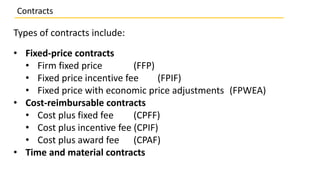
This document discusses different types of contracts used in project management. It describes contracts as legal agreements between two or more parties. There are two main types of contracts: fixed-price contracts, used when requirements are well-defined, and cost-reimbursable contracts, best used when the scope is expected to change. Specific contract types are defined, including firm fixed price (FFP), fixed price incentive fee (FPIF), cost plus fixed fee (CPFF), and time and material (T&M) contracts.