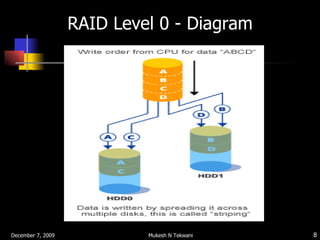
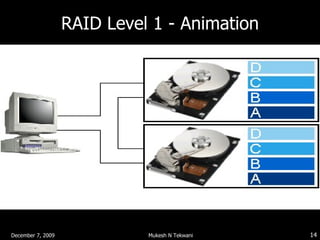
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) distributes data across multiple disks to improve performance and provide redundancy. The common characteristics of RAID levels are that multiple physical disks act as a single logical disk, data is distributed across disks, and redundant parity information is used to recover data if a disk fails. RAID level 0 stripes data without parity for increased speed but no fault tolerance, while RAID level 1 uses mirroring to provide redundancy by writing all data to two disks.