Embed presentation





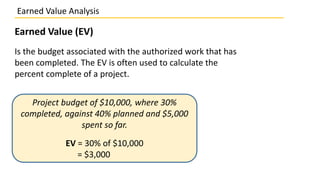


Earned value analysis is a project management technique that compares the planned value of work scheduled to the actual cost of work performed and work earned. It measures project performance and progress in three dimensions: planned value, earned value, and actual cost. Planned value defines the work that should have been completed, earned value is the budget associated with work actually completed, and actual cost is the total cost incurred so far. Variance analysis using metrics like the cost performance index, schedule performance index, cost variance, and schedule variance allows evaluation of how a project's performance compares to its plan.







