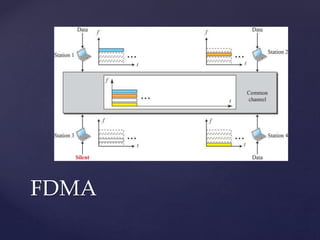
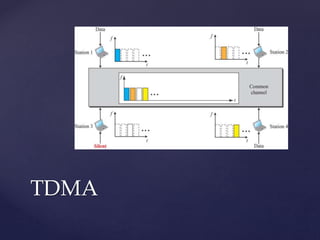
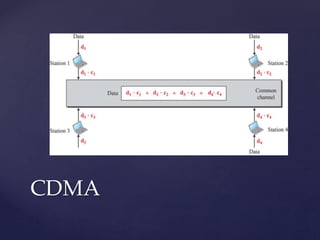
Medium access control protocols can be classified as random access, controlled access, or channelization protocols. Random access protocols have no central control and stations decide independently when to transmit. Common random access protocols include ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CD, and CSMA/CA. Controlled access protocols require stations to get permission before transmitting, using methods like reservation, polling, or token passing. Channelization protocols divide the channel bandwidth by frequency (FDMA), time (TDMA), or code (CDMA).