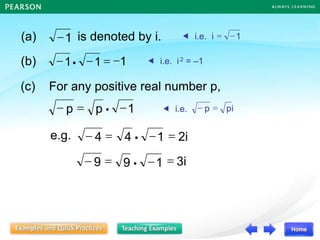
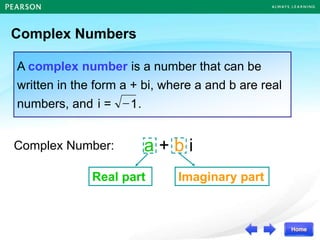
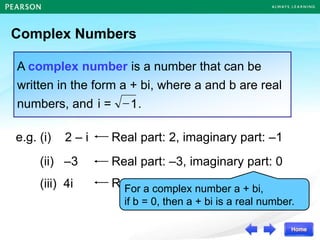
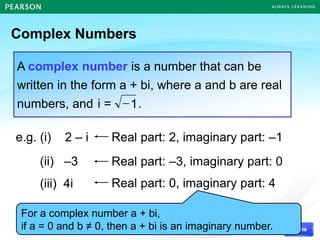
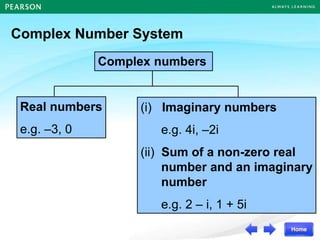
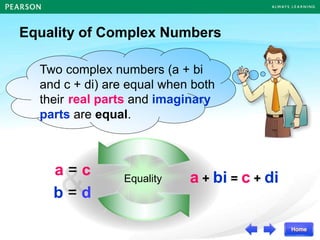
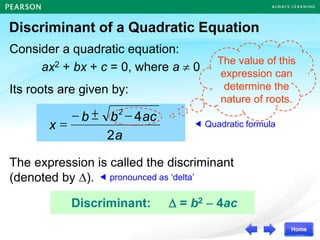
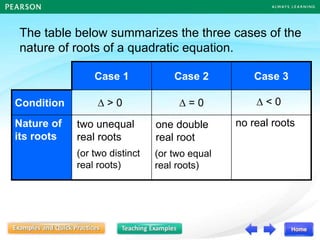
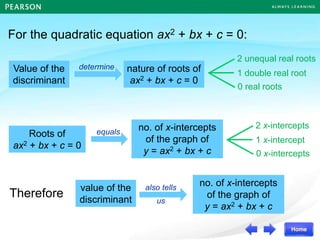
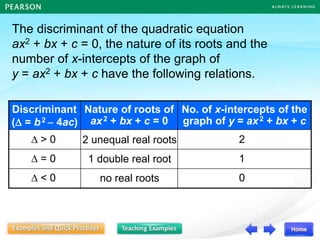
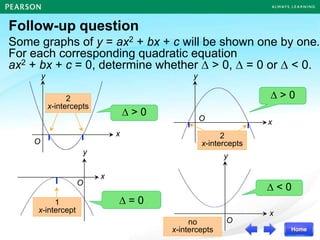
The document discusses the nature of roots of a quadratic equation and how it relates to the discriminant. It begins by recalling the quadratic formula and defining the discriminant. It then describes the three cases for the nature of roots based on the discriminant:
1) If the discriminant is greater than 0, there are two unequal real roots.
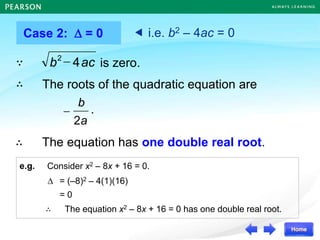
2) If the discriminant is equal to 0, there is one double real root.
3) If the discriminant is less than 0, there are no real roots.
Some examples are provided to illustrate each case. Finally, it summarizes that the value of the discriminant determines the nature of the roots, which also corresponds to the number of x-











