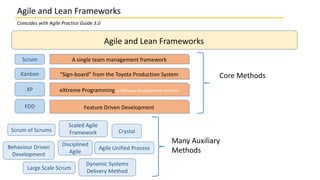
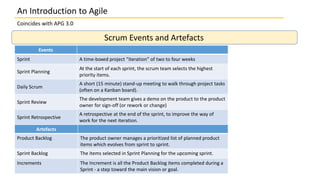
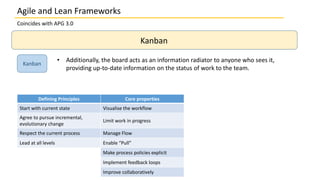
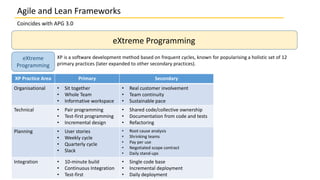
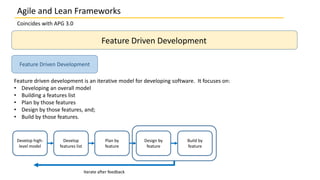
This document discusses several agile and lean frameworks including Scrum, Kanban, eXtreme Programming (XP), Feature Driven Development (FDD), and others. It provides overviews of each framework, describing their core practices, events, artifacts, principles, and how they relate to agile development.