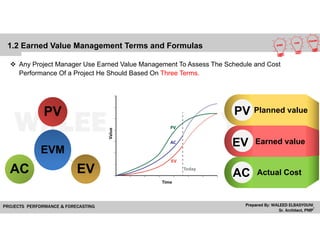
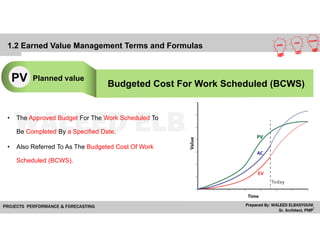
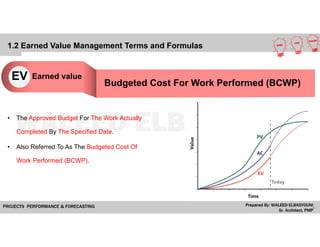
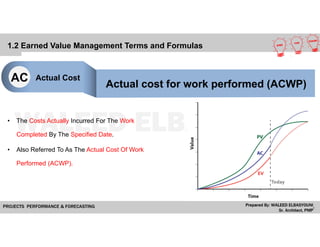
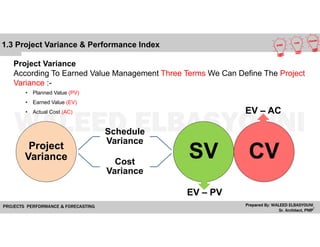
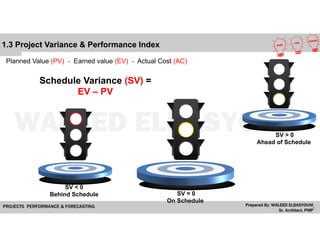
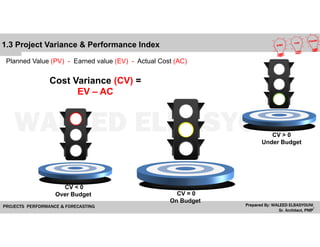
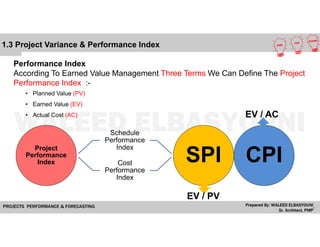
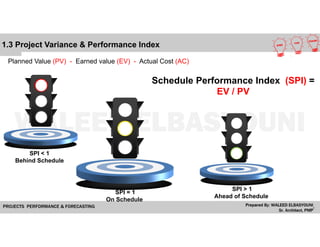
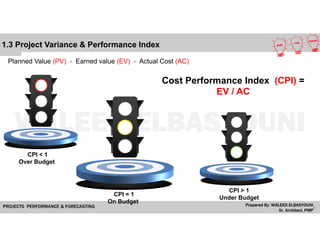
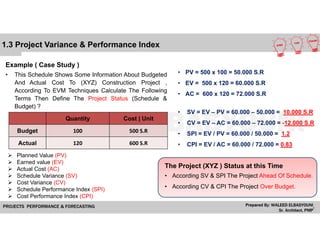
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Earned Value Management (EVM), detailing its importance in project performance measurement through key performance indicators (KPIs). It explains key terms such as Planned Value, Earned Value, Actual Cost, and various performance indices that help project managers assess schedule and cost performance. Additionally, it includes a case study example illustrating how to calculate and interpret project variances and forecasting metrics.






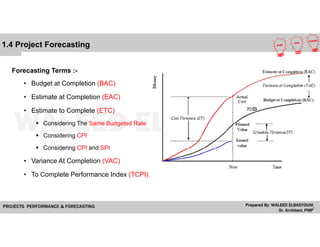
![1.4 Project Forecasting
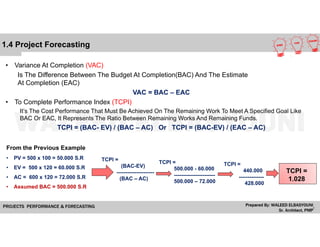
• Estimate To Complete (ETC)
Is The Estimated Cost Required To Complete The Remainder Of
The Project There Are Various Methods To Calculate The (ETC):-
Considering The Same Budgeted Rate
EAC = AC + (BAC – EV)
Considering CPI
EAC = BAC / CPI
Considering CPI and SPI
EAC = AC + [ (BAC – EV) / (CPI x SPI) ]
• Budget At Completion (BAC)
Is The Total Budget Allocated To The Project
• Estimate At Completion (EAC)
Is The Expected Total Cost Of A Schedule Activity Component, EAC Is Equal To The Actual Cost Of Work Performed
(ACWP) + The Estimate To Complete (ETC) For All Of The Remaining Work.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectsperformanceanalysisforecasting-161210050805/85/Projects-Performance-Analysis-Forecasting-22-320.jpg)