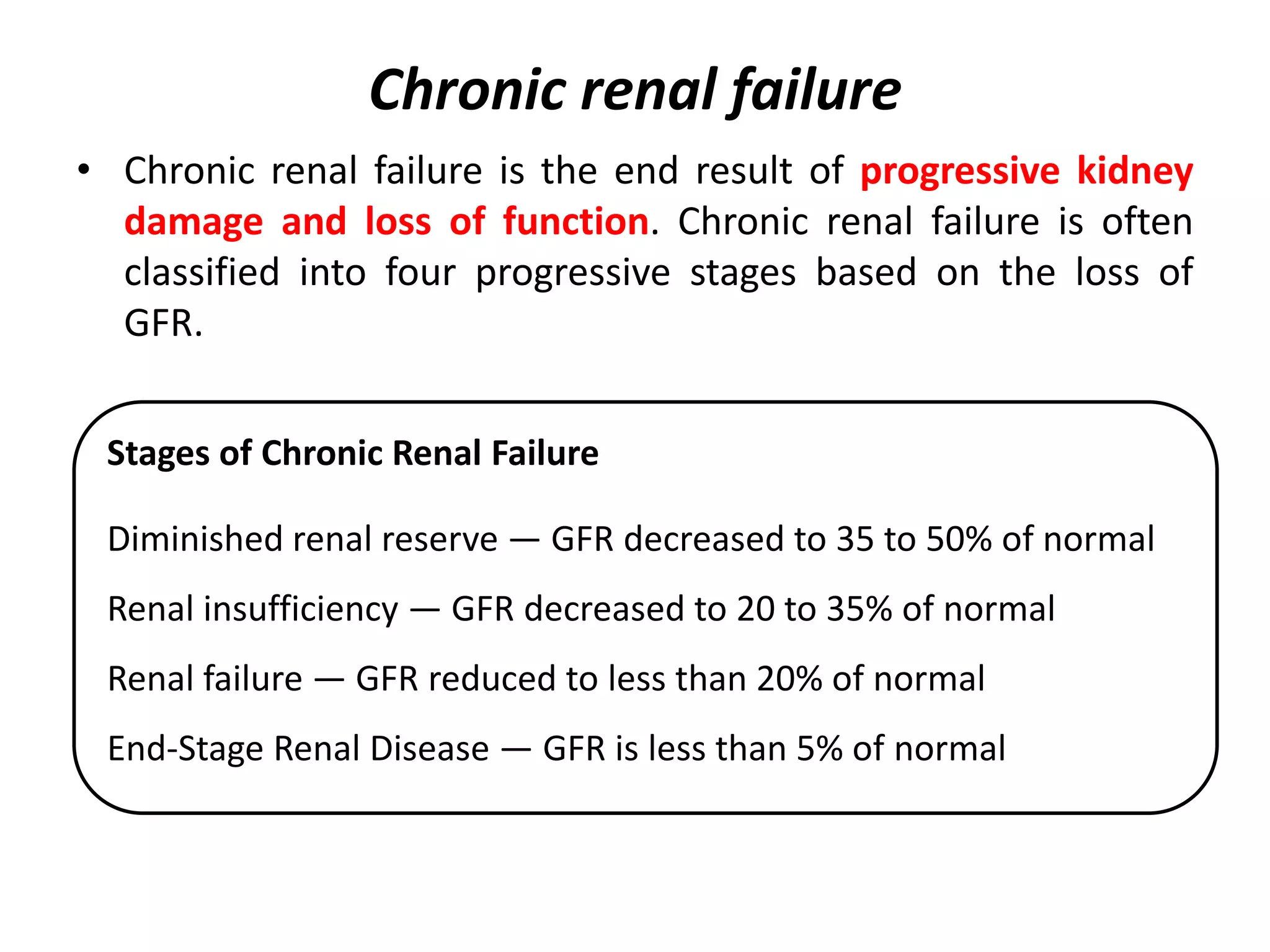
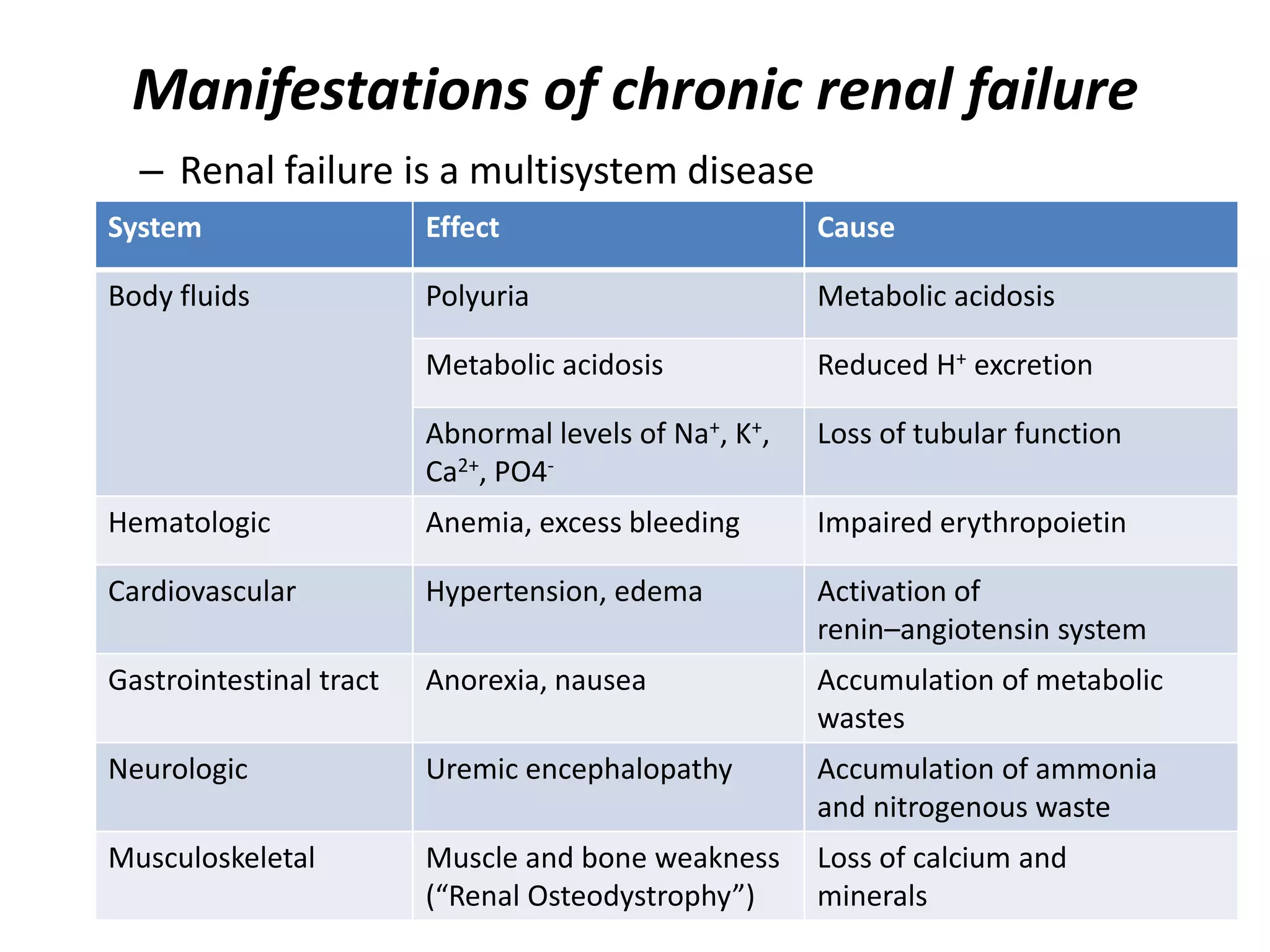
This document discusses acute and chronic renal failure. It defines renal failure and describes how acute failure has a sudden onset and may be reversible, while chronic failure progresses slowly over months and can lead to permanent damage. Causes of acute failure include reduced blood flow or obstruction, while chronic failure may result from conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or glomerulonephritis. Symptoms depend on the type and stage of renal failure. Treatment involves managing fluid, electrolytes, diet, and potentially dialysis or transplantation.