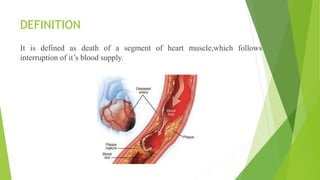
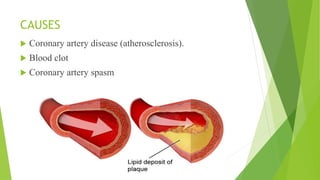
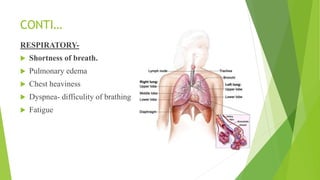
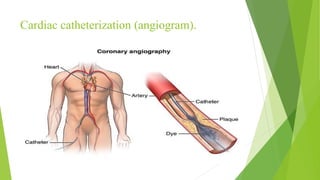
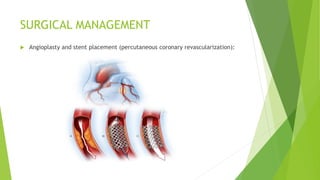
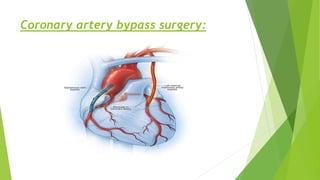
Myocardial infarction is defined as the death of heart muscle due to interrupted blood supply, with notable incidence rates varying by gender and geography. Risk factors include both modifiable factors like tobacco use and obesity, as well as nonmodifiable factors such as family history and age. Prevention and management strategies involve lifestyle modifications, medications, and surgical interventions to address coronary artery disease and its complications.