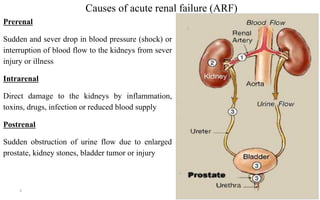
The document discusses renal failure, detailing kidney anatomy, functions, and the definitions of acute and chronic renal failure. It outlines the causes, symptoms, and stages of renal failure, as well as treatment options and prevention strategies. The content emphasizes the importance of maintaining kidney health through proper hydration, weight management, and controlling diabetes and blood pressure.

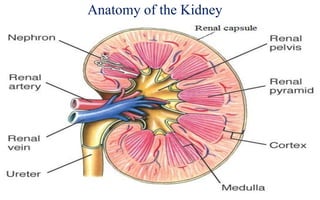
![Functions of the Kidneys
A – maintaining ACID-base balance
W – maintaining WATER balance
E – ELECTROLYTE balance
T – TOXIN removal
B – BLOOD Pressure control
E – making ERYTHROPOIETIN [85% kidney, 15% Liver]
D – Vitamin D metabolism
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/renalfailure-181127161025/85/Renal-failure-5-320.jpg)


![Common causes of chronic renal failure (ESRD)
1. Diabetes mellitus
2. Hypertension
3. Recurrent or untreated Urinary tract infection
4. Genetic diseases (diseases you are born with), such as polycystic kidney disease
5. Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus
6. Obstructions
7. Heart attack [Not enough blood flowing to the kidneys]
8. Prolonged renal ischemia
9. Illegal drug use and drug abuse
10. Lack of fluid volume in the body
11. Nephrotic syndrome
12. Glomerulonephritis
13. Certain medications
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/renalfailure-181127161025/85/Renal-failure-9-320.jpg)
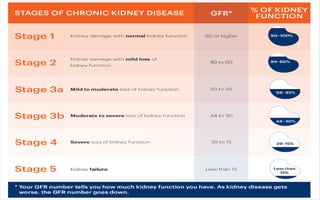
![Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
• Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR): is a test used to check how
well the kidneys are working. Specifically, it estimates how much
blood passes through the glomeruli each minute. Glomeruli are the
tiny filters in the kidneys that filter waste from the blood.
• Normal Results: According to the National Kidney Foundation,
normal results range [from 90 to 120 ml/min/1.73 m2], older
people have lower than normal GFR levels, because GFR decreases
with age.10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/renalfailure-181127161025/85/Renal-failure-10-320.jpg)