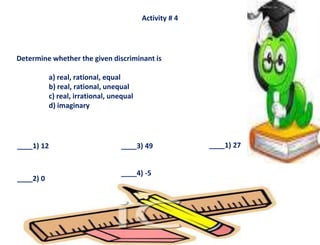
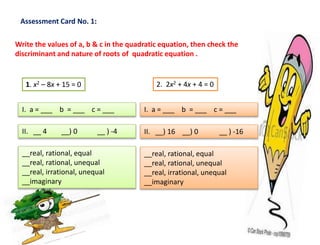
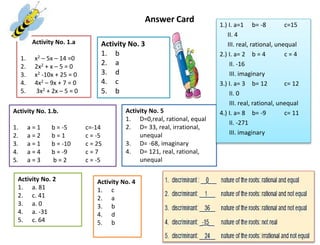
This document provides guidance on identifying the nature of roots of quadratic equations. It begins by identifying the least mastered skill of identifying the nature of roots. It then reviews the standard form of a quadratic equation and the quadratic formula. The key concept of the discriminant is explained, which determines the number and type of roots. Examples are provided to show how to find the discriminant and use it to describe the nature of roots. Activities are included for students to practice rewriting equations in standard form, finding a, b, c values, calculating discriminants, and determining the nature of roots. An assessment card with example problems is provided to check understanding.