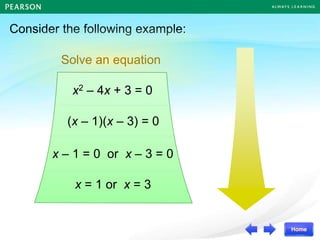

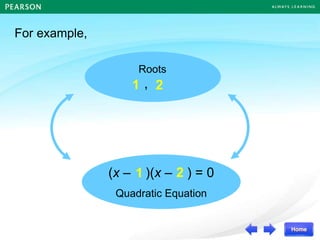
![For example,
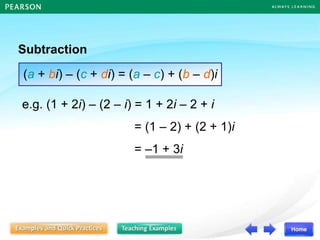
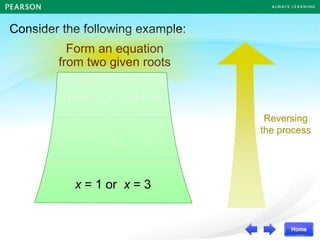
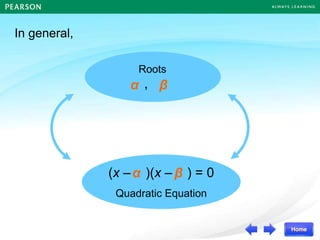
Roots
,
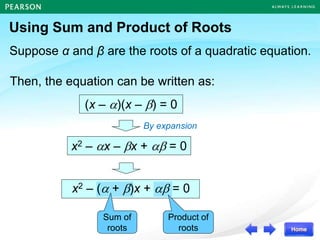
(x – )(x – ) = 0
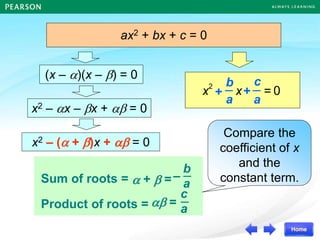
Quadratic Equation
α β
1 2
0 –4
Quadratic Equation
(–4)
(x – )[x – ] = 0
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13377237-221011115813-57407bb8/85/DISCRIMINANT-ppt-23-320.jpg)
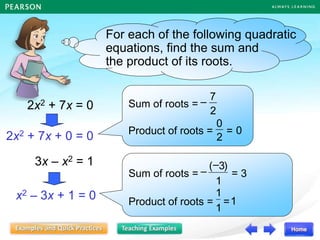
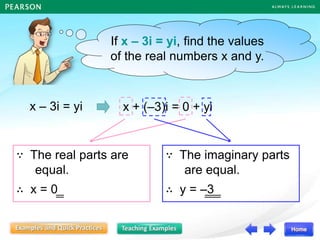
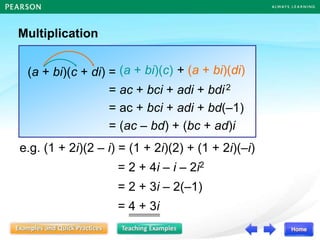
![Follow-up question
In each of the following, form a quadratic equation in x
with the given roots, and write the equation in the
general form.
(a) –1, –5 (b)
3
1
4,
(a) The required quadratic equation is
[x – (–1)][x – (–5)] = 0
(x + 1)(x + 5) = 0
x2 + x + 5x + 5 = 0
x2 + 6x + 5 = 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13377237-221011115813-57407bb8/85/DISCRIMINANT-ppt-25-320.jpg)

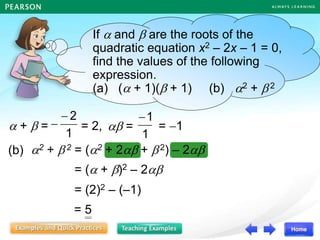
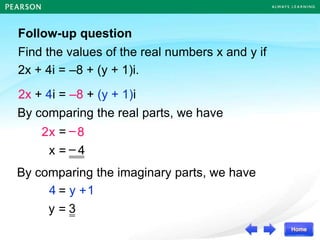
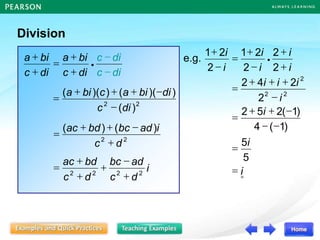
![I am trying to form a
quadratic equation whose
roots are and ,
2
1+ 2
1
but it is too tedious to
expand the left hand side
of the equation
0.
)]
2
(1
)][
2
(1
[ =
+
x
x
In fact, there is another method
to form a quadratic equation. It
helps you form this quadratic
equation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13377237-221011115813-57407bb8/85/DISCRIMINANT-ppt-27-320.jpg)