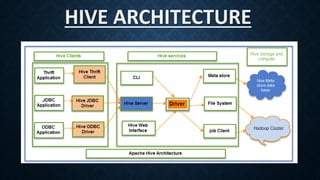
Apache Hive is an open-source data warehouse software built on Apache Hadoop that enables querying and managing large datasets using an SQL-like interface. It supports batch processing through Apache Tez or MapReduce and organizes data into tables, partitions, and buckets, facilitating scalability and flexible schema design. While Hive is ideal for structured data analysis, it has limitations like issues with OLTP processing and no support for updates.