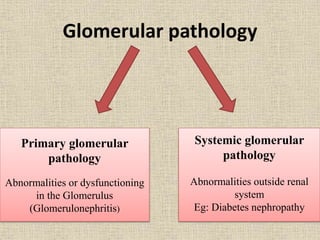
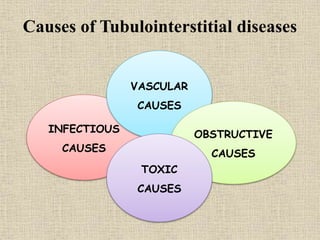
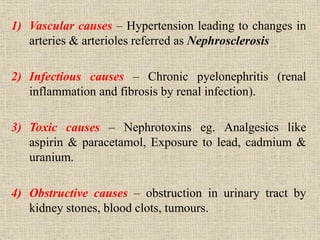
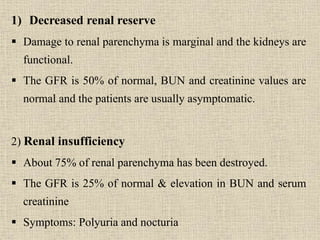
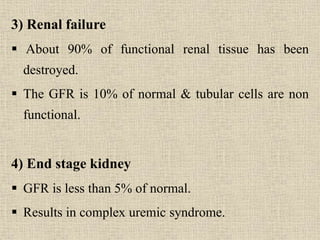
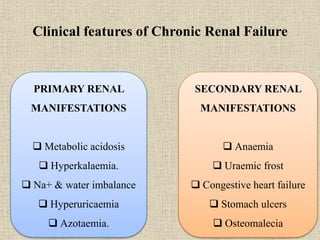
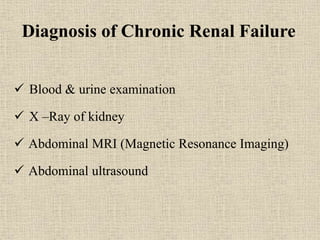
Chronic renal failure is characterized by the progressive and irreversible deterioration of renal function that eventually leads to death. It is caused by the slow destruction of renal parenchyma over time from diseases like glomerulonephritis, diabetes nephropathy, hypertension, infections, toxins, and obstructions. The stages of chronic renal failure progress from a decreased renal reserve with normal lab values and no symptoms, to renal insufficiency with elevated BUN and creatinine and symptoms like polyuria, to renal failure with severe loss of renal function, to end stage kidney disease requiring dialysis or transplant. Chronic renal failure results in both primary renal manifestations like metabolic acidosis and secondary manifestations affecting other organs systems like anemia